Abstract
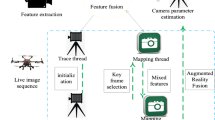
This paper presents an improved key frame based augmented reality registration algorithm for real-time motion tracking in outdoor environment. In such applications, wide-baseline feature matching is a critical problem. In this paper, we apply randomized tree method to match key points extracted from the input image to those key frames as a classification problem. Extended Kalman filter is also utilized for jitter correction. A video see-through mobile augmented reality system is built for the on-site digital reconstruction of Yuanmingyuan Garden. Experimental results demonstrate that this algorithm is real-time, robust and effective for outdoor tracking.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azuma R, Baillot Y, Behringer R, et al. Recent advances in augmented reality. Comput Graph Appl, 2001, 21: 34–47
State A, Chen D T, Chris T, et al. Case study: observing a volume-rendered fetus within a pregnant patient. In: Proceeding of IEEE Visualization. Los Alamitos: IEEE Computer Society Press, 1994. 364–368
Zaeh M, Vogl W. Interactive laser-projection for programming industrial robots. Manufact Tech, 2008, 57: 37–40
Stricker D, Daehne P, Seibert F, et al. Design and development issues for an archeoguide: an augmented reality based cultural heritage on-site guide. In: International Conference on Augmented, Virtual Environments and Three-Dimensional Imaging, Mykonos, Greece, 2001
Papagiannakis G, Schertenleib S. Mixing virtual and real scenes in the site of ancient Pompeii. J Comput Animat Virtual Worlds, 2005, 16: 11–24
Julier S, Baillot Y, Lanzagorta M. BARS: batterfield augmented reality system. In: NATO Symposium on Information Processing Techniques for Military Systems. Istanbul: IEEE Computer Society Press, 2000. 9–11
Gerhard R, Drummond T. Going out: robust model-based tracking for outdoor augmented reality. In: The Proceeding of Symposium on Augmented Reality. Santa Barbara: IEEE Computer Society Press, 2006. 109–118
Simon G, Fitzgibbon A, Zisserman A. Markerless tracking using planar structures in the scene. In: Proc International Symposium on Augmented Reality, Munich, 2000
Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. Int J Comput Vision, 2004, 60: 91–110
Lepetit V, Pilet J, Fua P. Point matching as a classification problem for fast and robust object pose estimation. In: Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington: IEEE Computer Society Press, 2004. 244–250
Lepetit V, Fua P. Towards recognizing feature points using classification trees. Technical Report, IC/2004/74, EPFL, 2004
Lindeberg T. Scale-space theory: a basic tool for analyzing structures at different scales. J Appl Statist, 1994, 21: 224–270
Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C. An affine invariant interest point detector. In: European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Copenhagen, Denmark, 2002. 128–142
Morel J M, Yu G. ASIFT: a new framework for fully affine invariant image comparison. SIAM J Imag Sci, 2009, 2: 438–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J., Wang, Y., Guo, J. et al. Augmented reality registration algorithm based on nature feature recognition. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 53, 1555–1565 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-4026-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-010-4026-5