Abstract
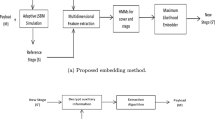
For steganalysis of JPEG images, features derived in the embedding domain appear to achieve a preferable performance. However, with the existing JPEG steganography, the minor changes due to the hidden secret data are not easy to be explored directly from the quantized block DCT (BDCT) coefficients in that the energy of the carrier image is much larger than that of the hidden signal. In this paper, we present an improved calibration-based universal JPEG steganalysis, where the microscopic and macroscopic calibrations are combined to calibrate the local and global distribution of the quantized BDCT coefficients of the test image. All features in our method are generated from the difference signal between the quantized BDCT coefficients of the test image and its corresponding microscopic calibrated image, or calculated as the difference between the signal extracted from test image and its corresponding macroscopic calibrated image. The extracted features will be more effective for our classification. Moreover, through using the Markov empirical transition matrices, both magnitude and sign dependencies along row scanning and column scanning patterns existed in intra-block and inter-block quantized BDCT coefficients are employed in our method. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed scheme outperforms the best effective JPEG steganalyzers having been presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Westfeld A. High capacity despite better steganalysis (F5-a steganographic algorithm). In: Information Hiding, 4th International Workshop, volume 2137 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2001. 289–302. Software available at http://www.rn.inf.tu-dresden.de/westfeld/f5.html
Sallee P. Model based methods for steganography and steganalysis. Int J Image Graphics, 2005, 5(1): 167–190. Software available at http://www.philsallee.com/mbsteg/index.html
Provos N. Defending against statistical steganalysis. In: 10th USENIX Security Symposium, Washington DC, USA, 2001. Software available at http://www.outguess.org
Fridrich J, Goljan M, Hogea, D. Steganalysis of JPEG images: Breaking the F5 algorithm. In: Information Hiding, 5th InternationalWorkshop, volume 2578 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2003. 310–323
Böhme R, Westfeld A. Breaking Cauchy model-based JPEG steganography with first order statistics. In: 9th European Symposium on Research in Computer Security, volume 3193 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2004, 125–140
Farid H, Siwei L. Detecting hidden messages using higher-order statistics and support vector machines. In: Information Hiding, 5th International Workshop, volume 2578 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2002. 340–354
Xuan G, Shi Y Q, Gao J, et al. Steganalysis based on multiple features fromed by statistical moments of wavelet characteristic function. In: Information Hiding, 7th International Workshop, volume 3727 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2005. 262–277
Shi Y Q, Xuan G, Zou D, et al. Steganalysis based on moments of characteristic functions using wavelet decomposition, prediction-error image, and nerual network. In: International Conference on Multimedia and Expro, Amsterdam, Netherlands, July 2005
Fridrich J. Feature-based steganalysis for JPEG images and its implications for future design of steganographic schemes. In: Information Hiding, 6th International Workshop, volume 3200 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2004. 67–81
Shi Y Q, Chen C, Chen W. A Markov process based approach to effective attacking JPEG steganography. In: Information Hiding, 8th International Workshop, volume 4437 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 2007. 249–264
Fu D, Shi Y Q, Zou D, et al. JPEG steganalysis using empirical transition matrix in blick DCT domain. In: International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing, Victoria, BC, Canada, 2006
Pevny T, Fridrich J. Merging Markov and DCT features for multi-class JPEG steganalysis. In: Proceedings of SPIE Electronic Imaging, Security, Steganography, and Watermarking of Multimedia Contents IX, 2007, 6505: 650503-1–650503-13
Tu C, Tran T D. Context-based entropy coding of block transform coefficients form image compression. IEEE Trans Image Process, 2002, 11(11): 1271–1283
Gonzalez R C, Woods R E. Digital Image Processing. 2nd ed. Prentice Hall: Pearson Education, Inc., 2002
Schaefer G, Stich M. UCID—An uncompressed colour image database. Technical Report, School of Computing and Mathematics, Nottingham Trent University, UK, 2003
Sallee P. http://redwood.ucdavis.edu/phil/demos/jpegtbx/jpegtbx.htm
Chang C -C, Lin C -J. LIBSVM: a library for support vector machines, 2001. Software available at http://www.csie.ntu.edu.tw/cjlin/libsvm
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (Grant No. 2006CB303104), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 90604008 and 60633030), the Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (Grant No. 20070558054)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, F., Huang, J. Calibration based universal JPEG steganalysis. Sci. China Ser. F-Inf. Sci. 52, 260–268 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-009-0033-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-009-0033-9