Abstract
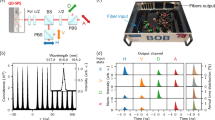
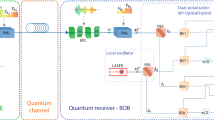
Self-stabilizing the quantum key distribution (QKD) system is essential to evaluate eavesdroppers’ information accurately. We develop and verify a polarization-insensitive time-bin decoder chip for QKD with the hybrid asymmetric Faraday-Michelson interferometer (AFMI) based on the planar lightwave circuit (PLC). Compared with existing chip-based QKD works, the scheme can intrinsically compensate for the polarization perturbation to quantum signals and thus work at arbitrary temperatures. We experimentally verify the chips in a time-bin QKD system at the clocking rate of 1.25 GHz and obtain an average secure key rate (SKR) of 1.34 Mbps over a 50 km fiber channel with an optimized analysis model. The steady variations of the quantum bit error and SKR with random polarization disturbance demonstrate that PLC-based AFMIs are available for developing self-stable QKD systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gisin N, Ribordy G, Tittel W, et al. Quantum cryptography. Rev Mod Phys, 2002, 74: 145–195
Bennett C H, Brassard G. Quantum cryptography: public key distribution and coin tossing. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Computers, Systems & Signal Processing, 1984. 175–179
Bennett C H, Bessette F, Brassard G, et al. Experimental quantum cryptography. J Cryptology, 1992, 5: 3–28
Li L L, Li J, Chang Y, et al. Quantum key distribution based on single-particle and EPR entanglement. Sci China Inf Sci, 2020, 63: 169501
Yang Y G, Yang J J, Zhou Y H, et al. Quantum network communication: a discrete-time quantum-walk approach. Sci China Inf Sci, 2018, 61: 042501
Xu F, Ma X, Zhang Q, et al. Secure quantum key distribution with realistic devices. Rev Mod Phys, 2020, 92: 025002
Ding Y Y, Chen H, Wang S, et al. Polarization variations in installed fibers and their influence on quantum key distribution systems. Opt Express, 2017, 25: 27923–27936
Dixon A R, Dynes J F, Lucamarini M, et al. High speed prototype quantum key distribution system and long term field trial. Opt Express, 2015, 23: 7583–7592
Ding Y Y, Chen W, Chen H, et al. Polarization-basis tracking scheme for quantum key distribution using revealed sifted key bits. Opt Lett, 2017, 42: 1023–1026
Zbinden H, Gautier J D, Gisin N, et al. Interferometry with Faraday mirrors for quantum cryptography. Electron Lett, 1997, 33: 586–588
Wang S, Chen W, Yin Z Q, et al. Field and long-term demonstration of a wide area quantum key distribution network. Opt Express, 2014, 22: 21739–21756
Sibson P, Kennard J E, Stanisic S, et al. Integrated silicon photonics for high-speed quantum key distribution. Optica, 2017, 4: 172
Geng W, Zhang C, Zheng Y L, et al. Stable quantum key distribution using a silicon photonic transceiver. Opt Express, 2019, 27: 29045
Sibson P, Erven C, Godfrey M, et al. Chip-based quantum key distribution. Nat Commun, 2017, 8: 13984
Semenenko H, Sibson P, Hart A, et al. Chip-based measurement-device-independent quantum key distribution. Optica, 2020, 7: 238
Honjo T, Inoue K, Takahashi H. Differential-phase-shift quantum key distribution experiment with a planar light-wave circuit Mach-Zehnder interferometer. Opt Lett, 2004, 29: 2797–2799
Choe J S, Ko H, Choi B S, et al. Silica planar lightwave circuit based integrated 1 × 4 polarization beam splitter module for free-space BB84 quantum key distribution. IEEE Photon J, 2018, 10: 1–8
Takesue H, Sasaki T, Tamaki K, et al. Experimental quantum key distribution without monitoring signal disturbance. Nat Photon, 2015, 9: 827–831
Nambu Y, Yoshino K, Tomita A. Quantum encoder and decoder for practical quantum key distribution using a planar lightwave circuit. J Modern Opt, 2008, 55: 1953–1970
Li X, Ren M Z, Zhang J S, et al. Interference at the single-photon level based on silica photonics robust against channel disturbance. Photon Res, 2021, 9: 222–228
Zhang G W, Ding Y Y, Chen W, et al. Polarization-insensitive interferometer based on a hybrid integrated planar light-wave circuit. Photon Res, 2021, 9: 2176–2181
Rusca D, Boaron A, Grünenfelder F, et al. Finite-key analysis for the 1-decoy state QKD protocol. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112: 171104
Brassard G, Lütkenhaus N, Mor T, et al. Limitations on practical quantum cryptography. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85: 1330–1333
Roberts G L, Pittaluga M, Minder M, et al. Patterning-effect mitigating intensity modulator for secure decoy-state quantum key distribution. Opt Lett, 2018, 43: 5110
Boaron A, Korzh B, Houlmann R, et al. Simple 2.5 GHz time-bin quantum key distribution. Appl Phys Lett, 2018, 112: 171108
Fan-Yuan G J, Wang C, Wang S, et al. Afterpulse analysis for quantum key distribution. Phys Rev Appl, 2018, 10: 064032
Wang F X, Chen W, Li Y P, et al. Non-Markovian property of afterpulsing effect in single-photon avalanche detector. J Lightwave Technol, 2016, 34: 3610–3615
Fan-Yuan G J, Wang S, Yin Z Q, et al. Modeling alignment error in quantum key distribution based on a weak coherent source. Phys Rev Appl, 2019, 12: 064044
Chen W, Han Z F, Mo X F, et al. Active phase compensation of quantum key distribution system. Sci Bull, 2008, 53: 1310–1314
Zhang L J, Wang Y G, Yin Z Q, et al. Real-time compensation of phase drift for phase-encoded quantum key distribution systems. Chin Sci Bull, 2011, 56: 2305–2311
Fan-Yuan G J, Chen W, Lu F Y, et al. A universal simulating framework for quantum key distribution systems. Sci China Inf Sci, 2020, 63: 180504
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Key Research and Development Program of China (Grant No. 2018YFA0306400), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 61627820, 61622506, 61822115), Anhui Initiative in Quantum Information Technologies (Grant No. AHY030000). This work was partially carried out at the USTC Center for Micro and Nanoscale Research and Fabrication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, GW., Chen, W., Fan-Yuan, GJ. et al. Polarization-insensitive quantum key distribution using planar lightwave circuit chips. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 65, 200506 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-022-3514-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11432-022-3514-3