Abstract
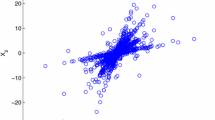
Bofill et al. discussed blind source separation (BSS) of sparse signals in the case of two sensors. However, as Bofill et al. pointed out, this method has some limitation. The potential function they introduced is lack of theoretical basis. Also the method could not be extended to solve the problem in the case of more than three sensors. In this paper, instead of the potential function method, a K-PCA method (combining K-clustering with PCA) is proposed. The new method is easy to be used in the case of more than three sensors. It is easy to be implemented and can provide accurate estimation of mixing matrix. Some criterion is given to check the effect of the mixing matrix A. Some simulations illustrate the availability and accuracy of the method we proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tong L, Liu R, Soon V C, et al. Indeterminacy and identifiability of blind identification. IEEE Trans Circuits and Systems, 1991, 38(5): 499–506
Cao X R, Liu RW. General approach to blind source separation. IEEE Trans Signal Processing, 1996, 44: 562–571
Li Y Q, Wang J. Blind extraction of singularly mixed source signals. IEEE Trans Signal Processing, 2000, 11: 1413–1422
Zhang J L, Xie S L, He Z S. Separability theory for blind signal separation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2004, 30(3): 337–344
Hyvarinen A. A fast and robust fixed-point algorithms for independent component analysis. IEEE Trans Neural Networks, 1999, 10(3): 626–634
Comon P. Independent component analysis, a new concept? Signal Processing, 1992, 36(3): 287–314
Cardoso J F. Source separation using higher order-moments. In: Proc ICASSP89, Glasgow, Scotland. 1989, 4: 2109–2112
Bell A, Sejnowski T. An information maximization approach to blind separation and blind deconvolution. Neural Computation, 1995, 7: 1129–1159
Yang H H. Adaptive on-line learning algorithms for blind separation-maximum entropy and minimum mutual information. Neural Computation, 1997, 9: 1457–1482
Amari S, Cichocki A, Yang H H. A new algorithm for blind source separation. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing (Proc. NIPS’95). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 1996. 757–763
He Z Y, Liu J, Yang L X. An ICA and EC based approach for blind equalization and channel parameter estimation. Sci China Ser E-Tech Sci, 2000, 43(1): 1–8
He Z Y, Yang L X, Liu J. Blind source separation using cluster-based multivariate density estimation algorithm. IEEE Trans Signal Processing, 2000, 48(2): 575–579
Zhang X D, Zhu X L, Bao Z. Blind signal separation based on learning in stages. Sci China Ser F-Inf Sci, 2003, 46(1): 31–44
Bofill P, Zibulevsky M. Underdetermined blind source separation using sparse representations, Signal Processing, 2001, 81(11): 2353–2362
Li Y Q, Cichocki A, Amari S. Analysis of sparse representation and blind source separation. Neural Computation, 2004, 16: 1193–1234
Zibulevsky M, Pearmutter B A. Blind source separation by sparse decomposition in a signal dictionary. Neural Computation, 2001, 13: 863–882
Pearlmutter B A, Potluru V K. Sparse separation: Principles and tricks. In: Proc SPIE volume 5102, “Independent Component Analyses, Wavelets, and Neural Networks”, Orlando, FL: SPIE Org., 2003. 1–4
Lee T W, Lewicki M S, Girolami M, et al. Blind source separation of more sources than mixtures using over-complete representations. IEEE Signal Process Lett, 1999, 6(4): 87–90
Lewiski M S, Sejnowski T J. Learning overcomplete representations. Neural Comput, 2000, 12(2): 337–365
Olshause B A N, Field D J. Sparse coding with an overcomplete basis set: a strategy employed by V1? Vision Res, 1997, 37: 3311–3325
Zibulevsky M, Pearlmutter B A. Blind source separation by sparse decomposition. Technicial Report No. CS99-1. University of New Mexico, Albuquerque, July 1999, http://www.cs.unm.edu/:_bap/papers/sparse-ica-99a.ps.gz
Wang X R, Wang G S. Applied Multi-variables Statistical Analysis (in Chinese). Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific Press, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Z., Xie, S. & Fu, Y. Sparse representation and blind source separation of ill-posed mixtures. SCI CHINA SER F 49, 639–652 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-006-2020-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-006-2020-8