Abstract
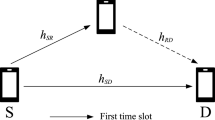
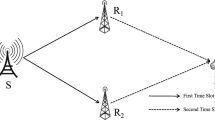
We investigate the multiple access channels (MAC) where sources can cooperate via half-duplex relaying and refer to it as cooperative MAC channels (CMAC). Assuming perfect channel state information (CSI) at the transmitters and the receivers, we determine the bounds on the achievable rate region of a Gaussian CMAC channel and an inner bound on the outage capacity region of a fading CMAC channel. Based on superposition modulation, a half-duplex cooperative relay scheme with optimal resource allocation is proposed to achieve the bounds of capacity region. Analytical results and simulation results show that the achievable rate region of a Gaussian CMAC channel is larger than that of a Gaussian MAC channel with direct transmission (DT) schemes. But they have the same achievable sum rate. Moreover, the proposed scheme can provide higher outage capacity region than DT schemes in a fading MAC channel due to the fact that sources can share the resources with each other to reduce outages.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liao H. Multiple access channels. Ph.D. dissertation. Hawaii: Hawaii University, 1972
Gallager R. A perspective on multiaccess channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1985, 31(2): 124–142
Bross S I, Lapidoth A. An improved achievable region for the discrete memoryless two-user multiple-access channel with noiseless feedback. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2005, 51(3): 811–833
Cover T, Thomas J. Elements of Information Theory. New York: Wiley, 1991
Li L, Jindal N, Goldsmith A. Outage capacities and optimal power allocation for fading multiple-access channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2005, 51(4): 1326–1347
Jafar S, Goldsmith A. On the capacity of the vector MAC with feedback. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2006, 52(7): 3259–3264
Hunter T E, Hedayat A. Cooperative communication in wireless networks. IEEE Commun Mag, 2004, 42(10): 74–80
Sendonaris A, Erkip E, Aazhang B. User cooperation diversity—part I: System description. IEEE Trans Commun, 2003, 51(11): 1927–1948
Laneman J N, Tse D N C, Wornell G W. Cooperative diversity in wireless networks: Efficient protocols and outage behavior. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2004, 50(12): 3062–3080
Van der Meulen E C. Three-terminal communication channels. Adv Appl Prob, 1971, 3: 120–154
Cover T M, EI Gamal A A. Capacity theorems for the relay channel. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1979, 25(5): 572–584
Kramer G, Gastpar M, Gupta P. Cooperative strategies and capacity theorems for relay networks. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2005, 51(9): 3037–3063
Host-Madsen A, Zhang J. Capacity bounds and power allocation for wireless relay channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2005, 51(6): 2020–2040
Host-Madsen A. Capacity bounds for cooperative diversity. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1522–1544
Avestimehr A S, Tse D N C. Outage capacity of the fading relay channel in the low-SNR regime. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2007, 53(4): 1401–1415
Kramer G. Van Wijngaarden A J. On the white Gaussian multiple-access relay channel. In: Viterbo E, ed. Proceedings of IEEE Int Symp Inform Theory. Sorrento: IEEE, 2000. 40
Sankaranarayanan L, Kramer G, Mandayam N B. Capacity theorems for the multiple-access relay channel. In: Quentin A, ed. Proceedings of the 42nd Annu Allerton Conf Communications, Control, and Computing. Monticello: Allerton House, 2004. 1782–1791
Willems F M J. The discrete memoryless multiple access channel with partially cooperating encoders. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1983, 29(3): 441–445
Willems F M J, Meulen E C V D. The discrete memoryless multiple-access channel with cribbing encoders. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1985, 31(3): 313–327
Larsson E G, Vojcic B R. Cooperative transmit diversity based on superposition modulation. IEEE Commun Lett, 2005, 9(9): 778–780
Liang Y, Kramer G. Rate regions for relay broadcast channels. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 2007, 53(10): 3517–3535
Chen B, Willett P. The theoretical bandwidth advantage of CDMA over FDMA in a Gaussian MAC. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1999, 45(6): 2046–2053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported partially by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 60672079), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (Grant No. BK2006701), and the Natinoal High-Tech Research & Development Program of China (Grant No. 2007AA01Z267)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, C., Cai, Y. & Xu, Y. Cooperative multiple access channels: Achievable rates and optimal resource allocation. Sci. China Ser. F-Inf. Sci. 52, 1428–1438 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-009-0078-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-009-0078-9