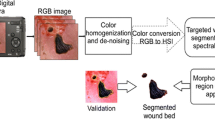
Abstract
A pressure ulcer is a clinical pathology of localised damage to the skin and underlying tissue caused by pressure, shear or friction. Reliable diagnosis supported by precise wound evaluation is crucial in order to success on treatment decisions. This paper presents a computer-vision approach to wound-area detection based on statistical colour models. Starting with a training set consisting of 113 real wound images, colour histogram models are created for four different tissue types. Back-projections of colour pixels on those histogram models are used, from a Bayesian perspective, to get an estimate of the posterior probability of a pixel to belong to any of those tissue classes. Performance measures obtained from contingency tables based on a gold standard of segmented images supplied by experts have been used for model selection. The resulting fitted model has been validated on a training set consisting of 322 wound images manually segmented and labelled by expert clinicians. The final fitted segmentation model shows robustness and gives high mean performance rates [(AUC: .9426 (SD .0563); accuracy: .8777 (SD .0799); F-score: 0.7389 (SD .1550); Cohen’s kappa: .6585 (SD .1787)] when segmenting significant wound areas that include healing tissues.









Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The authors guarantee that the study from which this paper has been motivated has adhered to all ethical aspects that ensure the privacy of all personal information from the individuals who participated in the research. The Ethical Commission of the Health District of Málaga (Spain) authorised the study, and all the participants were informed in writing on their participation in the study.
The CIELUV colour space was adopted by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) in 1976.
Since the original JPEG pictures were taken in nonlinear sRGB, the usual procedure for sRGB\(\rightarrow\)CIELUV conversion was followed: after inverting gamma, the images were first converted to CIE XYZ and then to CIELUV.
References
Arifin MS, Kibria MG, Firoze A, Amin MA, Yan H (2012) Dermatological disease diagnosis using color-skin images. In: ICMLC, IEEE p 1675–1680. http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/conf/icmlc/icmlc2012.html#ArifinKFAY12
Azevedo-Marques P, Pereira S, Frade M, Rangayyan R (2013) Segmentation of dermatological ulcers using clustering of color components. Electrical and computer engineering (CCECE), 2013 26th annual IEEE Canadian conference on, pp 1–4. doi:10.1109/CCECE.2013.6567776
Beeckman D, Schoonhoven L, Fletcher J, Furtado K, Gunningberg L, Heyman H, Lindholm C, Paquay L, Verdu J, Defloor T (2007) EPUAP classification system for pressure ulcers: European reliability study. J Adv Nurs 60(6):682–691
Ben-David A (2007) A lot of randomness is hiding in accuracy. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence 20(7):875–885. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2007.01.001. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0952197607000061
Bradley A (1997) The use of the area under the ROC curve in the evaluation of machine learning algorithms. Pattern Recognit 30(7):1145–1159
Bradski G (2000) The OpenCV Library 25(11):120, 122–125. http://www.ddj.com/ftp/2000/2000_11/opencv.txt
Bradski GR (1998) Computer vision face tracking for use in a perceptual user interface. Intel Technol J. http://opencv.jp/opencv-1.0.0_org/docs/papers/camshift.pdf
Carreira-Perpinan M (2006) Acceleration strategies for Gaussian mean-shift image segmentation. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on, 1:1160–1167. doi:10.1109/CVPR.2006.44
CIE (2004) Colorimetry (3rd edn) Tech Rep CIE 15:2004, Commission Internationale de l’Eclairage. CIE Central Bureau, Vienna. ISBN 3901906339
Comaniciu D, Meer P (2002) Mean shift: a robust approach toward feature space analysis. IEEE Trans Pattern Analysis Machine Intell 24(5):603–619
Cula O, Dana K, Murphy F, Rao B (2005) Skin texture modeling. Int J Comput Vis 62(1–2):97–119
Drira F, Lebourgois F, Emptoz H (2008) A modified mean shift algorithm for efficient document image restoration. In: Damiani E, Yetongnon K, Schelkens P, Dipanda A, Legrand L, Chbeir R (eds) Signal processing for image enhancement and multimedia processing, multimedia systems and applications series, vol 31. Springer, US, pp 13–25. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-72500-0_2
Edsberg LE (2007) Pressure ulcer tissue histology: an appraisal of current knowledge. Ostomy Wound Manag 53(10):40–49. http://www.o-wm.com/article/7934
European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (2009) Treatment of pressure ulcers: quick reference guide. National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel, Washington, DC
European Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel (EPUAP) (1999) Guidelines on treatment of pressure ulcers. EPUAP Rev 1:31–33
Gawlitta D, Li W, Oomens CWJ, Baaijens FPT, Bader DL, Bouten CVC (2007) The relative contributions of compression and hypoxia to development of muscle tissue damage: an in vitro study. Ann Biomed Eng 35(2):273–284
Gonzalez RC, Woods R (2002) Digital image processing, 2nd edn. Prentice Hall, New Jersey
Hao J, Li M, Tang F (2008) Adaptive segmentation of cerebrovascular tree in time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography. Med Biol Eng Comput 46(1):75–83. doi:10.1007/s11517-007-0244-4
Ion A (2011) Towards improving medical image diagnosis. In: Telecommunications Forum (TELFOR), 2011 19th, pp 1187–1190. doi:10.1109/TELFOR.2011.6143762
Jebara TS, Pentland A (1997) Parametrized structure from motion for 3D adaptive feedback tracking of faces. In: Proceedings of computer vision and pattern recognition. pp 144–150
Jones E, Oliphant T, Peterson P et al. (2001) SciPy: open source scientific tools for Python. http://www.scipy.org/
Jones MJ, Rehg JM (2002) Statistical color models with application to skin detection. Int J Comput Vis 46(1):81–96. http://www.cc.gatech.edu/~rehg/Papers/SkinDetect-IJCV-lowres.pdf
Jones TD, Plassmann P (2000) An active contour model for measuring the area of leg ulcers. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 19(12):1202–1210. doi:10.1109/42.897812. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=897812&isnumber=19435
Karkanis SA, Iakovidis DK, Maroulis DE, Karras DA, Tzivras M (2003) Computer-aided tumor detection in endoscopic video using color wavelet features. IEEE Trans Inf Technol Biomed 7(3):141–152
Kjeldsen R, Kender JR (1996) Finding skin in color images. In: Automatic face and gesture recognition, 1996, proceedings of the second international conference on. pp 312–317. doi:10.1109/AFGR.1996.557283
Kosmopoulos D, Tzevelekou F (2007) Automated pressure ulcer lesion diagnosis for telemedicine systems. IEEE Eng Med Biol 26(5):18–22. doi:10.1109/EMB.2007.901786. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/51/4303486/04312663.pdf?tp=&isnumber=4303486&arnumber=4312663&punumber=51
Landi F, Onder G, Russo A, Bernabei R (2007) Pressure ulcer and mortality in frail elderly people living in community. Arch Gerontol Geriatr 44(Supplement 1):217–223. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2007.01.030. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6T4H-4N3M3DN-13/2/e3d4d12edc612e2bd418df9cecfd3521
Laplaud AL, Blaizot X, Gaillard C, Morice A, Lebreuilly I, Clément C, Parienti JJ, Dompmartin A (2010) Wound debridement: comparative reliability of three methods for measuring fibrin percentage in chronic wounds. Wound Repair Regen 18(1):13–20. doi:10.1111/j.1524-475X.2009.00555.x
Loizou CP, Kasparis T, Mitsi O, Polyviou M (2012) Evaluation of wound healing process based on texture analysis. In: BIBE IEEE computer society, pp 709–714. http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/conf/bibe/bibe2012.html#LoizouKMP12
Mukherjee R, Manohar DD, Das DK, Achar A, Mitra A, Chakraborty C (2014) Automated tissue classification framework for reproducible chronic wound assessment. BioMed Res Int, Article ID 851,582. doi:10.1155/2014/851582
National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel Board of Directors (2001) Pressure ulcers in America: prevalence, incidence, and implications for the future: an executive summary of the National Pressure Ulcer Advisory Panel monograph. Adv Skin Wound Care 14(4):208–215
Papazoglou ES, Zubkov L, Mao X, Neidrauer M, Rannou N, Weingarten MS (2010) Image analysis of chronic wounds for determining the surface area. Wound Repair Regen 18(4):349–358
R Core Team (2014) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/
Rijsbergen CJV (1979) Information retrieval, 2nd edn. Butterworth–Heinemann. http://www.dcs.gla.ac.uk/Keith/Preface.html
Salem S, Salem N, Nandi A (2007) Segmentation of retinal blood vessels using a novel clustering algorithm (RACAL) with a partial supervision strategy. Med Biol Eng Comput 45(3):261–273. doi:10.1007/s11517-006-0141-2
Schiele B, Waibel A (1995) Gaze tracking based on face-color. In: International workshop on automatic face- and Gesture-recognition (IWAFGR). Zurich, Switzerland, pp 344–349
Sirotkovic J, Dujmic H, Papic V (2013) Accelerating mean shift image segmentation with IFGT on massively parallel GPU. In: Information communication technology electronics microelectronics (MIPRO), 2013 36th international convention on. pp 279–285
Stanescu L, Burdescu DD, Brezovan M (2011) A comparative study of some methods for color medical images segmentation. EURASIP J Adv Sig Proc 2011:128. http://dblp.uni-trier.de/db/journals/ejasp/ejasp2011.html#StanescuBB11; doi:10.1186/1687-6180-2011-128; http://www.bibsonomy.org/bibtex/2aadb18d57e42a5c328849a1530dd7ba0/dblp
Stratton R, Green C, Elia M (2003) Disease-related malnutrition: an evidence-based approach to treatment. CABI Publishing, Wallingford
Sussman C, Bates-Jensen B (eds) (2001) Wound care: a collaborative practice manual for physical therapists and nurses. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia
Sutor S, Röhr R, Pujolle G, Reda R (2008) Efficient mean shift clustering using exponential integral kernels. Int Sci Ind 2(10):324–328. http://waset.org/Publications?p=22
Swain M, Ballard D (1990) Indexing via color histograms. In: Computer Vision, 1990. Proceedings, third international conference on. pp 390–393. doi:10.1109/ICCV.1990.139558
Tafavogh S, Navarro K, Catchpoole D, Kennedy P (2013) Non-parametric and integrated framework for segmenting and counting neuroblastic cells within neuroblastoma tumor images. Med Biol Eng Comput 51(6):645–655. doi:10.1007/s11517-013-1034-9
Tsuji S, Ichioka S, Sekiya N, Nakatsuka T (2005) Analysis of ischemia-reperfusion injury in a microcirculatory model of pressure ulcers. Wound Repair Regen 13(2):209–215
Veredas F, Mesa H, Morente L (2010) Binary tissue classification on wound images with neural networks and bayesian classifiers. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(2):410–427
Vieira P, Ramos J, Barbosa D, Roupar D, Silva C, Correia H, Lima C (2012) Segmentation of small bowel tumor tissue in capsule endoscopy images by using the MAP algorithm. In: Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), 2012 Annual international conference of the IEEE. pp 4010–4013. doi:10.1109/EMBC.2012.6346846
Wannous H, Lucas Y, Treuillet S (2011) Enhanced assessment of the wound-healing process by accurate multiview tissue classification. Med Imaging IEEE Trans 30(2):315–326. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=5582291
Wannous H, Treuillet S, Lucas Y (2010) Robust tissue classification for reproducible wound assessment in telemedicine environments. J Electr Imaging 19(2):023,002–023,002
Xiao C, Liu M (2010) Efficient mean-shift clustering using Gaussian KD-tree. Comput Graph Forum 29(7):2065–2073. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8659.2010.01793.x
Yang C, Duraiswami R, Davis L (2005) Efficient mean-shift tracking via a new similarity measure. In: Computer vision and pattern recognition, 2005. CVPR 2005. IEEE Computer society conference on, vol 1, pp 176–183 doi:10.1109/CVPR.2005.139
Yang C, Duraiswami R, DeMenthon D, Davis L (2003) Mean-shift analysis using Quasi–Newton methods. In: International conference on image processing, vol. 2, pp II-447-50 vol. 3. doi:10.1109/ICIP.2003.1246713. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/iel5/8824/27931/01246713.pdf?tp=&isnumber=27931&arnumber=1246713&punumber=8824
Yang J, Lu W, Waibel A (1997) Skin-color modeling and adaptation. In: Chin R, Pong TC (eds) Computer vision - ACCV’98, lecture notes in computer science, vol 1352. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 687–694. doi:10.1007/3-540-63931-4_278
Acknowledgments
This research has been funded by Consejería de Salud y Bienestar Social, Servicio Andaluz de Salud, Junta de Andalucía, project PI-0027/2012.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Veredas, F.J., Mesa, H. & Morente, L. Efficient detection of wound-bed and peripheral skin with statistical colour models. Med Biol Eng Comput 53, 345–359 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1240-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-014-1240-0