Abstract
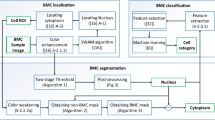
Abnormal localization of immature precursors (ALIP) aggregating and clustering in bone marrow biopsy appears earlier than that of bone marrow smears in detection of the relapse of acute myelocytic leukemia (AML). But traditional manual ALIP recognition has many shortcomings such as prone to false alarms, neglect of distribution law before three immature precursor cells gathered, and qualitative analysis instead of quantitative one. So, it is very important to develop a novel automatic method to identify and localize immature precursor cells for computer-aided diagnosis, to disclose their patterns before ALIP with the development of AML. The contributions of this paper are as follows. (1) After preprocessing the image with Otsu method, we identify both precursor cells and trabecular bone by multiple morphological operations and thresholds. (2) We localize the precursors in different regions according to their distances with the nearest trabecular bone based on chamfer distance transform, followed by discussion for the presumptions and limitations of our method. The accuracy of recognition and localization is evaluated based on a comparison with visual evaluation by two blinded observers.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Kofahi Y, Lassoued W, Lee W, Roysam B (2009) Improved automatic detection and segmentation of cell nuclei in histopathology images. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(4):841–852
Boykov Y, Jolly MP (2001) Interactive graph cuts for optimal boundary and region segmentation of objects in ND images. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis 1:105–112
Cao GT, Zhong C, Li L, Dong J (2009) Detection of red blood cell in urine micrograph. In: The 3rd international conference on bioinformatics and biomedical engineering (ICBBE2009), Beijing, China, pp 1–4. doi:10.1109/ICBBE.2009.5162609
Corneliu T, Nedevschi S (2008) Real-time pedestrian classification exploiting 2D and 3D information. Intell Transp Syst IET 2:201–210
Fernandez DC, Bhargava R, Hewitt SM, Levin IW (2005) Infrared spectroscopic imaging for histopathologic recognition. Nat Biotechnol 23:469–474
Fu X, You H, Fu K (2012) A statistical approach to detect edges in SAR images based on square successive difference of averages. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens Lett 9:1094–1098
Gopi Krishna S, Sreenivasulu Reddy T, Rajini GK (2012) Removal of high density salt and pepper noise through modified decision based unsymmetric trimmed median filter. Int J Eng Res Appl 2:090–094
Hajdu A, Hajdu L, Tijdeman R (2012) Approximation of the Euclidean distance by chamfer distances. Acta Cybern 20(3):399–417
Huang PW, Lai YH (2010) Effective segmentation and classification for HCC biopsy images. Pattern Recognit 43:1550–1563
Huang XW, Li H, Qiu YS, Xie SS (2006) Image processing technology in leukemia diagnosis. Laser Optoelectron Progress 43(10):42–46
Kong H, Gurcan M, Belkacem-Boussaid K (2011) Partitioning histopathological images: an integrated framework for supervised color-texture segmentation and cell splitting. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 30(9):1661–1677
Li SZ (2001) Markov random field modeling in computer vision. Springer, New York
Li L, Cao GT, Shi J, Wu H, Zhang XY (2010) Detecting immature precursor cells in pathological images of bone marrow based on morphology. 7th IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD2010), Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Beijing, China, pp 2190–2194. doi:10.1109/FSKD.2010.5569552
Marchand-Maillet S, Sharaiha YM (1999) Euclidean ordering via chamfer distance calculations. Comput Vis Image Underst 73:404–413
Morillas S, Gregori V, Sapena A (2011) Adaptive marginal median filter for colour images. Sensors 11:3205–3213
Mullikin JC (1992) The vector distance transform in two and three dimensions. CVGIP: Graph Model Image Process 54:526–535
Nedevschi S, Bota S, Tomiuc C (2009) Stereo-based pedestrian detection for collision-avoidance applications. IEEE Trans Intell Transp Syst 10:380–391
Nedzved A, Pitas I (2000) Morphological segmentation of histology cell images. IEEE Int Conf Pattern Recogn 1:500–503
Nilsson B, Heyden A (2005) Segmentation of complex cell clusters in microscopic images: application to bone marrow samples. Cytometry A 66(1):24–31. doi:10.1002/cyto.a.20153
Nipon TU (2005) White blood cell segmentation and classification in microscopic bone marrow images. In: Second International Conference on Fuzzy Systems and Knowledge Discovery (FSKD), pp 787–796
Ortiz F, Torres F (2004) Vectorial morphological reconstruction for brightness elimination in colour images. Real-Time Imaging 10:379–387
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histogram. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Syst 9:62–66
Rosenfeld A, Pfaltz JL (1966) Sequential operations in digital picture processing. J Assoc Comput Mach 13:471–494
Sertel O, Kong J, Catalyurek U, Lozanski G, Saltz J, Gurcan M (2009) Histopathological image analysis using model-based intermediate representation and color texture: follicular lymphoma grading. J Signal Process Syst 55(1):169–183
Sertel O, Lozanski G, Shana’ah A, Gurcan M (2010) Computer-aided detection of centroblasts for follicular lymphoma grading using adaptive likelihood based cell segmentation. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(10):2613–2616
Shi J, Malik J (2000) Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 22(8):888–905
Tricot G, De Wolf-Peeters C, Vlietinck R, Verwilghen RL (1984) Bone marrow histology in myelodysplastic syndrome prognostic value of abnormal localization of immature precursors in MDS. Br J Haematol 58(2):217–225
Vairalkar MK, Nimbhorkar SU (2012) Edge detection of images using sobel operator. Int J Emerg Technol Adv Eng 2:291–293
Vese LA, Chan TF (2002) A multiphase level set framework for image segmentation using the mumford and shah model. Int J Comput Vis 50(3):271–293
Wang J, Athitsos V, Sclaroff S, Betke M (2008) Detecting objects of variable shape structure with hidden state shape models. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30:477–492
Wang M, Shi J, Tao Y, Liu Y, Pu Q (2009) Correlation analysis of the characteristics of ALP with AML relapse. J Clin Hematol 22:345–346
Wen Q, Chang H, Parvin B (2009) A delaunay triangulation approach for segmenting clumps of nuclei. In: IEEE international symposium on biomedical imaging: from nano to macro, 2009 (ISBI09), pp 9–12. doi:10.1109/ISBI.2009.5192970
Yang DG, Dou WC, Cai SJ et al (2004) The application of HSI color model on the segmentation of karyocyte image. Comput Appl Softw 21(9):72–74
Yang L, Meer P, Foran D (2005) Unsupervised segmentation based on robust estimation and color active contour models. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 9(3):475–486
Zhou X, Liu KY, Bradley P, Perrimon N, Wong ST (2005) Towards automated cellular image segmentation for RNAI genome-wide screening. IEEE Conf Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 1:885–892
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61340036,81170507 and 81101119) and National Key Basic Research Program (No. 2011CB707104).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, G., Li, L., Chen, W. et al. Effective identification and localization of immature precursors in bone marrow biopsy. Med Biol Eng Comput 53, 215–226 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1223-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1223-1