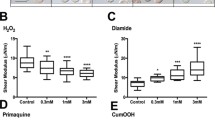
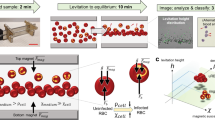
Abstract
Investigation of the homeostasis of red blood cells upon infection by Plasmodium falciparum poses complex experimental challenges. Changes in red cell shape, volume, protein, and ion balance are difficult to quantify. In this article, we review a wide range of optical techniques for quantitative measurements of critical homeostatic parameters in malaria-infected red blood cells. Fluorescence lifetime imaging and tomographic phase microscopy, quantitative deconvolution microscopy, and X-ray microanalysis, are used to measure haemoglobin concentration, cell volume, and ion contents. Atomic force microscopy is briefly reviewed in the context of these optical methodologies. We also describe how optical tweezers and optical stretchers can be usefully applied to empower basic malaria research to yield diagnostic information on cell compliance changes upon malaria infection. The combined application of these techniques sheds new light on the detailed mechanisms of malaria infection providing potential for new diagnostic or therapeutic approaches.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aikawa M (1997) Studies on falciparum malaria with atomic-force and surface-potential microscopes. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 91(7):689–692
Aikawa M, Kamanura K, Shiraishi S, Matsumoto Y, Arwati H, Torii M, Ito Y, Takeuchi T, Tandler B (1996) Membrane knobs of unfixed Plasmodium falciparum infected erythrocytes: new findings as revealed by atomic force microscopy and surface potential spectroscopy. Exp Parasitol 84(3):339–343
Akaki M, Nagayasu E, Nakano Y, Aikawa M (2002) Surface charge of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites as revealed by atomic force microscopy with surface potential spectroscopy. Parasitol Res 88(1):16–20
Allen RJ, Kirk K (2004) Cell volume control in the Plasmodium-infected erythrocyte. Trends Parasitol 20(1):7–10; discussion 10-1
Block SM (1990) Optical tweezers: a new tool for biophysics. In: Grinstein S, Foskett JK (ed) Noninvasive techniques in cell biology. Wiley-Liss, New York, p 375
Boutet de Monvel J, Le Calvez S, Ulfendahl M (2001) Image restoration for confocal microscopy: improving the limits of deconvolution, with application to the visualization of the mammalian hearing organ. Biophys J 80(5):2455–2470
Bronkhorst PJ, Streekstra GJ, Grimbergen J, Nijhof EJ, Sixma JJ, Brakenhoff GJ (1995) A new method to study shape recovery of red blood cells using multiple optical trapping. Biophys J 69(5):1666–1673
Choi W, Fang-Yen C, Badizadegan K, Oh S, Lue N, Dasari RR, Feld MS (2007) Tomographic phase microscopy. Nat Methods 4(9):717–719
De Cian A, Grellier P, Mouray E, Depoix D, Bertrand H, Monchaud D, Teulade-Fichou MP, Mergny JL, Alberti P (2008) Plasmodium telomeric sequences: structure, stability and quadruplex targeting by small compounds. ChemBioChem 9(16):2730–2739
Degliesposti G, Kasam V, Da Costa A, Kang HK, Kim N, Kim DW, Breton V, Kim D, Rastelli G (2009) Design and discovery of plasmepsin II inhibitors using an automated workflow on large-scale grids. ChemMedChem 4(7):1164–1173
Dobbe JG, Hardeman MR, Streekstra GJ, Strackee J, Ince C, Grimbergen CA (2002) Analyzing red blood cell-deformability distributions. Blood Cells Mol Dis 28(3):373–384
Elder AD, Domin A, Schierle GSK, Lindon C, Pines J, Esposito A, Kaminski CF (2009) A quantitative protocol for dynamic measurements of protein interactions by Forster resonance energy transfer-sensitized fluorescence emission. J R Soc Interface 6:S59–S81
Elder AD, Kaminski CF, Frank JH (2009) phi2FLIM: a technique for alias-free frequency domain fluorescence lifetime imaging. Optics Express 17(25):23181–23203
Elliott JL, Saliba KJ, Kirk K (2001) Transport of lactate and pyruvate in the intraerythrocytic malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. Biochem J 355(Pt 3):733–739
Elliott DA, McIntosh MT, Hosgood HD III, Chen S, Zhang G, Baevova P, Joiner KA (2008) Four distinct pathways of hemoglobin uptake in the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(7):2463–2468
Esposito A, Choimet J-B, Skepper J, Mauritz JM, Lew VL, Kaminski C, Tiffert T (2010) Quantitative imaging of human red blood cells infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Biophys J (in press)
Esposito A, Tiffert T, Mauritz JMA, Schlachter S, Bannister LH, Kaminski CF, Lew VL (2008) FRET imaging of hemoglobin concentration in Plasmodium falciparum-infected red cells. PLoS ONE 3(11):e3780
Fernandez-Segura E, Warley A (2008) Electron probe X-ray microanalysis for the study of cell physiology. Methods Cell Biol 88:19–43
Francis LW, Lewis PD, Wright CJ, Conlan RS (2010) Atomic force microscopy comes of age. Biol Cell 102(2):133–143
Garcia CR, Takeuschi M, Yoshioka K, Miyamoto H (1997) Imaging Plasmodium falciparum-infected ghost and parasite by atomic force microscopy. J Struct Biol 119(2):92–98
Glushakova S, Yin D, Li T, Zimmerberg J (2005) Membrane transformation during malaria parasite release from human red blood cells. Curr Biol 15(18):1645–1650
Glushakova S, Yin D, Gartner N, Zimmerberg J (2007) Quantification of malaria parasite release from infected erythrocytes: inhibition by protein-free media. Malar J 6:61
Guck J, Ananthakrishnan R, Moon TJ, Cunningham CC, Kas J (2000) Optical deformability of soft biological dielectrics. Phys Rev Lett 84(23):5451–5454
Guck J, Ananthakrishnan R, Mahmood H, Moon TJ, Cunningham CC, Kas J (2001) The optical stretcher: a novel laser tool to micromanipulate cells. Biophys J 81(2):767–784
Guck J, Schinkinger S, Lincoln B, Wottawah F, Ebert S, Romeyke M, Lenz D, Erickson HM, Ananthakrishnan R, Mitchell D, Kas J, Ulvick S, Bilby C (2005) Optical deformability as an inherent cell marker for testing malignant transformation and metastatic competence. Biophys J 88(5):3689–3698
Henon S, Lenormand G, Richert A, Gallet F (1999) A new determination of the shear modulus of the human erythrocyte membrane using optical tweezers. Biophys J 76(2):1145–1151
Kaminski CF (2005) Fluorescence imaging of reactive processes. Zeitschrift Fur Physikalische Chemie—Int J Res Phys Chem Chem Phys 219(6):747–774
Kasas S, Thomson NH, Smith BL, Hansma PK, Miklossy J, Hansma HG (1997) Biological applications of the AFM: from single molecules to organs. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 8(2):151–161
Kirk K (2001) Membrane transport in the malaria-infected erythrocyte. Physiol Rev 81(2):495–537
Kreysing MK, Kiessling T, Fritsch A, Dietrich C, Guck JR, Kas JA (2008) The optical cell rotator. Opt Express 16(21):16984–16992
Krugliak M, Zhang J, Ginsburg H (2002) Intraerythrocytic Plasmodium falciparum utilizes only a fraction of the amino acids derived from the digestion of host cell cytosol for the biosynthesis of its proteins. Mol Biochem Parasitol 119(2):249–256
Kuhn Y, Rohrbach P, Lanzer M (2007) Quantitative pH measurements in Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes using pHluorin. Cell Microbiol 9(4):1004–1013
Lautenschlager F, Paschke S, Schinkinger S, Bruel A, Beil M, Guck J (2009) The regulatory role of cell mechanics for migration of differentiating myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(37):15696–15701
Lee P, Ye Z, Van Dyke K, Kirk RG (1988) X-ray microanalysis of Plasmodium falciparum and infected red blood cells: effects of qinghaosu and chloroquine on potassium, sodium, and phosphorus composition. Am J Trop Med Hyg 39(2):157–165
Lew VL, Tiffert T (2007) Is invasion efficiency in malaria controlled by pre-invasion events? Trends Parasitol 23(10):481–484
Lew VL, Tiffert T, Ginsburg H (2003) Excess hemoglobin digestion and the osmotic stability of Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells. Blood 101(10):4189–4194
Lincoln B, Schinkinger S, Travis K, Wottawah F, Ebert S, Sauer F, Guck J (2007) Reconfigurable microfluidic integration of a dual-beam laser trap with biomedical applications. Biomed Microdevices 9(5):703–710
Lincoln B, Wottawah F, Schinkinger S, Ebert S, Guck J (2007) High-throughput rheological measurements with an optical stretcher. Methods Cell Biol 83:397–423
Marinkovic M, Diez-Silva M, Pantic I, Fredberg JJ, Suresh S, Butler JP (2009) Febrile temperature leads to significant stiffening of Plasmodium falciparum parasitized erythrocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296(1):C59–C64
Mauritz J, Tiffert T, Seear R, Lautenschlager F, Esposito A, Lew V, Guck J, Kaminski CF (2010) Detection of Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells by optical stretching. J Biomed Opt 15:030517
Mauritz JM, Esposito A, Ginsburg H, Kaminski CF, Tiffert T, Lew VL (2009) The homeostasis of Plasmodium falciparum-infected red blood cells. PLoS Comput Biol 5(4):e1000339
Mens PF, van Overmeir C, Bonnet M, Dujardin JC, d’Alessandro U (2008) Real-time PCR/MCA assay using fluorescence resonance energy transfer for the genotyping of resistance related DHPS-540 mutations in Plasmodium falciparum. Malar J 7:48
Nagao E, Kaneko O, Dvorak JA (2000) Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes: qualitative and quantitative analyses of parasite-induced knobs by atomic force microscopy. J Struct Biol 130(1):34–44
Nagao E, Nishijima H, Akita S, Nakayama Y, Dvorak JA (2000) The cell biological application of carbon nanotube probes for atomic force microscopy: comparative studies of malaria-infected erythrocytes. J Electron Microsc 49(3):453–458
Nash GB, O’Brien E, Gordon-Smith EC, Dormandy JA (1989) Abnormalities in the mechanical properties of red blood cells caused by Plasmodium falciparum. Blood 74(2):855–861
Park YK, Diez-Silva M, Popescu G, Lykotrafitis G, Choi WS, Feld MS, Suresh S (2008) Refractive index maps and membrane dynamics of human red blood cells parasitized by Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(37):13730–13735
Peter M, Ameer-Beg SM (2004) Imaging molecular interactions by multiphoton FLIM. Biol Cell 96(3):231–236
Remmerbach TW, Wottawah F, Dietrich J, Lincoln B, Wittekind C, Guck J (2009) Oral cancer diagnosis by mechanical phenotyping. Cancer Res 69(5):1728–1732
Rohrbach P, Friedrich O, Hentschel J, Plattner H, Fink RH, Lanzer M (2005) Quantitative calcium measurements in subcellular compartments of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Biol Chem 280(30):27960–27969
Safeukui I, Millet P, Boucher S, Melinard L, Fregeville F, Receveur MC, Pistone T, Fialon P, Vincendeau P, Fleury H, Malvy D (2008) Evaluation of FRET real-time PCR assay for rapid detection and differentiation of Plasmodium species in returning travellers and migrants. Malar J 7:70
Saliba KJ, Horner HA, Kirk K (1998) Transport and metabolism of the essential vitamin pantothenic acid in human erythrocytes infected with the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Biol Chem 273(17):10190–10195
Sleep J, Wilson D, Simmons R, Gratzer W (1999) Elasticity of the red cell membrane and its relation to hemolytic disorders: an optical tweezers study. Biophys J 77(6):3085–3095
Staines HM, Ellory JC, Kirk K (2001) Perturbation of the pump-leak balance for Na(+) and K(+) in malaria-infected erythrocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 280(6):C1576–C1587
Suresh S (2006) Mechanical response of human red blood cells in health and disease: some structure-property-function relationships. J Mater Res 21(8):1871–1877
Suresh S, Spatz J, Mills JP, Micoulet A, Dao M, Lim CT, Beil M, Seufferlein T (2005) Connections between single-cell biomechanics and human disease states: gastrointestinal cancer and malaria. Acta Biomater 1(1):15–30
Tokumasu F, Dvorak J (2003) Development and application of quantum dots for immunocytochemistry of human erythrocytes. J Microsc 211(Pt 3):256–261
Tokumasu F, Fairhurst RM, Ostera GR, Brittain NJ, Hwang J, Wellems TE, Dvorak JA (2005) Band 3 modifications in Plasmodium falciparum-infected AA and CC erythrocytes assayed by autocorrelation analysis using quantum dots. J Cell Sci 118(Pt 5):1091–1098
Warley A (1997) X-ray microanalysis for biologists. In: Glauert AM (ed) Practical methods in electron microscopy, vol 16. Portland Press, London and Miami
Warley A, Skepper JN (2000) Long freeze-drying times are not necessary during the preparation of thin sections for X-ray microanalysis. J Microsc 198(Pt 2):116–123
Yoon YZ, Kotar J, Yoon G, Cicuta P (2008) The nonlinear mechanical response of the red blood cell. Phys Biol 5(3):36007
Zanner MA, Galey WR, Scaletti JV, Brahm J, Vander Jagt DL (1990) Water and urea transport in human erythrocytes infected with the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol 40(2):269–278
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by funds from the EPSRC (EP/E059384), BBSRC (BB/E008542/1) and by a grant from the Isaac Newton Trust to TT. YZ is supported by the Korea Foundation for International Cooperation of Science & Technology (KICOS) through a grant provided by the Korean Ministry of Education Science & Technology (MEST) in 2009 (No. 2009-00591). AE is supported by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council UK (EP/F044011/1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mauritz, J.M.A., Esposito, A., Tiffert, T. et al. Biophotonic techniques for the study of malaria-infected red blood cells. Med Biol Eng Comput 48, 1055–1063 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-010-0668-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-010-0668-0