Abstract
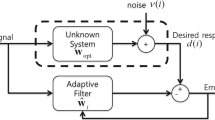
In this paper, an innovative recursive filtering algorithm (RFA) is proposed for a class of nonlinear systems (NSs) subject to multiplicative noises (MNs) and measurement outliers (MOs). Initially, the MNs are employed to formulate the random influence on the NSs with the stochastic noises. Next, the outlier phenomenon could occur unpredictably during measurement transmission. Then, a self-adaptive saturation function is introduced to the constructed filter to mitigate the influence of MOs on the filter performance. In this paper, we design a resistant-outlier filter for NSs with MNs and MOs, and the filter gain ensures that the trace of the filtering error covariance matrix is minimized by solving the constructed Riccati-like difference equations. Moreover, the exponential boundedness of the filtering error in the sense of mean square is analyzed. Finally, the feasibility of the proposed RFA is illustrated by a simulation example when the MOs occur.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kalman R E. A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J Basic Eng, 1960, 82: 35–45
Wan E A, Merwe R V D. The unscented Kalman filter for nonlinear estimation. In: Proceedings of IEEE Adaptive Systems for Signal Processing, Communications, and Control Symposium, 2000
Wang X M, He X K, Bao Y, et al. Parameter estimates of Heston stochastic volatility model with MLE and consistent EKF algorithm. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 042202
Li Q, Shen B, Wang Z D, et al. Event-triggered H∞ state estimation for state-saturated complex networks subject to quantization effects and distributed delays. J Franklin Inst, 2018, 355: 2874–2891
Sheng S Y, Zhang X M. H∞ filtering for T-S fuzzy complex networks subject to sensor saturation via delayed information. IET Control Theory Appl, 2017, 11: 2370–2382
Zhao S Y, Shmaliy Y S, Shi P, et al. Fusion Kalman/UFIR filter for state estimation with uncertain parameters and noise statistics. IEEE Trans Ind Electron, 2017, 64: 3075–3083
Caballero-Águila R, Hermoso-Carazo A, Linares-Pérez J. New distributed fusion filtering algorithm based on covariances over sensor networks with random packet dropouts. Int J Syst Sci, 2017, 48: 1805–1817
Julier S J, Uhlmann J K. New extension of the Kalman filter to nonlinear systems. In: Proceedings of SPIE 3068, Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition VI, 1997. 182–193
Bai W Y, Xue W C, Huang Y, et al. On extended state based Kalman filter design for a class of nonlinear time-varying uncertain systems. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 042201
Mao W H, Deng F Q, Wan A H. Robust H2/H∞ global linearization filter design for nonlinear stochastic time-varying delay systems. Sci China Inf Sci, 2016, 59: 032204
Liu Y J, Tong S C. Barrier lyapunov functions for nussbaum gain adaptive control of full state constrained nonlinear systems. Automatica, 2017, 76: 143–152
Hu J, Wang Z D, Shen B, et al. Quantised recursive filtering for a class of nonlinear systems with multiplicative noises and missing measurements. Int J Control, 2013, 86: 650–663
Rajasekaran P, Satyanarayana N, Srinath M. Optimum linear estimation of stochastic signals in the presence of multiplicative noise. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst, 1971, 7: 462–468
Dong H L, Wang Z D, Ding S X, et al. Event-based H∞ filter design for a class of nonlinear time-varying systems with fading channels and multiplicative noises. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2015, 63: 3387–3395
Liu W. Optimal estimation for discrete-time linear systems in the presence of multiplicative and time-correlated additive measurement noises. IEEE Trans Signal Process, 2015, 63: 4583–4593
Zhang L X, Zhu Y Z, Shi P, et al. Resilient asynchronous H∞ filtering for markov jump neural networks with unideal measurements and multiplicative noises. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2015, 45: 2840–2852
Li Y Y, Karimi H R, Zhong M Y, et al. Fault detection for linear discrete time-varying systems with multiplicative noise: the finite-horizon case. IEEE Trans Circ Syst I, 2018, 65: 3492–3505
Song X M, Park J H. Linear minimum mean-square estimation for discrete-time measurement-delay systems with multiplicative noise and Markov jump. IET Control Theory Appl, 2016, 10: 1161–1169
Yang F, Dong H L, Wang Z D, et al. A new approach to non-fragile state estimation for continuous neural networks with time-delays. Neurocomputing, 2016, 197: 205–211
Gao H Y, Han F, Jiang B, et al. Recursive filtering for time-varying systems under duty cycle scheduling based on collaborative prediction. J Franklin Inst, 2020, 357: 13189–13204
Wang C, Han F, Zhang Y, et al. An SAE-based resampling SVM ensemble learning paradigm for pipeline leakage detection. Neurocomputing, 2020, 403: 237–246
Li J H, Dong H L, Wang Z D, et al. Partial-neurons-based passivity-guaranteed state estimation for neural networks with randomly occurring time delays. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2020, 31: 3747–3753
Gao Y B, Luo W S, Liu J X, et al. Integral sliding mode control design for nonlinear stochastic systems under imperfect quantization. Sci China Inf Sci, 2017, 60: 120206
Li X R, Han F, Hou N, et al. Set-membership filtering for piecewise linear systems with censored measurements under Round-Robin protocol. Int J Syst Sci, 2020, 51: 1578–1588
Peng H, Lu R Q, Xu Y, et al. Dissipative non-fragile state estimation for Markovian complex networks with coupling transmission delays. Neurocomputing, 2018, 275: 1576–1584
Rakkiyappan R, Sivaranjani K. Sampled-data synchronization and state estimation for nonlinear singularly perturbed complex networks with time-delays. Nonlinear Dyn, 2016, 84: 1623–1636
Zhou D H, Qin L G, He X, et al. Distributed sensor fault diagnosis for a formation system with unknown constant time delays. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 112205
Meinhold R J, Singpurwalla N D. Robustification of Kalman filter models. J Am Stat Assoc, 1989, 84: 479–486
Huang Y L, Zhang Y G, Xu B, et al. A new outlier-robust student’s t based gaussian approximate filter for cooperative localization. IEEE/ASME Trans Mechatron, 2017, 22: 2380–2386
de Palma D, Indiveri G. Output outlier robust state estimation. Int J Adapt Control Signal Proces, 2017, 31: 581–607
Alessandri A, Zaccarian L. Results on stubborn Luenberger observers for linear time-invariant plants. In: Proceedings of European Control Conference (ECC), Linz, 2015. 2920–2925
Alessandri A, Zaccarian L. Stubborn state observers for linear time-invariant systems. Automatica, 2018, 88: 1–9
Gao H Y, Dong H L, Wang Z D, et al. An event-triggering approach to recursive filtering for complex networks with state saturations and random coupling strengths. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst, 2020, 31: 4279–4289
Li W L, Sun J, Jia Y M, et al. Variance-constrained state estimation for nonlinear complex networks with uncertain coupling strength. Digit Signal Process, 2017, 67: 107–115
Wang Y Y, Xie L H, de Souza C E. Robust control of a class of uncertain nonlinear systems. Syst Control Lett, 1992, 19: 139–149
Wang L C, Wang Z D, Huang T W, et al. An event-triggered approach to state estimation for a class of complex networks with mixed time delays and nonlinearities. IEEE Trans Cybern, 2016, 46: 2497–2508
Reif K, Gunther S, Yaz E, et al. Stochastic stability of the discrete-time extended Kalman filter. IEEE Trans Autom Control, 1999, 44: 714–728
Liu S. Schur complement. In: Encyclopedia of Statistical Sciences. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2008
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61873058, 61933007) and in part by Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (Grant No. ZD2019F001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, B., Gao, H., Han, F. et al. Recursive filtering for nonlinear systems subject to measurement outliers. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 64, 172206 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3135-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3135-y