Abstract
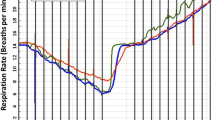
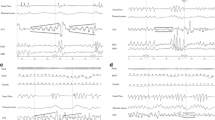
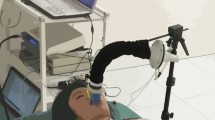
The aim of this study was to investigate whether respiratory information can be derived from pulse oximetry plethysmogram (pleth) recordings in acutely wheezy preschool children. A digital pulse oximeter was connected via ‘Bluetooth’ to a notebook computer in order to acquire pleth data. Low pass filtering and frequency analysis were used to derive respiratory rate from the pleth trace; the ratio of heart rate to respiratory rate (HR/RR) was also calculated. Recordings were obtained during acute wheezy episodes in 18 children of median age 31 months and follow-up recordings from 16 of the children were obtained when they were wheeze-free. For the acutely wheezy children, frequency analysis of the pleth waveform was within 10 breaths/min of clinical assessment in 25 of 29 recordings in 15 children. For the follow-up measurements, frequency analysis of the pleth waveform showed similarly good agreement in recordings on 15 of the 16 children. Respiratory rate was higher (p < 0.001), and HR/RR ratio was lower (p = 0.03) during acute wheeze than at follow-up. This study suggests that respiratory rate can be derived from pleth traces in wheezy preschool children.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FFT:
-
Fast Fourier transform
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- LPF:
-
Low pass filter
- Pleth:
-
Pulse oximetry plethysmogram
- RR:
-
Respiratory rate
- SpO2 :
-
Oxygen saturation
References
Al-Khalidi FQ, Saatchi R, Burke D, Elphick H, Tan S (2011) Respiration rate monitoring methods: a review. Pediatr Pulmonol 46:523–529
Fleming S, Thompson M, Stevens R, Heneghan C, Plüddemann A, Maconochie I, Tarassenko L, Mant D (2011) Normal ranges of heart rate and respiratory rate in children from birth to 18 years of age: a systematic review of observational studies. Lancet 377(9770):1011–1018
Foo JY, Wilson SJ (2005) Estimation of breathing interval from the photoplethysmographic signals in children. Physiol Meas 26:1049–1058
Leonard P, Beattie TF, Addison PS, Watson JN (2003) Standard pulse oximeters can be used to monitor respiratory rate. Emerg Med J 20:524–525
Leonard PA, Clifton D, Addison PS, Watson JN, Beattie T (2006) An automated algorithm for determining respiratory rate by photoplethysmogram in children. Acta Paediatr 95:1124–1128
Pinsky MR (2007) At the threshold of noninvasive functional hemodynamic monitoring. Anesthesiology 106:1084–1085
Ranganathan S, Goetz I, Hoo AF, Castle R, Stocks J, London Collaborative Cystic Fibrosis Group (2003) Assessment of tidal breathing parameters in infants with cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J 22:761–766
Shamir M, Eidelman LA, Floman Y, Kaplan L, Pizov R (1999) Pulse oximetry plethysmographic waveform during changes in blood volume. Br J Anaesth 82:178–181
Shelley KH, Jablonka DH, Awad AA, Stout RG, Rezkanna H, Silverman DG (2006) What is the best site for measuring the effect of ventilation on the pulse oximeter waveform? Anesth Analg 103:372–377
Smyth RL (2011) Lessons from normal heart and respiratory rates in children. Lancet 377(9770):974–975
Wertheim D, Olden C, Savage E, Seddon P (2009) Extracting respiratory data from pulse oximeter plethysmogram traces in newborn infants. Arch Dis Child 94:F301–F303
Young Infants Clinical Signs Study Group (2008) Clinical signs that predict severe illness in children under age 2 months: a multicentre study. Lancet 371(9607):135–142
Zotter H, Kerbl R, Reiterer F, Pichler G, Hanzer M, Mueller W (2009) Unchanged heart rate-respiratory frequency ratio in preterm infants during spontaneous arousals. Acta Paediatr 98:47–51
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for assistance received from the nursing staff of the Royal Alexandra Children’s Hospital, Brighton.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This report presents independent research commissioned by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) under the Research for Patient Benefit Programme (PB-PG-0706-10504). The views expressed in this publication are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wertheim, D., Olden, C., Symes, L. et al. Monitoring respiration in wheezy preschool children by pulse oximetry plethysmogram analysis. Med Biol Eng Comput 51, 965–970 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-013-1068-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-013-1068-z