Abstract
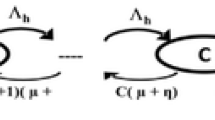
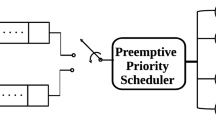
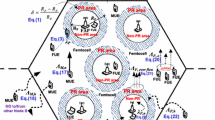
In heterogeneous wireless networks, both terminal heterogeneity and network heterogeneity give rise to the fairness problem of resource allocation. Due to the capability of exploiting the resources of multiple networks, the behavior of multi-mode terminals will have a great effect on single-mode terminals, and this influence becomes more severe when considering the different demands of different traffic. In this article, we propose a novel joint call admission control (JCAC) scheme to address this problem. The JCAC problem is modeled as a semi-Markov decision process (SMDP) with the aim of maximizing the average network revenue under the constraints of the fairness among different terminals and traffic classes. Based on the SMDP, we design an algorithm to achieve a good tradeoff between revenue and fairness by dynamically adjusting the threshold of fairness constraints imposed on heterogeneous terminals. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme can significantly improve the fairness among heterogeneous terminals and guarantee the priority and fairness among different traffic classes with little loss of network revenue compared with other schemes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frattasi S, Fathi H, Fitzek F, et al. Defining 4G technology from the users perspective. IEEE Netw, 2006, 20: 35–41
Nasser N, Hassanein H. An optimal and fair call admission control policy for seamless handoff in multimedia wireless networks with QoS guarantees. In: Proceedings of IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, Dallas, 2004. 3926–3930
Rong B, Qian Y, Lu K J, et al. Call admission control optimization in WiMAX networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2008, 57: 2509–2522
Hwang R H, Chi C F. Fairness in QoS guaranteed networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communications, Alaska, 2003. 218–222
Falowo E, Chan H. Joint call admission control algorithms: requirements, approaches, and design considerations. Comput Commun, 2008, 31: 1200–1217
Chen H, Cheng C, Yeh H. Guard-channel-based incremental and dynamic optimization on call admission control for next-generation QoS-aware heterogeneous systems. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2008, 57: 3064–3082
Yu F, Krishnamurthy V. Optimal joint session admission control in integrated WLAN and CDMA cellular networks with vertical handoff. IEEE Trans Mob Comput, 2007, 6: 126–139
Gelabert X, Pérez-romero J, Sallent O, et al. On the suitability of load balancing principles in heterogeneous wireless access networks. In: Proceedings of International Symposium on Wireless Personal Multimedia, Aalborg, 2005. 1503–1507
Pérez-romero J, Salient O, Agusti R. On the optimum traffic allocation in heterogeneous CDMA/TDMA networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2007, 6: 3170–3174
Bühler J, Wunder G. Traffic-aware optimization of heterogeneous access management. IEEE Trans Commun, 2010, 58: 1737–1747
Ibrahim M, Khawam K, Tohme S. Network-centric joint radio resource policy in heterogeneous WiMAX-UMTS networks for streaming and elastic traffic. In: Proceedings of IEEE Wireless Communication and Networking Conference, Budapest, 2009. 1–6
Falowo O. Joint call admission control algorithm for fair radio resource allocation in heterogeneous wireless networks supporting heterogeneous mobile terminals. Int J Commun Netw Syst Sci, 2012, 5: 392–404
Giupponi L, Agusti R, Pérez-romero J, et al. A framework for JRRM with resource reservation and multiservice provisioning in heterogeneous networks. Mob Netw Appl, 2006, 11: 825–846
Giupponi L, Agusti R, Pérez-romero J, et al. A novel approach for joint radio resource management based on fuzzy neural methodology. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2007, 57: 1789–1805
Gelabert X, Pérez-romero J, Sallent O, et al. A markovian approach to radio access technology selection in heterogeneous multiaccess/multiservice wireless networks. IEEE Trans Mob Comput, 2008, 7: 1257–1270
Puterman M. Markov Decision Processes: Discrete Stochastic Dynamic Programming. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 1994
Jain D, Hawe W. A quantitative measure of fairness and discrimination for resource allocation in shared computer systems. DEC Research Report TR-301, 1984
Tijms H. A First Course in Stochastic Models. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons Ltd, 2003
Boyd S, Vandenberghe L. Convex Optimization. New York: Cambridge University Press, 2004
Lobo M, Vandenberghe L, Boyd S, et al. Applications of second-order cone programming. Linear Algebra Appl, 1998, 284: 193–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G., Sheng, M., Wang, X. et al. Fairness-based joint call admission control for heterogeneous wireless networks: an SMDP approach. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 57, 1–12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5128-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-014-5128-2