Abstract
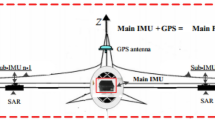
An airborne distributed position and orientation system (POS) appears to satisfy the requirement of multi-point motion parameters measurement. This relies on transfer alignment from a high precision master system to slave systems to obtain high accuracy motion parameters of all points. A key problem for a distributed POS involves determining a method to treat the aircraft flexure appropriately and achieve high precision transfer alignment. In this study, the effect of aircraft flexure on transfer alignment accuracy for airborne earth observation is first analyzed. Based on this, the error model of transfer alignment that considers three-dimensional flexure angles are established, and a transfer alignment based on parameter identification unscented Rauch-Tung-Striebel smoother (PIURTSS) is proposed. The simulations results show that the transfer alignment method based on PIURTSS effectively improves the estimation accuracy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xu W, Deng Y K, Wang R. Multichannel synthetic aperture radar systems with a planar antenna for future spaceborne microwave remote sensing. IEEE Aerosp Electron Syst Mag, 2012, 27: 26–30
Scherbaum P, Brauchle J, Kraft T, et al. MACS-Mar — a real-time capable multisensor remote sensing system for maritime applications. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Aerospace Electronics and Remote Sensing Technology, Bali, 2015
Chen N C, Pu F L, Hu C L, et al. Scientific issues and progress of the chinese integrated earth observation sensor web project. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Manchester, 2013. 1058–1062
Mostafa M M R, Hutton J. Direct positioning and orientation systems: how do they work? What is the attainable accuracy? In: Proceedings of American Society of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing Annual Meeting, St. Louis, 2001
Nagai M, Chen T, Shibasaki R, et al. UAV-borne 3-D mapping system by multisensor integration. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens, 2009, 47: 701–708
Chen S Y, Ma H C, Zhang Y C, et al. Boresight calibration of airborne Lidar system without ground control points. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett, 2012, 9: 85–89
Quan W, Li J L, Gong X L, et al. INS/CNS/GNSS Integrated Navigation Technology. Beijing: National Industry Press, 2015
Huang P P, Tan W X, Su Y. MIMO-SAR imaging technology for helicopter-borne based on ARC antenna array. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Milan, 2015. 1801–1804
Yan X G, Spurgeon S K, Edwards C. State and parameter estimation for nonlinear delay systems using sliding mode techniques. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2013, 58: 1023–1029
Yan X G, Lam J, Xie L H. Robust observer design for non-linear interconnected systems using structural characteristics. Int J Control, 2003, 76: 741–746
Mochalov A V, Kazantasev A V. Use of ring laser units for measurement of the moving object deformations. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Lasers Measurement and Information Transfer, St. Petersburg, 2002. 85–92
Groves P D. Optimising the transfer alignment of weapon INS. J Navigation. 2003, 56: 323–335
Kain J, Cloutier J. Rapid transfer alignment for tactical weapon application. In: Proceedings of AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference, Boston, 1989. 1290–1300
Spalding K. An efficient rapid transfer alignment filter. In: Proceedings of AIAA Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference, Hilton Head Island, 1992. 1276–1286
Yan Z P, Lan J, Zhang Y C. Hybrid-system-based multiple-model approach for transfer alignment with dynamic flexure in IIN. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Multisensor Fusion and Information Integration for Intelligent Systems, Beijing, 2014. 1–8
Gebre-Egziabher D, Shao Y F. Model for JPALS/SRGPSflexure and attitude error allocation. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst, 2010, 46: 483–495
Gao Q W, Zhao G R, Wang X B. Transfer alignment error compensator design for flexure and lever-arm effect. In: Proceedings of the 4th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, Xi’an, 2009. 1819–1822
Wu W, Chen S, Qin S Q. Online estimation of ship dynamic flexure model parameters for transfer alignment. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol, 2013, 21: 1666–1678
Gong X L, Fan W, Fang J C. An innovationalrransfer alignment method based on parameter identification UKF for airborne distributed POS. Measurement, 2014, 58: 103–114
Fearnhead P, Wyncoll D, Tawn J. A sequential smoothing algorithm with linear computational cost. Biometrika, 2010, 97: 447–464
Meditch J. A survey of data smoothing for linear and nonlinear dynamic systems. Automatica, 1973, 9: 151–162
Simon D. Optimal State Estimation, Kalman, H∞ and Nonlinear Approaches. New Jersey: John Wiley and Sons, 2006
Sarkka S. Unscented rauch–tung–striebel smoother. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 2008, 53: 845–849
Titterton D, Weston J. Strapdown Inertial Navigation Technology. 2nd ed. London: Institution of Engineering and Technology, 2004
Bekir E. Introduction to Modern Navigation Systems. Singapore: World Scientific, 2007
Goshen-Meskin D, Bar-itzhack I Y. Unified approach to inertial navigation system error modeling. J Guid Control Dynam, 1992, 15: 648–653
Zhang H T, Rong J, Zhong X C. The performance comparison and algorithm analysis of first order EKF, second order EKF and smoother for GPS/DR navigation. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Communication Technology, Hangzhou, 2008. 432–437
Allerton D J, Jia H M. Redundant multi-mode filter for a navigation system. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst, 2007, 43: 371–391
Lu Y, Cheng X H. Random misalignment and lever arm vector online estimation in shipborne aircraft transfer alignment. Measurement, 2014, 47: 756–764
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61473020, 61421063, 61233005), National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (Grant Nos. 2015AA124001, 2015AA124002), and International (Regional) Cooperation and Communication Project (Grant No. 61661136007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X., Chen, L., Fang, J. et al. A transfer alignment method for airborne distributed POS with three-dimensional aircraft flexure angles. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 61, 092204 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-017-9213-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-017-9213-9