Abstract
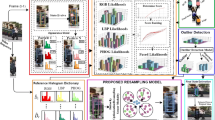
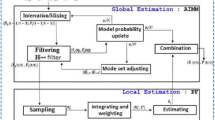
Robust visual tracking has become an important topic in the field of computer vision. Integrating multiple cues has proved to be a promising approach to visual tracking in situations where no single cue is suitable. In this work, a new particle filter based visual tracking algorithm is proposed. By introducing a new cooperative fusion strategy, the proposed tracker has better fault tolerance ability than the traditional methods. Experiments are performed in various tracking scenes to evaluate the proposed algorithm, and the results show improved tracking accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yilmaz A, Javed O, Shah M. Object tracking: a survey. ACM Comput Surv, 2006, 38: 1–45
Greiffenhagen H N M, Comaniciu D, Ramesh V. Design, analysis and engineering of video monitoring systems: an approach and a case study. IEEE Proc, 2001, 89: 1498–1517
Bradski G R. Computer vision face tracking as a component of a perceptual user interface. In: IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision, Princeton, 1998. 214–219
Breitenstein M D, Reichlin F, Leibe B, et al. Online multi-person tracking-by-detection from a single, uncalibrated camera. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 2010, 32: 1–14
Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P. Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 2003, 25: 564–577
Chen J, Zhang S, An G, et al. A generalized mean shift tracking algorithm. Sci China Inf Sci, 2011, 54: 2373–2385
Isard M, Blake A. Condensation-conditional density propagation for visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis, 1998, 29: 5–28
Birchfield S. Elliptical head tracking using intensity gradients and color histograms. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Santa Barbara, 1998. 232–237
Triesch J, Malsburg C V D. Self-organized integration of adaptive visual cues for face tracking. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition, Grenoble, 2000. 102–107
Torr P H S, Szeliski R, An P. An integrated bayesian approach to layer extraction from image sequences. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 2001, 23: 983–990
Triesch J, Malsburg C V D. Democratic integration: self-organized integration of adaptive cues. Neural Comput, 2001, 13: 2049–2074
Shen C, Hengel A V D, Dick A. Probabilistic multiple cue integration for particle filter based tracking. In: Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications, Sydney, 2003. 399–408
Spengler M, Schiele B. Towards robust multi-cue integration for visual tracking. Mach Vision Appl, 2003, 14: 50–58
Perez P, Vermaak J, Blake A. Data fusion for visual tracking with particles. Proc IEEE, 2004, 92: 495–513
Chen Y, Rui Y. Real-time speaker tracking using particle filter sensor fusion. Proc IEEE, 2004, 92: 485–494
Li P, Chaumette F. Image cues fusion for object tracking based on particle filter. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Workshop on Articulated Motion and Deformable Objects, Palma de Mallorca, 2004. 99–107
Brasnett P, Mihaylova L, Bull D, et al. Sequential monte carlo tracking by fusing multiple cues in video sequences. Image Vis Comput, 2007, 25: 1217–1227
Yin Z, Porikli F, Collins R T. Likelihood map fusion for visual object tracking. In: IEEE Computer Society Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision, Copper Mountain, 2008. 1–7
Moreno-Noguer F, Sanfeliu A, Samaras D. Dependent multiple cue integration for robust tracking. IEEE Trans Patt Anal Mach Intell, 2008, 30: 670–685
Du W, Piater J H. A probabilistic approach to integrating multiple cues in visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin/Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2008. 225–238
Wang X, Tang Z. Modified particle filter-based infrared pedestrian tracking. Infrared Phys Technol, 2010, 53: 280–287
Cui P, Sun L, Yang S. Adaptive mixture observation models for multiple object tracking. Sci China Ser F-Inf Sci, 2009, 52: 226–235
Arulampalam M S, Maskell S, Gordon N. A tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-gaussian bayesian tracking. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2002, 50: 174–188
Bircheld S T, Rangarajan S. Spatiograms versus histograms for region-based tracking. In: IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington D. C.: IEEE, 2005. 1158–1163
OConaire C, OConnor N, Smeaton A. Feature fusion for object tracking using multiple spatiogram trackers. Mach Vision Appl, 2008, 19: 483–494
Hu M K. Visual pattern recognition by moment invariants. IEEE Trans Inf Theory, 1962, IT-8: 179–187
Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Diego, 2005. 886–893
Nummiaro K, Koller-Meier E, Gool L V. An adaptive color-based particle filter. Image Vis Comput, 2002, 21: 99–110
Collins R, Zhou X, Teh S K. An open source tracking testbed and evaluation web site. In: IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance, Breckenridge, 2005. 1–8
Grabner H, Grabner M, Bischof H. Real-time tracking via on-line boosting. In: British Machine Vision Conference, Edinburgh, 2006. 47–56
Kalal Z, Matas J, Mikolajczyk K. P-N learning: bootstrapping binary classifiers by structural constraints. In: IEEE Conference on Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, San Francisco, 2010. 49–56
Kalal Z, Mikolajczyk K, Matas J. Face-TLD: tracking-learning-detection applied to faces. In: International Conference on Image Processing, Hong Kong, 2010. 3789–3792
Mei X, Ling H. Robust visual tracking using l 1 minimization. In: IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, 2009. 1436–1443
Ross D A, Lim J, Lin R S, et al. Incremental learning for robust visual tracking. Int J Comput Vis, 2008, 77: 125–141
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Yan, H. & Pan, C. Cooperative fusion particle filter tracker. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 57, 1–14 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-013-4853-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-013-4853-2