Abstract
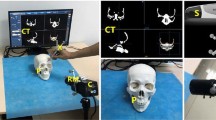
In this paper, a computer-aided system for orbital prosthesis rehabilitation is introduced. With the system, a 3D model of the orbital prosthesis can be easily reconstructed from the CT image of a patient by referring to the normal eye of the patient, and the rehabilitation result by the model can be simulated before the surgery. This facilitates surgeons to design appropriate orbital prosthesis and improve rehabilitation esthetics. Based on the system, the preoperative surgery planning for orbital implant can also be made. This improves the reliability, safety and intuition of the rehabilitation surgery well. The system has been applied to clinical CT images of patients, and the experimental results show effectiveness and acceptability of the system in the clinic.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen PF, Watson G, Stassen L, McMillan AS (2000) Peri-implant soft tissue maintenance in patients with craniofacial implant retained prostheses. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 29:99–103
Ariani N, Visser A, van Oort RP, Kusdhany L, Rahardjo TB, Krom BP, van der Mei HC, Vissink A (2012) Current state of craniofacial prosthetic rehabilitation. Int J Prosthodont 26:57–67
Artopoulou LL, Montgomery PC, Wesley PJ, Lemon JC (2006) Digital imaging in the fabrication of ocular prostheses. J Prosthet Dent 95:327–330
Chiarelli T, Lamma E, Sansoni T (2010) A fully 3D work context for oral implant planning and simulation. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 5:57–67
Dam EB, Koch M, Lillholm M (1998) Quaternions, interpolation and animation. Technical Report DIKU-TR-98-5
Fernandes CMS, Mattos BSC, Cavalcanti MDGP, Fonseca LC, Serra MDC (2012) Peri-orbital bone dimensional analysis using computed tomography for placement of osseointegrated implants. Braz J Oral Sci 11:1–9
Granstrom G (2005) Osseointegration in irradiated cancer patients: an analysis with respect to implant failures. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63:579–585
Karakoca S, Aydin C, Yilmaz H, Bal BT (2008) Survival rates and periimplant soft tissue evaluation of extraoral implants over a mean follow-up period of three years. J Prosthes Dent 100:458–464
Karakoca S, Aydin C, Yilmaz H, Korkmaz T (2008) An impression technique for implant-retained orbital prostheses. J Prosthet Dent 100:52–55
Klein M, Menneking H, Neumann K, Hell B, Bier J (1997) Computed tomographic study of bone availability for facial prosthesis-bearing endosteal implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 26:268–271
Kovacs AF (2000) A follow-up study of orbital prostheses supported by dental implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 58:19–23
Lorensen WE, Cline HE (1987) Marching cubes: a higher solution surface construction algorithm. Comput Graph (SIGGRAPH’87) 21:163–169
Roumanas ED, Freymiller EG, Chang TL, Aghaloo T, Beumer J (2002) Implant-retained prostheses for facial defects: an up to 14-year follow-up report on the survival rates of implants at UCLA. Int J Prosthodont 15:325–332
Salinas TJ (2010) Prosthetic rehabilitation of defects of the head and neck. Semin Plastic Surg 24:299–308
Tolman DE, Tjellstrom A, Woods JE (1998) Reconstructing the human face by using the tissue-integrated prosthesis. Mayo Clin Proc 73:1171–1175
Veerareddy C, Nair KC, Reddy GR (2012) Simplified technique for orbital prosthesis fabrication: a clinical report. J Prosthodont 21:561–568
Verstreken K, Cleynenbreugel JV, Martens K, Marchal G, Steenberghe DV, Suetens P (1998) An image-guided planning system for endosseous oral implants. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 17:842–852
Wong KCH, Siu TYH, Heng PA, Sun HQ (1998) Interactive volume cutting. Graph Interface 98:99–106
Zhang X, Chen S, Huang Y, Chang S (2007) Computer-assisted design of orbital Implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implant 22:132–137
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61375020), the National 973 Program of China (2013CB329401) and Cross Research Fund of Biomedical Engineering of Shanghai JiaoTong University (YG2013ZD02, YG2012MS19).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shuang Li and Caiwen Xiao have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Xiao, C., Duan, L. et al. CT image-based computer-aided system for orbital prosthesis rehabilitation. Med Biol Eng Comput 53, 943–950 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1307-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1307-6