Abstract
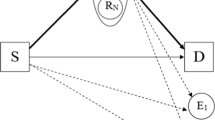
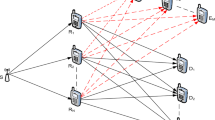
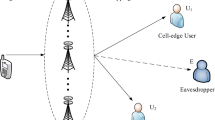
In this paper, the impact of both maximal ratio combining (MRC) and relay selection on the physical layer security in wireless communication systems is investigated by analyzing critical issues such as the probability characteristics of the legitimate receiver (Bob) and malicious eavesdropper (Eve)’s end-to-end signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), the secrecy outage probability and the average secrecy channel capacity over Rayleigh fading Channel, etc. Unlike the conventional physical layer security schemes, we assume that Bob receives its data from both the relay and the source via cooperative relay, provided that MRC is employed at the receiver. Particularly, compared to the conventional MRC methods, the proposed method is capable of achieving a higher spatial diversity order by performing relay selection, as validated by performing the theoretical analysis as well as numerical simulation. Furthermore, the closed-form expressions in terms of secrecy outage probability and average secrecy capacity are all consistent with the numerical results. Finally, the proposed scheme may be substantially affected by a number of parameters such as the number of relays, the SNR of links and the ratio of main-to-eavesdropper ratio (MER) λME.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nabar R U, Bolcskei H, Kneubuhler F W. Fading relay channels: performance limits and space-time signal design. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2004, 22: 1099–1109
Sendonaris A, Erkip E, Aazhang B. User cooperation diversity-Part I: system description. IEEE Trans Commun, 2003, 51: 1927–1938
Xing C, Xia M, Gao F, et al. Robust transceiver with tomlinson-harashima precoding for amplify-and-forward MIMO relaying systems. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2012, 30: 1370–1382
Zhou Y, Liu H, Pan Z, et al. Two-stage cooperative multicast transmission with optimized power consumption and guaranteed coverage. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun, 2014, 32: 1–11
Zhang Z, Long K, Wang J. Self-organization paradigms and optimization approaches for cognitive radio technologies: a survey. IEEE Wirel Commun, 2013, 20: 36–42
Chai X M, Xu X, Zhang Z S. A user-selected uplink power control algorithm in the two-tier femtocell network. Sci China Inf Sci, 2015, 58: 042303
Li Y, Xu X, Zhang D D, et al. Optimal pilots design for frequency offsets and channel estimation in OFDM modulated single frequency networks. Sci China Inf Sci, 2014, 57: 042301
Zhang Z, Long K, Wang J, et al. On swarm intelligence inspired self-organized networking: its bionic mechanisms, designing principles and optimization approaches. IEEE Commun Surv Tut, 2014, 16: 513–537
Zhang Z, Zhang W, Tellambura C. OFDMA uplink frequency offset estimation via cooperative relaying. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2009, 8: 4450–4456
Zhang Z S, Huangfu W, Long K P, et al. On the designing principles and optimization approaches of bio-inspired self-organized network: a survey. Sci China Inf Sci, 2013, 56: 071301
Jia J, Zhang J, Zhang Q. Cooperative relay for cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM, Rio de Janeiro, 2009. 2304–2312
Michalopoulos D S, Karagiannidis G K, Schober R. Amplify-and-forward relay selection with outdated channel estimates. IEEE Trans Commun, 2012, 60: 1278–1290
Zhuang W, Ismail M. Cooperation in wireless communication networks. IEEE Wirel Commun, 2012, 19: 10–20
Xing C, Ma S, Fei Z, et al. A general robust linear transceiver design for multi-hop amplify-and-forward MIMO relaying systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2013, 61: 1196–1209
Xing C, Ma S, Wu Y C. Robust joint design of linear relay precoder and destination equalizer for dual-hop amplifyand-forward MIMO relay systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2010, 58: 2273–2283
Xing C, Ma S, Zhou Y. Matrix-monotonic optimization for MIMO systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2015, 63: 334–348
Xing C W, Fei Z S, Li N, et al. Statistically robust resource allocation for distributed multi-carrier cooperative networks. Sci China Inf Sci, 2013, 56: 022315
Wang H M, Xia X G. Enhancing wireless secrecy via cooperation: signal design and optimization. IEEE Commun Mag, in press. 2015 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2370754
Zheng T X, Wang H M, Liu F, et al. Outage constrained secrecy throughput maximization for df relay networks. IEEE Trans Commun, 2015, 63: 1741–1755
Wang C, Wang H M, Ng D W K, et al. Joint beamforming and power allocation for secrecy in peer-to-peer relay networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2015, 14: 3280–3293
Wang C, Wang H M, Xia X G, et al. Uncoordinated jammer selection for securing simome wiretap channels: a stochastic geometry approach. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun, 2015, 14: 2596–2612
Wang H M, Liu F, Yang M. Joint cooperative beamforming, jamming and power allocation to secure af relay systems. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, in press. 2015 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2014.2370754
Elkashlan M, Wang L, Duong T Q, et al. On the security of cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol, 2015, 64: 3790–3795
Liu Y, Wang L, Duy T T, et al. Relay selection for security enhancement in cognitive relay networks. IEEE Commun Lett, 2015, 4: 46–49
Wang L, Kim K J, Duong T Q, et al. Security enhancement of cooperative single carrier systems. IEEE Trans Inf Foren Secur, 2015, 10: 90–103
Zou Y, Wang X, Shen W. Physical-layer security with multiuser scheduling in cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Commun, 2013, 61: 5103–5113
Wang L, Yang N, Elkashlan M, et al. Physical layer security of maximal ratio combining in two-wave with diffuse power fading channels. IEEE Trans Inf Foren Secur, 2014, 9: 247–258
Zou Y, Yao Y D, Zheng B. Opportunistic distributed space-time coding for decode-and-forward cooperation systems. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2012, 60: 1766–1781
Dong L, Han Z, Petropulu A P, et al. Improving wireless physical layer security via cooperating relays. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2010, 58: 1875–1888
Zhang Z, Chai X, Long K, et al. Full-duplex techniques for 5G networks: self-interference cancellation, protocol design and relay selection. IEEE Commun Mag, 2015, 53: 128–137
Gradshteyn I S, Ryzhik I M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products. 7th ed. New York: Academic, 2007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhong, B., Wu, M., Li, T. et al. Physical layer security via maximal ratio combining and relay selection over Rayleigh fading channels. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 59, 062305 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-015-5406-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-015-5406-7