Abstract
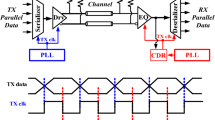
This paper proposes a synthesized injection-locked bang-bang phased-locked loop (SILBBPLL) with high digital controlled oscillator (DCO) frequency resolution. The SILBBPLL is expressed with hardware description language and automatically placed & routed (APR) by using standard digital circuit design flow. As the mismatch issues of the circuits are not considered carefully during the APR design flow, the phase noise performance is severely deteriorated. We adopt pulse injection locking technique to improve the phase noise performance. The DCO frequency resolution is critical for reducing the reference spur in a digital injection-locked PLL. Therefore, we propose novel frequency tuning circuits to increase the DCO frequency resolution so that the reference spurs are reduced. The frequency tuning circuits consist of a standard cell based high-linearity output feedback DAC (OFDAC) and two custom varactors. The OFDAC is used to tune the frequency of the DCO with the custom varactor precisely. The custom varactor is firstly designed, added into the standard cell library, and APR with the standard cells. The SILBBPLL chip with a core area of 0.008 mm2 is implemented in 65 nm CMOS process. When operating at 1.8 GHz, the measured results show that the root-mean-square (RMS) jitter integrated from 10 kHz to 100 MHz is 1.1 ps, and the power consumption is 1.5 mW with a 0.8-V supply. The proposed SILBBPLL achieves a figure-of-merit (FoM) of −237.4 dB and a reference spur of −50.9 dBc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Staszewski R B, Balsara P T. All-Digital Frequency Synthesizer in Deep-Submicron CMOS. Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons, 2006
Weaver S, Hershberg B, Moon U K. Digitally synthesized stochastic flash ADC using only standard digital cells. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2014, 61: 84–91
Waters A, Moon U K. A fully automated verilog-to-layout synthesized adc demonstrating 56 dB-SNDR with 2 MHz-BW. In: Proceedings of IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), 2015
Kim S J, Kim W, Song M Y, et al. 15.5 A 0.6 V 1.17 ps PVT-tolerant and synthesizable time-to-digital converter using stochastic phase interpolation with 16× spatial redundancy in 14 nm Fin-FET technology. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2015
Park Y, Wentzloff D D. An all-digital 12 pJ/pulse IR-UWB transmitter synthesized from a standard cell library. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2011, 46: 1147–1157
Choi Y H, Seong K, Kim B, et al. All-synthesizable 6 Gbps voltage-mode transmitter for serial link. In: Proceedings of IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), 2016. 245–248
Yang J C, Zhang Z, Liu L Y, et al. A 0.45-to-1.8 GHz fully synthesized injection locked bang-bang PLL with OFDAC to enhance DCO resolution. In: Proceedings of International Solid-State Device and Materials, 2017. 815–816
Zhang X Y, Jiang H J, Zhang L W, et al. An energy-efficient ASIC for wireless body sensor networks in medical applications. IEEE Trans Biomed Circ Syst, 2010, 4: 11–18
Zhang L W, Jiang H J, Wei J J, et al. A reconfigurable sliding-IF transceiver for 400 MHz/2.4 GHz IEEE 802.15.6/Zig-Bee WBAN hubs with only 21% tuning range VCO. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2013, 48: 2705–2716
Siriburanon T, Kondo S, Kimura K, et al. A 2.2 GHz −242 dB-FOM 4.2 mW ADC-PLL using digital sub-sampling architecture. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2016, 51: 1385–1397
Chen Z Z, Wang Y H, Shin J, et al. 14.9 sub-sampling all-digital fractional-N frequency synthesizer with −111 dBc/Hz in-band phase noise and an FOM of −242 dB. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2015
Elkholy A, Talegaonkar M, Anand T, et al. 10.7 A 6.75-to-8.25 GHz 2.25 mW 190 fsrms-integrated-jitter PVTinsensitive injection-locked clock multiplier using all-digital continuous frequency-tracking loop in 65 nm CMOS. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2015. 188–190
Elkholy A, Elmallah A, Elzeftawi M, et al. 10.6 A 6.75-to-8.25 GHz, 250 fsrms-integrated-jitter 3.25 mW rapid on/off PVT-insensitive fractional-N injection-locked clock multiplier in 65 nm CMOS. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2016. 192–194
Kuan T K, Liu S I. A bang bang phase-locked loop using automatic loop gain control and loop latency reduction techniques. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2016, 51: 821–831
Park Y, Wentzloff D D. An all-digital PLL synthesized from a digital standard cell library in 65 nm CMOS. In: Proceedings of IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), 2011
Faisal M, Wentzloff D D. An automatically placed-and-routed ADPLL for the medradio band using PWM to enhance DCO resolution. In: Proceedings of IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium (RFIC), 2013. 115–118
Kim W S, Park J, Park H, et al. Layout synthesis and loop parameter optimization of a low-jitter all-digital pixel clock generator. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2014, 49: 657–672
Kim S, Hong S, Chang K, et al. A 2 GHz synthesized fractional-N ADPLL with dual-referenced interpolating TDC. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2016, 51: 391–400
Yang D S, Deng W, Liu B A, et al. An LC-DCO based synthesizable injection-locked PLL with an FoM of −250.3 dB. In: Proceedings of the 42nd European Solid-State Circuits Conference, 2016. 197–200
Cho H, Seong K, Choi K H, et al. 8.7 A 0.0047 mm2 highly synthesizable TDC-and DCO-less fractional-N PLL with a seamless lock range of fREF to 1 GHz. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2017. 154–155
Deng W, Yang D S, Ueno T, et al. 15.1 A 0.0066 mm2 780 μW fully synthesizable PLL with a current-output DAC and an interpolative phase-coupled oscillator using edge-injection technique. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), 2014. 266–267
Deng W, Yang D S, Ueno T, et al. A fully synthesizable all-digital PLL with interpolative phase coupled oscillator, current-output DAC, and fine-resolution digital varactor using gated edge injection technique. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2015, 50: 68–80
Yang D S, Deng W, Narayanan A T, et al. A fully synthesizable injection-locked PLL with feedback current output DAC in 28 nm FDSOI. IEICE Electron Express, 2015, 12: 20150531
Deng W, Yang D S, Narayanan A T, et al. 14.1 A 0.048 mm2 3 mW synthesizable fractional-N PLL with a soft injection-locking technique. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), 2015
Tseng Y H, Yeh C W, Liu S I. A 2.25-2.7 GHz area-efficient subharmonically injection-locked fractional-N frequency synthesizer with a fast-converging correlation loop. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2017, 64: 811–822
Zanuso M, Tasca D, Levantino S, et al. Noise analysis and minimization in bang-bang digital PLLs. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II, 2009, 56: 835–839
Marucci G, Levantino S, Maffezzoni P, et al. Analysis and design of low-jitter digital bang-bang phase-locked loops. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2014, 61: 26–36
Tasca D, Zanuso M, Marzin G, et al. A 2.9-4.0-GHz fractional-N digital PLL with bang-bang phase detector and 560-fsrms integrated jitter at 4.5-mW power. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2011, 46: 2745–2758
Lee I T, Zeng K H, Liu S I. A 4.8-GHz dividerless subharmonically injection-locked All-digital PLL with a FOM of −252.5 dB. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II, 2013, 60: 547–551
Chen P L, Chung C C, Lee C Y. A portable digitally controlled oscillator using novel varactors. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II, 2005, 52: 233–237
Lee J, Wang H D. Study of subharmonically injection-locked PLLs. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2009, 44: 1539–1553
Zhang Z, Liu L Y, Wu N J. A novel 2.4-to-3.6 GHz wideband subharmonically injection-locked PLL with adaptivelyaligned injection timing. In: Proceedings of IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), 2014. 369–372
Wang R X, Dai F F. A 0.81.3 GHz multi-phase injection-locked PLL using capacitive coupled multi-ring oscillator with reference spur suppression. In: Proceedins of IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), 2017
Zhang Z, Liu L Y, Feng P, et al. A 2.4-3.6-GHz wideband subharmonically injection-locked PLL with adaptive injection timing alignment technique. IEEE Trans VLSI Syst, 2017, 25: 929–941
Choi S, Yoo S, Lim Y, et al. A PVT-robust and low-jitter ring-VCO-based injection-locked clock multiplier with a continuous frequency-tracking loop using a replica-delay cell and a dual-edge phase detector. IEEE J Solid-State Circ, 2016, 51: 1878–1889
Gao X, Klumperink E A M, Geraedts P F J, et al. Jitter analysis and a benchmarking figure-of-merit for phase-locked loops. IEEE Trans Circ Syst II, 2009, 56: 117–121
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Nature Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61331003, 61474108, 61234003), and National Key Technology Research and Development Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grant No. 2016ZX03001002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Zhang, Z., Qi, N. et al. A 0.45-to-1.8 GHz synthesized injection-locked bang-bang phase locked loop with fine frequency tuning circuits. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 62, 62405 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-018-9423-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-018-9423-y