Abstract
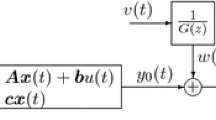
Identification of the Wiener system with the nonlinear block being a piecewise-linear function is considered in the paper, generalizing the results given by H. E. Chen to the case of noisy observation. Recursive algorithms are given for estimating all unknown parameters contained in the system, and their strong consistency is proved. The estimation method is similar to that used by H. E. Chen for Hammerstein systems with the same nonlinearity. However, the assumption imposed by H. E. Chen on the availability of an upper bound for the nonsmooth points of the piecewise-linear function has been removed in this paper with the help of designing an additional algorithm for estimating the upper bound.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen H F. Recursive identification for Wiener model with discontinuous piece-wise linear function. IEEE Trans Autom Contorl, 2006, 51(3): 390–400
Chen H F. Strong consistency of recursive identification for Hammerstein systems with discontinuous piecewise-linear memoryless block. IEEE Trans Autom Contorl, 2005, 50(10): 1612–1617
Bai EW. Identification of linear system with hard input nonlinearities of konwn structure. Automatica, 2002, 38(5): 853–860
Vörös J. Parameter identification of discontinuous Hammerstein systems. Automatica, 1997, 33(6): 1141–1146
Vörös J. Parameter identification of Wiener systems with discontinuous nonlinearities systems. Syst Control Lett, 2001, 44: 363–372
Vörös J. Recursive idetification of Hammerstein systems with discontinuous nonlinearities containing dead-zones. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2003, 48(12): 2203–2206
Chen H F. Pathwise convergence of recursive identification algorithms for Hammerstein systems. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2004, 49(10): 1641–1649
Greblicki W. Nonparameter approach to Wiener system identification. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Fundam Theory Appl, 1997, 44(6): 538–545
Greblicki W. Recursive identification of Wiener systems. Int J Appl Math Comput Sci, 2001, 11(4): 977–991
Hu X L, Chen H F. Strong consistence of recursive identification forWiener systems. Automatica, 2005, 41(11): 1905–1916
Chen H F. Stochastic Approximation and Its Applications. Dordrecht: Kluwer, 2002
Chow Y S, Teicher H. Probability Theory. New York: Springer, 1978
Chen H F, Guo L. Identification and Stochastic Adaptive Contorl. Boston: Birkhäuser, 1991
Ljung L. System Identification. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1999
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 60221301, 60334040, And 60474004)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Chen, H. & Fang, H. Identification of Wiener systems with nonlinearity being piecewise-linear function. Sci. China Ser. F-Inf. Sci. 51, 1–12 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-007-0071-0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-007-0071-0