Abstract
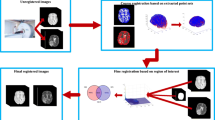
The widespread use of whole-body small animal in vivo imaging in preclinical research has proposed the new demands on imaging processing and analysis. Micro-CT provides detailed anatomical structural information for continuous detection and different individual comparison, but the body deformation happened during different data acquisition needs sophisticated registration. In this paper, we propose a hybrid method for registering micro-CT mice images, which combines the strengths of point-based and intensity-based registration methods. Point-based non-rigid method using thin-plate spline robust point matching algorithm is utilized to acquire a coarse registration. And then intensity-based non-rigid method using normalized mutual information, Halton sampling and adaptive stochastic gradient descent optimization is used to acquire precise registration. Two accuracy metrics, Dice coefficient and average surface distance are used to do the quantitative evaluation. With the intra- and intersubject micro-CT mice images registration assessment, the hybrid method has been proven capable of excellent performance on micro-CT mice images registration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
3DMed Institute of Automation Chinese Academy of Science, Medical Image Processing Group. 3DMed Software. http://www.3dmed.net
Ale A, Ermolayev V, Herzog E, Cohrs C, de Angelis MH, Ntziachristos V (2012) FMT-XCT: in vivo animal studies with hybrid fluorescence molecular tomography-X-ray computed tomography. Nat Methods 9(6):615–620
Audette MA, Ferrie FP, Peters TM (2000) An algorithmic overview of surface registration techniques for medical imaging. Med Image Anal 4(3):201–217
Bai J, Trinh TLH, Chuang KH, Qiu A (2012) Atlas-based automatic mouse brain image segmentation revisited: model complexity vs. image registration. Magn Reson Imaging 30(6):789–798
Baiker M, Milles J, Dijkstra J, Henning TD, Weber AW, Que I, Kaijzel EL, Löwik CW, Reiber JH, Lelieveldt BP (2010) Atlas-based whole-body segmentation of mice from low-contrast Micro-CT data. Med Image Anal 14(6):723–737
Besl PJ, McKay ND (1992) A method for registration of 3-D shapes. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 14:239–256
Chui H, Rangarajan A (2003) A new point matching algorithm for nonrigid registration. Comput Vis Image Underst 89(2–3):114–141
Franc BL, Acton PD, Mari C, Hasegawa BH (2008) Small-animal SPECT and SPECT/CT: important tools for preclinical investigation. J Nucl Med 49(10):1651–1663
Gold S, Rangarajan A, Lu CP, Pappu S, Mjolsness E (1998) New algorithms for 2D and 3D point matching: pose estimation and correspondence. Pattern Recogn 31:1019–1031
Gupta A, Verma HK, Gupta S (2013) A hybrid framework for registration of carotid ultrasound images combining iconic and geometric features. Med Biol Eng Comput 51(9):1043–1050
Hellier P, Barillot C (2003) Coupling dense and landmark-based approaches for nonrigid registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22(2):217–227
Johnson HJ, Christensen GE (2002) Consistent landmark and intensity-based image registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21(5):450–461
Joshi AA, Chaudhari AJ, Li C, Dutta J, Cherry SR, Shattuck DW, Toga AW, Leahy RM (2010) DigiWarp: a method for deformable mouse atlas warping to surface topographic data. Phys Med Biol 55(20):6197–6214
Klein S, Pluim JPW, Staring M, Viergever MA (2009) Adaptive stochastic gradient descent optimization for image registration. Int J Comput Vis 81(3):227–239
Li H, Zhang H, Tang Z, Hu G (2008) Micro-computed tomography for small animal imaging: technological details. Prog Nat Sci 18(5):513–521
Li X, Yankeelov TE, Peterson TE, Gore JC, Dawant BM (2008) Automatic nonrigid registration of whole body CT mice images. Med Phys 35(4):1507–1520
Liu J, Wang Y, Qu X, Li X, Ma X, Han R, Hu Z, Chen X, Sun D, Zhang R, Chen D, Chen D, Chen X, Liang J, Cao F, Tian J (2010) In vivo quantitative bioluminescence tomography using heterogeneous and homogeneous mouse models. Opt Express 18(12):13102–13113
Maes F, Collignon A, Vandermeulen D, Marchal G, Suetens P (1997) Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16(2):187–198
Massoud TF, Gambhir SS (2003) Molecular imaging in living subjects: seeing fundamental biological processes in a new light. Gene Dev 17(5):545–580
Papademetris X, Dione DP, Dobrucki LW, Staib LH, Sinusas AJ (2005) Articulated rigid registration for serial lower-limb mouse imaging. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 8(Pt 2):919–926
Radu CG, Shu CJ, Nair-Gill E, Shelly SM, Barrio JR, Satyamurthy N, Phelps ME, Witte ON (2008) Molecular imaging of lymphoid organs and immune activation by positron emission tomography with a new [18F]-labeled 2′-deoxycytidine analog. Nat Med 14(7):783–788
Ritman EL (2004) Micro-computed tomography-current status and developments. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 6:185–208
Sethian JA (1999) Fast marching methods. SIAM Rev 41(2):199–235
Thévenaz P, Bierlaire M, Unser M (2008) Halton sampling for image registration based on mutual information. Sampl Theory Signal Image Process 7(2):141–171
Wang H, Stout DB, Chatziioannou AF (2012) Estimation of mouse organ locations through registration of a statistical mouse atlas with micro-CT images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 31(1):88–102
Wang H, Stout DB, Chatziioannou AF (2013) A method of 2D/3D registration of a statistical mouse atlas with a planar X-ray projection and an optical photo. Med Image Anal 17(4):401–416
Weissleder R, Pittet MJ (2008) Imaging in the era of molecular oncology. Nature 452(7187):580–589
Willmann JK, van Bruggen N, Dinkelborg LM, Gambhir SS (2008) Molecular imaging in drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(7):591–607
Xiao D, Zahra D, Bourgeat P, Tamayo OA, Wimberley C, Gregoire MC, Salvado O (2010) An improved 3D shape context based non-rigid registration method and its application to small animal skeletons registration. Comput Med Imaging Gr 34(4):321–332
Xiao D, Zahra D, Bourgeat P, Berghofer P, Tamayo OA, Green H, Salvado O (2011) Mouse whole-body organ mapping by non-rigid registration approach. In: Proceedings of SPIE medical imaging 2011: biomedical applications in molecular, structural, and functional imaging, pp 79650E–796507
Zhuang X, Arridge S, Hawkes DJ, Ourselin SA (2011) A nonrigid registration framework using spatially encoded mutual information and free-form deformations. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 30(10):1819–1828
Acknowledgments
Authors are highly thankful to Jinwang Li and Lei Xiong for their assistance during the data acquisition. We thank Prof. Hongbing Lu and Junyan Rong for their valuable help in this work. This work is supported by the Program of the National Basic Research and Development Program of China (973) under Grant No. 2011CB707702 and the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant Nos. 81371589, 81090272 and 81101084, and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, X., Gao, X., Xu, X. et al. A hybrid registration-based method for whole-body micro-CT mice images. Med Biol Eng Comput 54, 1037–1048 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1386-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-015-1386-4