Abstract
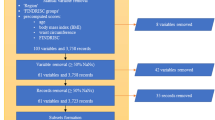
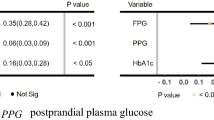
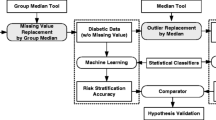
Glucose concentration in type 1 diabetes is a function of biological and environmental factors which present high inter-patient variability. The objective of this study is to evaluate a number of features, which are extracted from medical and lifestyle self-monitoring data, with respect to their ability to predict the short-term subcutaneous (s.c.) glucose concentration of an individual. Random forests (RF) and RReliefF algorithms are first employed to rank the candidate feature set. Then, a forward selection procedure follows to build a glucose predictive model, where features are sequentially added to it in decreasing order of importance. Predictions are performed using support vector regression or Gaussian processes. The proposed method is validated on a dataset of 15 type diabetics in real-life conditions. The s.c. glucose profile along with time of the day and plasma insulin concentration are systematically highly ranked, while the effect of food intake and physical activity varies considerably among patients. Moreover, the average prediction error converges in less than d/2 iterations (d is the number of features). Our results suggest that RF and RReliefF can find the most informative features and can be successfully used to customize the input of glucose models.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu-Rmileh A, Garcia-Gabin W, Zambrano D (2010) A robust sliding mode controller with internal model for closed-loop artificial pancreas. Med Biol Eng Comput 48(12):1191–1201. doi:10.1007/s11517-010-0665-3
Ambroise C, McLachlan GJ (2002) Selection bias in gene extraction on the basis of microarray gene-expression data. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 99(10):6562–6566. doi:10.1073/pnas.102102699
American Diabetes A (2014) Standards of medical care in diabetes-2014. Diabetes Care 37(Suppl 1):S14–80. doi:10.2337/dc14-S014
Bergenstal RM, Klonoff DC, Garg SK, Bode BW, Meredith M, Slover RH, Ahmann AJ, Welsh JB, Lee SW, Kaufman FR, Group AI-HS (2013) Threshold-based insulin-pump interruption for reduction of hypoglycemia. New Engl J Med 369(3):224–232. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1303576
Breiman L (2001) Random forests. Mach Learn 45(1):5–32. doi:10.1023/A:1010933404324
Buckingham B, Cameron F, Calhoun P, Maahs DM, Wilson DM, Chase HP, Bequette BW, Lum J, Sibayan J, Beck RW, Kollman C (2013) Outpatient safety assessment of an in-home predictive low-glucose suspend system with type 1 diabetes subjects at elevated risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia. Diabetes Technol Ther 15(8):622–627. doi:10.1089/dia.2013.0040
Cryer PE (2008) The barrier of hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes 57(12):3169–3176. doi:10.2337/db08-1084
Daskalaki E, Norgaard K, Zuger T, Prountzou A, Diem P, Mougiakakou S (2013) An early warning system for hypoglycemic/hyperglycemic events based on fusion of adaptive prediction models. J Diabetes Sci Technol 7(3):689–698
Derouich M, Boutayeb A (2002) The effect of physical exercise on the dynamics of glucose and insulin. J Biomech 35(7):911–917
Di Camillo B, Sanavia T, Martini M, Jurman G, Sambo F, Barla A, Squillario M, Furlanello C, Toffolo G, Cobelli C (2012) Effect of size and heterogeneity of samples on biomarker discovery: synthetic and real data assessment. PLoS ONE. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0032200
Dua P, Doyle FJ 3rd, Pistikopoulos EN (2009) Multi-objective blood glucose control for type 1 diabetes. Med Biol Eng Comput 47(3):343–352. doi:10.1007/s11517-009-0453-0
Eren-Oruklu M, Cinar A, Quinn L (2010) Hypoglycemia prediction with subject-specific recursive time-series models. J Diabetes Sci Technol 4(1):25–33
Eren-Oruklu M, Cinar A, Rollins DK, Quinn L (2012) Adaptive System Identification for estimating future glucose concentrations and hypoglycemia alarms. Automatica: J IFAC 48(8):1892–1897. doi:10.1016/j.automatica.2012.05.076
Froy O (2010) Metabolism and circadian rhythms—implications for obesity. Endocr Rev 31(1):1–24. doi:10.1210/er.2009-0014
Furlanello C, Serafini M, Merler S, Jurman G (2003) Entropy-based gene ranking without selection bias for the predictive classification of microarray data. BMC Bioinform. doi:10.1186/1471-2105-4-54
Gani A, Gribok AV, Rajaraman S, Ward WK, Reifman J (2009) Predicting subcutaneous glucose concentration in humans: data-driven glucose modeling. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 56(2):246–254. doi:10.1109/TBME.2008.2005937
Georga E, Protopappas V, Guillen A, Fico G, Ardigo D, Arredondo MT, Exarchos TP, Polyzos D, Fotiadis DI (2009) Data mining for blood glucose prediction and knowledge discovery in diabetic patients: the METABO diabetes modeling and management system. In: Conference proceedings: annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society Conference 2009, pp 5633–5636. doi:10.1109/IEMBS.2009.5333635
Georga E, Protopappas VC, Ardigo D, Marina M, Zavaroni I, Polyzos D, Fotiadis D (2012) Multivariate prediction of subcutaneous glucose concentration in type 1 diabetes patients based on support vector regression. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. doi:10.1109/TITB.2012.2219876
Georga EI, Protopappas VC, Ardigo D, Polyzos D, Fotiadis DI (2013) A glucose model based on support vector regression for the prediction of hypoglycemic events under free-living conditions. Diabetes Technol Ther 15(8):634–643. doi:10.1089/dia.2012.0285
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. Mach Learn 46(1–3):389–422. doi:10.1023/A:1012487302797
Huang W, Ramsey KM, Marcheva B, Bass J (2011) Circadian rhythms, sleep, and metabolism. J Clin Investig 121(6):2133–2141. doi:10.1172/JCI46043
Hughes CS, Patek SD, Breton MD, Kovatchev BP (2010) Hypoglycemia prevention via pump attenuation and red–yellow–green “traffic” lights using continuous glucose monitoring and insulin pump data. J Diabetes Sci Technol 4(5):1146–1155
Kovatchev B, Clarke W (2008) Peculiarities of the continuous glucose monitoring data stream and their impact on developing closed-loop control technology. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2(1):158–163
Krzanowski WJ (1993) Discriminant-analysis and statistical pattern-recognition—Mclachlan, Gj. J Classif 10(1):128–130
Lehmann ED, Deutsch T (1992) A physiological model of glucose-insulin interaction in type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Biomed Eng 14(3):235–242
Miles PD, Levisetti M, Reichart D, Khoursheed M, Moossa AR, Olefsky JM (1995) Kinetics of insulin action in vivo. Identification of rate-limiting steps. Diabetes 44(8):947–953
Mougiakakou SG, Bartsocas CS, Bozas E, Chaniotakis N, Iliopoulou D, Kouris I, Pavlopoulos S, Prountzou A, Skevofilakas M, Tsoukalis A, Varotsis K, Vazeou A, Zarkogianni K, Nikita KS (2010) SMARTDIAB: a communication and information technology approach for the intelligent monitoring, management and follow-up of type 1 diabetes patients. IEEE Trans Inform Technol Biomed: Publ IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 14(3):622–633. doi:10.1109/TITB.2009.2039711
Perez-Gandia C, Facchinetti A, Sparacino G, Cobelli C, Gomez EJ, Rigla M, de Leiva A, Hernando ME (2010) Artificial neural network algorithm for online glucose prediction from continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol Ther 12(1):81–88. doi:10.1089/dia.2009.0076
Phillip M, Battelino T, Atlas E, Kordonouri O, Bratina N, Miller S, Biester T, Avbelj Stefanija M, Muller I, Nimri R, Danne T (2013) Nocturnal glucose control with an artificial pancreas at a diabetes camp. N Engl J Med 368(9):824–833. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1206881
Pickup JC (2012) Insulin-pump therapy for type 1 diabetes mellitus. New Engl J Med 366(17):1616–1624. doi:10.1056/NEJMct1113948
Rasmussen CE, Nickisch H (2010) Gaussian processes for machine learning (GPML) toolbox. J Mach Learn Res 11:3011–3015
Rasmussen MA, Bro R (2012) A tutorial on the Lasso approach to sparse modeling. Chemometr Intell Lab 119:21–31. doi:10.1016/j.chemolab.2012.10.003
Reifman J, Rajaraman S, Gribok A, Ward WK (2007) Predictive monitoring for improved management of glucose levels. J Diabetes Sci Technol 1(4):478–486
Robnik-Sikonja M, Kononenko I (2003) Theoretical and empirical analysis of ReliefF and RReliefF. Mach Learn 53(1–2):23–69. doi:10.1023/A:1025667309714
Roy A, Parker RS (2007) Dynamic modeling of exercise effects on plasma glucose and insulin levels. J Diabetes Sci Technol 1(3):338–347
Smola AJ, Scholkopf B (2004) A tutorial on support vector regression. Stat Comput 14(3):199–222. doi:10.1023/B:Stco.0000035301.49549.88
Sparacino G, Zanderigo F, Corazza S, Maran A, Facchinetti A, Cobelli C (2007) Glucose concentration can be predicted ahead in time from continuous glucose monitoring sensor time-series. IEEE T Bio-Med Eng 54(5):931–937. doi:10.1109/Tbme.2006.889774
Storn R, Price K (1997) Differential evolution—a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces. J Glob Optim 11(4):341–359. doi:10.1023/A:1008202821328
Strobl C, Malley J, Tutz G (2009) An introduction to recursive partitioning: rationale, application, and characteristics of classification and regression trees, bagging, and random forests. Psychol Methods 14(4):323–348. doi:10.1037/a0016973
Tarin C, Teufel E, Pico J, Bondia J, Pfleiderer HJ (2005) Comprehensive pharmacokinetic model of insulin Glargine and other insulin formulations. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 52(12):1994–2005. doi:10.1109/TBME.2005.857681
Turksoy K, Bayrak ES, Quinn L, Littlejohn E, Rollins D, Cinar A (2013) Hypoglycemia early alarm systems based on multivariable models. Ind Eng Chem Res. doi:10.1021/ie3034015
Turksoy K, Quinn L, Littlejohn E, Cinar A (2014) Multivariable adaptive identification and control for artificial pancreas systems. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 61(3):883–891. doi:10.1109/TBME.2013.2291777
Yamaguchi M, Kaseda C, Yamazaki K, Kobayashi M (2006) Prediction of blood glucose level of type 1 diabetics using response surface methodology and data mining. Med Biol Eng Comput 44(6):451–457. doi:10.1007/s11517-006-0049-x
Zarkogianni K, Vazeou A, Mougiakakou SG, Prountzou A, Nikita KS (2011) An insulin infusion advisory system based on autotuning nonlinear model-predictive control. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 58(9):2467–2477. doi:10.1109/TBME.2011.2157823
Zecchin C, Facchinetti A, Sparacino G, Cobelli C (2013) Reduction of number and duration of hypoglycemic events by glucose prediction methods: a proof-of-concept in silico study. Diabetes Technol Ther 15(1):66–77. doi:10.1089/dia.2012.0208
Zecchin C, Facchinetti A, Sparacino G, Cobelli C (2014) Jump neural network for online short-time prediction of blood glucose from continuous monitoring sensors and meal information. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 113(1):144–152. doi:10.1016/j.cmpb.2013.09.016
Zecchin C, Facchinetti A, Sparacino G, De Nicolao G, Cobelli C (2012) Neural network incorporating meal information improves accuracy of short-time prediction of glucose concentration. IEEE Trans Bio-Med Eng 59(6):1550–1560. doi:10.1109/TBME.2012.2188893
Zhao C, Dassau E, Jovanovic L, Zisser HC, Doyle FJ 3rd, Seborg DE (2012) Predicting subcutaneous glucose concentration using a latent-variable-based statistical method for type 1 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Sci Technol 6(3):617–633
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the research project “Development of an Information Environment for Diabetes Data Analysis and New Knowledge Mining” that has been co-financed by the European Union [European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)] and Greek national funds through the Operational Program “THESSALY-MAINLAND GREECE AND EPIRUS-2007-2013” of the National Strategic Reference Framework (NSRF 2007–2013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georga, E.I., Protopappas, V.C., Polyzos, D. et al. Evaluation of short-term predictors of glucose concentration in type 1 diabetes combining feature ranking with regression models. Med Biol Eng Comput 53, 1305–1318 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1263-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1263-1