Abstract
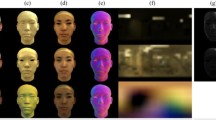
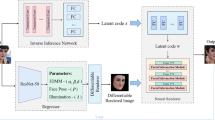
We introduce a deep-learning based algorithm to infer high-fidelity facial reflectance from a single image. The algorithm uses convolutional neural networks to encode the input image into a latent representation, from which a decoder and a detail enhancing network reconstruct decoupled facial reflectance (albedo, specular, and normal) as well as the environmental lighting. These decoupled components, together with a 3D facial mesh estimated from the image, are then fed into a differentiable renderer to produce a rendered facial image. This allows us to iteratively optimize the latent representation of the facial image by minimizing the image-space reconstruction loss. Experimental results show that optimizing the latent representation through the differentiable renderer can effectively reduce the discrepancy between the original image and the rendered one, leading to a more accurate reconstruction of characteristic facial features such as skin tone, lip color, and facial hair.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debevec P, Hawkins T, Tchou C, et al. Acquiring the reflectance field of a human face. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, 2000. 145–156
Ghosh A, Fyffe G, Tunwattanapong B, et al. Multiview face capture using polarized spherical gradient illumination. ACM Trans Graph, 2011, 30: 1–10
Ichim A E, Bouaziz S, Pauly M. Dynamic 3D avatar creation from hand-held video input. ACM Trans Graph, 2015, 34: 1–14
Hu L, Saito S, Wei L, et al. Avatar digitization from a single image for real-time rendering. ACM Trans Graph, 2017, 36: 1–14
Sengupta S, Kanazawa A, Castillo C D, et al. SfSNet: learning shape, reflectance and illuminance of faces in the wild. 2018. arXiv:1712.01261
Tewari A, Zollhfer M, Kim H, et al. MoFA: model-based deep convolutional face autoencoder for unsupervised monocular reconstruction. 2017. ArXiv:1703.10580
Genova K, Cole F, Maschinot A, et al. Unsupervised training for 3D morphable model regression. 2018. ArXiv:1806.06098
Deng Y, Yang J, Xu S, et al. Accurate 3D face reconstruction with weakly-supervised learning: from single image to image set. 2019. ArXiv:1903.08527
Tran L, Liu X. Nonlinear 3D face morphable model. In: Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, 2018
Tran L, Liu F, Liu X. Towards high-fidelity nonlinear 3D face morphable model. In: Proceedings of IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, 2019
Yamaguchi S, Saito S, Nagano K, et al. High-fidelity facial reflectance and geometry inference from an unconstrained image. ACM Trans Graph, 2018, 37: 1–14
Ma W C, Hawkins T, Peers P, et al. Rapid acquisition of specular and diffuse normal maps from polarized spherical gradient illumination. In: Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Rendering Techniques, Grenoble, 2007
Gotardo P, Riviere J, Bradley D, et al. Practical dynamic facial appearance modeling and acquisition. ACM Trans Graph, 2019, 37: 1–13
Beeler T, Bickel B, Beardsley P, et al. High-quality single-shot capture of facial geometry. ACM Trans Graph, 2010, 29: 1–9
Beeler T, Hahn F, Bradley D, et al. High-quality passive facial performance capture using anchor frames. ACM Trans Graph, 2011, 30: 1–10
Graham P, Tunwattanapong B, Busch J, et al. Measurement-based synthesis of facial microgeometry. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 2013
von der Pahlen J, Jimenez J, Danvoye E, et al. Digital Ira and Beyond: Creating a Real-Time Photoreal Digital Actor. Technical Report, 2014
Blanz V, Vetter T. A morphable model for the synthesis of 3D faces. In: Proceedings of ACM SIGGRAPH, 1999
Kemelmacher-Shlizerman I. Internet based morphable model. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2013. 3256–3263
Booth J, Roussos A, Zafeiriou S, et al. A 3D morphable model learnt from 10000 faces. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 2016. 5543–5552
Egger B, Smith W A P, Tewari A, et al. 3D morphable face models-past, present, and future. ACM Trans Graph, 2020, 39: 1–38
Thies J, Zollhofer M, Stamminger M, et al. Face2face: real-time face capture and reenactment of RGB videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016. 2387–2395
Garrido P, Zollhofer M, Casas D, et al. Reconstruction of personalized 3D face rigs from monocular video. ACM Trans Graph, 2016, 35: 1–15
Cao C, Hou Q, Zhou K. Displaced dynamic expression regression for real-time facial tracking and animation. ACM Trans Graph, 2014, 33: 1–10
Tewari A, Zollhöfer M, Garrido P, et al. Self-supervised multi-level face model learning for monocular reconstruction at over 250 Hz. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018. 2549–2559
Saito S, Wei L, Hu L, et al. Photorealistic facial texture inference using deep neural networks. 2017. arXiv:1612.00523
Gecer B, Ploumpis S, Kotsia I, et al. GANFIT: generative adversarial network fitting for high fidelity 3D face reconstruction. 2019. ArXiv:1902.05978
Huynh L, Chen W, Saito S, et al. Mesoscopic facial geometry inference using deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2018. 8407–8416
Sun T, Barron J T, Tsai Y T, et al. Single image portrait relighting. ACM Trans Graph, 2019, 38: 1–12
Zhou H, Hadap S, Sunkavalli K, et al. Deep single-image portrait relighting. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019. 7194–7202
Meka A, Häne C, Pandey R, et al. Deep reflectance fields. ACM Trans Graph, 2019, 38: 1–12
Liu S, Li T, Chen W, et al. Soft rasterizer: a differentiable renderer for image-based 3D reasoning. 2019. ArXiv:1904.01786
Chen W, Ling H, Gao J, et al. Learning to predict 3D objects with an interpolation-based differentiable renderer. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019. 9605–9616
Shu Z, Yumer E, Hadap S, et al. Neural face editing with intrinsic image disentangling. 2017. ArXiv:1704.04131
Aittala M, Aila T, Lehtinen J. Reflectance modeling by neural texture synthesis. ACM Trans Graph, 2016, 35: 1–13
Gao D, Li X, Dong Y, et al. Deep inverse rendering for high-resolution SVBRDF estimation from an arbitrary number of images. ACM Trans Graph, 2019, 38: 1–15
Nicodemus F E. Directional reflectance and emissivity of an opaque surface. Appl Opt, 1965, 4: 767–775
Calian D A, Lalonde J F, Gotardo P, et al. From faces to outdoor light probes. In: Proceedings of Computer Graphics Forum, 2018. 51–61
Dib A, Bharaj G, Ahn J, et al. Face reflectance and geometry modeling via differentiable ray tracing. 2019. ArXiv:1910.05200
Li T M, Aittala M, Durand F, et al. Differentiable Monte Carlo ray tracing through edge sampling. ACM Trans Graph, 2019, 37: 1–11
Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T, et al. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017. 1125–1134
Sloan P P, Kautz J, Snyder J. Precomputed radiance transfer for real-time rendering in dynamic, low-frequency lighting environments. ACM Trans Graph, 2002, 21: 527–536
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. 2015. ArXiv: 1505.04597
Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017. 4681–4690
Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. 2014. ArXiv:1409.1556
Sloan P P. Stupid spherical harmonics (SH) tricks. In: Proceedings of Game Developers Conference, 2008. 42
Snyder J. Code Generation and Factoring for Fast Evaluation of Low-order Spherical Harmonic Products and Squares. Microsoft TechReport MSR-TR-2006-53, 2006
Walter B, Marschner S R, Li H, et al. Microfacet models for refraction through rough surfaces. In: Proceedings of the Eurographics Symposium on Rendering Techniques, Grenoble, 2007
Lagarde S, de Rousiers C. Moving frostbite to physically based rendering. In: Proceedings of SIGGRAPH 2014 Conference, Vancouver, 2014
Gardner M A, Sunkavalli K, Yumer E, et al. Learning to predict indoor illumination from a single image. 2017. ArXiv:1704.00090
Sumner R W, Popovic J. Deformation transfer for triangle meshes. ACM Trans Graph, 2004, 23: 399–405
Ma D S, Correll J, Wittenbrink B. The Chicago face database: a free stimulus set of faces and norming data. Behav Res, 2015, 47: 1122–1135
Pérez P, Gangnet M, Blake A. Poisson image editing. ACM Trans Graph, 2003, 22: 313–318
Abadi M, Barham P, Chen J, et al. Tensorflow: a system for large-scale machine learning. In: Proceedings of the 12th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation, 2016. 265–283
Kingma D P, Ba J. Adam: a method for stochastic optimization. 2014. ArXiv:1412.6980
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Geng, J., Weng, Y., Wang, L. et al. Single-view facial reflectance inference with a differentiable renderer. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 64, 210101 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3236-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-020-3236-2