Abstract
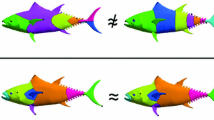
Surface deformations without tearing or stretching, preserving the intrinsic properties, are called isometries. This paper presents a new definition of Gaussian curvature moments (GCMs) by the integral of n power of Gaussian curvature. Then a series of moment invariants, called Gaussian curvature moment invariants (GCMIs), are derived via GCMs. These moment invariants share many good properties under rigid transformations and isometric non-rigid transformations, and Gaussian-Bonnet theorem is a special case of GCMI. GCMIs are invariant under isometry and scaling transformations. We construct an invariant vector as a descriptor for a surface via GCMIs, and a modified χ 2 distance is defined as a measure of similarity. Finally, experiments show that it is a reliable descriptor for isometric non-rigid shape.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Neill B. Elementary Differential Geometry. Revised Second Edition. Waltham, Massachusetts: Academic Press (Elsevier), 2006
Sadjadi F, Hall E. Three-dimensional moment invariants. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 1980, 2: 127–136
Xu D, Li H. Geometric moment invariant. Patt Recog, 2008, 41: 240–249
Canterakis N. 3D zernike moments and zernike affine invariants for 3D image analysis and recognition. In: 11th Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis, Kangerlussuaq, Greenland, 1999. 85–93
Osada R, Funkhouser T, Chazelle B, et al. Shape distributions. ACM Trans Graph, 2002, 21: 807–832
Funkhouser T, Min P, Kazhdan M, et al. A search engine for 3D models. ACM Trans Graph, 2003, 22: 83–105
Horn B. Extended Gaussian image. Proc IEEE, 1984, 12: 1671–1686
Johnson A, Hebert M. Using spin images for efficient object recognition in cluttered 3D scenes. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 1999, 21: 433–449
Vránic D, Saupe D D. 3D shape descriptor based on 3D Fourier transform. In: Proceedings of the EURASIP Conference on Digital Signal Processing for Multimedia Communications and Services (ECMCS 2001), Budapest, Hungary, 2001. 271–274
Paquet E, Murching A, Naveen T, et al. Description of shape information for 2-D 3-D objects. Signal Process Image Commun J, 2000, 16: 103–122
Sundar H, Silver D, Gagvani N, et al. Skeleton based shape matching and retrieval. In: Shape Modeling and Applications Conference, Seoul, Korea. IEEE Computer Society, 2003. 130–142
Ip H, Wong W. 3D head models retrieval based on hierarchical facial region similarity. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Vision Interface, Calgary, Canada, 2002. 314–319
Adan A, Adan M. A flexible similarity measure for 3D shapes recognition. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 2004, 26: 1507–1520
Hilaga M, Shinagawa Y, Komura T, et al. Topology matching for fully automatic similarity estimation of 3D shapes. In: Proceedings of the 28th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2001. 203–212
Hamza A, Krim H. Geodesic object representation and recognition. In: International Conference on Discrete Geometry for Computer Imagery, Naples, 2003. 2886: 378–387
Elad A, Kimmel R. On bending invariant signatures for surfaces. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 2003, 26: 1285–1295
Bronstein A, Bronstein M, Kimmel R. Generalized multidimensional scaling: a framework for isometry-invariant partial surface matching. Proc Nat Acad Sci (PNAS), 2006, 103: 1168–1172
Bronstein A, Bronstein M, Kimmel R. Numerical Geometry of Non-Rigid Shapes. Berlin: Springer, 2008
Mémolif F, Sapiro G. A theoretical and computational framework for isometry invariant recognition of point cloud data. Found Comput Math, 2005, 5: 313–347
Memoli F. On the use of Gromov-Hausdorff distances for shape comparison. In: Proceedings of EG/IEEE Symposium on Point-Based Graphics, Prague, Czech, 2007. 81–90
Bronstein A, Bronstein M, Kimmel R. Efficient computation of isometry-invariant distances between surfaces. SIAM J Sci Comput, 2006, 28: 1812–1836
Bronstein A, Bronstein M, Kimmel R, et al. A Gromov-Hausdorff framework with diffusion geometry for topologicallyrobust non-rigid shape matching. Int J Comput Vision, 2010, 89: 266–286
Bronstein M, Bronstein A. Shape recognition with spectral distances. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 2011, 33: 1065–1071
Reuter M, Wolter F, Peinecke N. Laplace-Beltrami spectra as ‘Shape-DNA’ of surfaces and solids. Comput-Aid Design, 2006, 38: 342–366
Reuter M, Biasotti S, Giorgi D, et al. Discrete Lapalece-Beltrami operators for shape analysis and segmentation. Comput Graph, 2009, 33: 381–390
Rustamov R. Laplace-Beltrami eigenfunctions for deformation invariant shape representation. In: Proceedings Symposium on Geometry Processing (SGP), Barcelona, Spain, 2007. 225–233
Ruggeri M, Saupe D. Isometry-invariant matching of point set surfaces. In: Proceedings Eurographics Workshop on 3D Object Retrieval, Crete, Greece, 2008
Polonsky O, Patane G, Biasotti S, et al. What’s in an image: towards the computation of the “best” view of an object. Visual Comput, 2005, 21: 840–847
Yamauchi H, Gumhold S, Zayer R, et al. Mesh segmentation driven by Gaussian curvature. Visual Comput, 2005, 21: 659–668
Ip C, Regli W. A 3D object classifier for discriminating manufacturing processes. Comput Graph, 2006, 30: 903–916
Sukumar S, Page D, Koschan A, et al. Shape measure for identifying perceptually informative parts of 3D objects. In: Proc. IEEE 3rd International Symposium on 3D Data Processing, Visualization and Transmission 3DPVT, Chapel Hill, NC, 2006. 679–686
Tosranon P, Sanpanich A, Bunluechokchai C, et al. Gaussian curvature-based geometric invariance. In: The 6th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information technology, Chonburi Thailand, 2009. 1124–1127
Guo K, Li M. A novel shape descriptor: Gaussian curvature moment invariants. In: The 1st International Conference on Information Science and Engineering (ICISE2009), Nanjing, China, 2009. 1087–1090
Pottmann H, Wallner J, Huang Q, et al. Integral invariants for robust geometry processing. Comput Aided Geom D, 2009, 26: 37–60
Xu G. Convergence analysis of a discretization scheme for Gaussian curvature over triangular surfaces. Comput Aid Geometric Design, 2006, 23: 193–207
Surazhsky T, Magid E, Soldea O, et al. A comparison of Gaussian and mean curvatures estimation methods on triangular meshes. In: 2003 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation (ICRA2003), Taipei, Taiwan, China, 2003. 1021–1026
Sumner R W, Popovic J. Deformation transfer for triangle meshes. ACM Trans Graph, 2004, 23: 399–405
Mahmoudi M, Sapiro G. Three-dimensional point cloud recognition via distributions of geometric distances. Graph Models, 2009, 71: 22–31
Surazhsky V, Surazhsky T, Kirsanov D, et al. Fast exact and approximate geodesics on meshes. ACM Trans Graph, 2005, 24: 553–560
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, W., Hu, P., Liu, Y. et al. Gaussian-curvature-derived invariants for isometry. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 56, 1–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4453-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-011-4453-y