Abstract
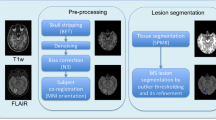
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a neurodegenerative disease with increasing importance in recent years, in which the T2 weighted with fluid attenuation inversion recovery (FLAIR) MRI imaging technique has been addressed for the hyperintense MS lesion assessment. Many automatic lesion segmentation approaches have been proposed in the literature in order to assist health professionals. In this study, a new hybrid lesion segmentation approach based on logistic classification (LC) and the iterative contrast enhancement (ICE) method is proposed (LC+ICE). T1 and FLAIR MRI images from 32 secondary progressive MS (SPMS) patients were used in the LC+ICE method, in which manual segmentation was used as the ground truth lesion segmentation. The DICE, Sensitivity, Specificity, Area under the ROC curve (AUC), and Volume Similarity measures showed that the LC+ICE method is able to provide a precise and robust lesion segmentation estimate, which was compared with two recent FLAIR lesion segmentation approaches. In addition, the proposed method also showed a stable segmentation among lesion loads, showing a wide applicability to different disease stages. The LC+ICE procedure is a suitable alternative to assist the manual FLAIR hyperintense MS lesion segmentation task.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zivadinov R, Stosic M, Cox JL, Ramasamy DP, Dwyer MG (2008) The place of conventional MRI and newly emerging MRI techniques in monitoring different aspects of treatment outcome. J Neurol 255(SUPPL.1):61–74
Neema M, Stankiewicz J, Arora A, Guss ZD, Bakshi R (2007) MRI In multiple sclerosis: what’s inside the toolbox?. Neurotherapeutics 4(4):602–617
Miller DH, Grossman RI, Reingold SC, McFarland HF (1998) The role of magnetic resonance techniques in understanding and managing multiple sclerosis. Brain 121:3–24
Polman CH, Reingold SC, Banwell B, Clanet M, Cohen JA, Filippi M, Fujihara K, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Lublin FD, Montalban X, O’Connor P, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Thompson AJ, Waubant E, Weinshenker B, Wolinsky JS (2011) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 revisions to the McDonald criteria. Ann Neurol 69:292–302
McDonald WI, Compston A, Edan G, Goodkin D, Hartung HP, Lublin FD, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Polman CH, Reingold SC, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Sibley W, Thompson A, Van Den noort S, Weinshenker BY, Wolinsky JS (2001) Recommended diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines from the international panel on the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 50(1):121–127
Neema M, Stankiewicz J, Arora A, Guss ZD, Bakshi R (2007) MRI in multiple sclerosis: what’s inside the toolbox?. Neurotherapeutics : The Journal of the American Society for Experimental NeuroTherapeutics 4:602–17
Filippi M, Stefano ND, Dousset V, McGowan J (2005) MR imaging in white matter diseases of the brain and spinal cord, vol 58 of medical radiology diagnostic imaging. Springer, Berlin
Sahraian MA, Radue E-W (2008) MRI atlas of MS lesions, vol 1. Springer, Berlin
Jain S, Sima DM, Ribbens A, Cambron M, Maertens A, Van hecke W, De Mey J, Barkhof F, Steenwijk MD, Daams M, Maes F, Van Huffel S, Vrenken H, Smeets D (2015) Automatic segmentation and volumetry of multiple sclerosis brain lesions from MR images. NeuroImage: Clinical 8:367–75
Yoo BI, Lee JJ, Han JW, Oh SYW, Lee EY, MacFall JR, Payne ME, Kim TH, Kim JH, Kim KW (2014) Application of variable threshold intensity to segmentation for white matter hyperintensities in fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance images. Neuroradiology 56:265–281
Cabezas M, Oliver A, Roura E, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira À, Lladó X (2014) Automatic multiple sclerosis lesion detection in brain MRI by FLAIR thresholding. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 115(3):147–161
Souplet J-C, Lebrun-Frenay C, Ayache N,Malandain G (2008) An automatic segmentation of T2-FLAIR multiple sclerosis lesions. In: Grand challenge work.: mult. scler. lesion segm. challenge
Van Leemput K, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Colchester A, Suetens P (2001) Automated segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions by model outlier detection. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:677–88
Ganiler O, Oliver A, Diez Y, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Beltran B, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira À, Lladó X (2014) A subtraction pipeline for automatic detection of new appearing multiple sclerosis lesions in longitudinal studies. Neuroradiology 56(5):363–374
García-Lorenzo D, Prima S, Arnold DL, Collins DL, Barillot C (2011) Trimmed-likelihood estimation for focal lesions and tissue segmentation in multisequence MRI for multiple sclerosis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 30:1455–1467
Khayati R, Vafadust M, Towhidkhah F, Nabavi M (2008) Fully automatic segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MR FLAIR images using adaptive mixtures method and markov random field model. Comput Biol Med 38:379–390
Elliott C, Arnold DL, Collins DL, Arbel T (2013) Temporally consistent probabilistic detection of new multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MRI. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 32:1490–503
Yamamoto D, Arimura H, Kakeda S, Magome T, Yamashita Y, Toyofuku F, Ohki M, Higashida Y, Korogi Y (2010) Computer-aided detection of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain magnetic resonance images: false positive reduction scheme consisted of rule-based, level set method, and support vector machine. Comput Med Imaging Graph 34(5):404–413
Lao Z, Shen D, Liu D, Jawad AF, Melhem ER, Launer LJ, Bryan RN, Davatzikos C (2008) Computer-assisted segmentation of white matter lesions in 3D MR images using support vector machine. Acad Radiol 15:300–313
Mortazavi D, Kouzani AZ, Soltanian-Zadeh H (2012) Segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in MR images: a review. Neuroradiology 54:299–320
García-Lorenzo D, Francis S, Narayanan S, Arnold DL, Collins DL (2013) Review of automatic segmentation methods of multiple sclerosis white matter lesions on conventional magnetic resonance imaging. Med Image Anal 17(1):1–18
Lladó X, Oliver A, Cabezas M, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Quiles A, Valls L, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira À (2012) Segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MRI: a review of automated approaches. Inf Sci 186:164–185
Lladó X, Oliver A, Cabezas M, Freixenet J, Vilanova JC, Quiles A, Valls L, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira À (2012) Segmentation of multiple sclerosis lesions in brain MRI: a review of automated approaches. Inf Sci 186:164–185
Giorgio A, Battaglini M, Smith SM, De Stefano N (2008) Brain atrophy assessment in multiple sclerosis: importance and limitations. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 18:675–86, xi
Klein A, Andersson J, Ardekani BA, Ashburner J, Avants B, Chiang M-C, Christensen GE, Collins DL, Gee J, Hellier P, Song JH, Jenkinson M, Lepage C, Rueckert D, Thompson P, Vercauteren T, Woods RP, Mann JJ, Parsey RV (2009) Evaluation of 14 nonlinear deformation algorithms applied to human brain MRI registration. NeuroImage 46:786–802
Evans AC, Janke AL, Collins DL, Baillet S (2012) Brain templates and atlases
Mazziotta J, Toga A, Evans A, Fox P, Lancaster J, Zilles K, Woods R, Paus T, Simpson G, Pike B, Holmes C, Collins L, Thompson P, MacDonald D, Iacoboni M, Schormann T, Amunts K, Palomero-Gallagher N, Geyer S, Parsons L, Narr K, Kabani N, Goualher GL, Boomsma D, Cannon T, Kawashima R, Mazoyer B (2001) A probabilistic atlas and reference system for the human brain: international consortium for brain mapping (ICBM). Philos Trans R Soc, B Biol Sci 356:1293–1322
Lavdas E, Tsougos I, Kogia S, Gratsias G, Svolos P, Roka V, Fezoulidis IV, Kapsalaki E (2014) T2 FLAIR artifacts at 3-T brain magnetic resonance imaging. Clin Imaging 38(2):85–90
Zhang Y, Brady M, Smith S (2001) Segmentation of brain MR images through a hidden Markov random field model and the expectation-maximisation algorithm. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20:45–57
Woolrich MW, Jbabdi S, Patenaude B, Chappell M, Makni S, Behrens T, Beckmann C, Jenkinson M, Smith SM (2009) Bayesian analysis of neuroimaging data in FSL. NeuroImage 145(1 Suppl):S173–S186
Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Zheng Y, Egan A, Yushkevich PA, Gee JC (2010) N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29:1310–1320
Boyes RG, Gunter JL, Frost C, Janke AL, Yeatman T, Hill DLG, Bernstein MA, Thompson PM, Weiner MW, Schuff N, Alexander GE, Killiany RJ, DeCarli C, Jack CR, Fox NC, Study ADNI (2008) Intensity non-uniformity correction using N3 on 3-T scanners with multichannel phased array coils. NeuroImage 39:1752–62
da S Senra Filho AC, Garrido Salmon CE, Murta Junior LO (2015) Anomalous diffusion process applied to magnetic resonance image enhancement. Phys Med Biol 60:2355–2373
Filho ACdSS, Barbosa JHO, Salmon CEGS, Junior LOM (2014) Anisotropic anomalous diffusion filtering applied to relaxation time estimation in magnetic resonance imaging. In: Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE, Piscataway, pp 3893–3896
Filho ACdSS, Rondinoni C, dos Santos AC, Junior LOM (2014) Brain activation inhomogeneity highlighted by the isotropic anomalous diffusion filter. In: Annual international conference of the ieee engineering in medicine and biology society. IEEE, Chicago, pp 3313–3316
Barkhof F, Filippi M, Miller DH, Scheltens P, Campi A, Polman CH, Comi G, Adèr HJ, Losseff N, Valk J (1997) Comparison of MRI criteria at first presentation to predict conversion to clinically definite multiple sclerosis. Brain 11:120
Pieper S, Lorensen B, Schroeder W (2006) The NA-MIC Kit: ITK, VTK, pipelines, grids and 3D slicer as an open platform for the medical image computing community. In: 3rd IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging: From Nano to Macro, (Arlington, USA), pp 698–701
Kuncheva L (2000) Fuzzy classifier design. Studies in Fuzziness and Soft Computing. Physica-Verlag, HD
Kapur J, Sahoo P, Wong A (1985) A new method for gray-level picture thresholding using the entropy of the histogram. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing 29(3):273–285
Otsu N (1979) A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern 9:62–66
Tsai W-H (1985) Moment-preserving thresolding: a new approach. Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing 29:377–393
Cotton F, Kremer S, Hannoun S, Vukusic S, Dousset V (2015) OFSEP, a nationwide cohort of people with multiple sclerosis: consensus minimal MRI protocol. J Neuroradiol 42:133–140
Akhondi-Asl A, Hoyte L, Lockhart ME, Warfield SK (2014) A logarithmic opinion pool based STAPLE algorithm for the fusion of segmentations with associated reliability weights. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33:1997–2009
Udupa JK, LeBlanc VR, Zhuge Y, Imielinska C, Schmidt H, Currie LM, Hirsch BE, Woodburn J (2006) A framework for evaluating image segmentation algorithms. Comput Med Imaging Graph 30:75–87
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26:297–302
Taha AA, Hanbury A (2015) Metrics for evaluating 3D medical image segmentation: analysis, selection, and tool. BMC Med Imaging 15:29
Schmidt P, Gaser C, Arsic M, Buck D, Förschler A, Berthele A, Hoshi M, Ilg R, Schmid VJ, Zimmer C, Hemmer B, Mühlau M (2012) An automated tool for detection of FLAIR-hyperintense white-matter lesions in multiple Sclerosis. NeuroImage 59:3774–83
Obuchowski NA (2003) Receiver operating characteristic curves and their use in radiology. Radiology 229:3–8
Lladó X., Ganiler O, Oliver A, Martí R, Freixenet J, Valls L, Vilanova JC, Ramió-Torrentà L, Rovira Á (2012) Automated detection of multiple sclerosis lesions in serial brain MRI. Neuroradiology 54:787–807
Sotiras A, Davatzikos C, Paragios N (2013) Deformable medical image registration: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 32:1153–1190
Cabezas M, Oliver A, Lladó X, Freixenet J, Bach cuadra M (2011) A review of atlas-based segmentation for magnetic resonance brain images. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 104:e158–e177
Boesen K, Rehm K, Schaper K, Stoltzner S, Woods R, Lüders E, Rottenberg D (2004) Quantitative comparison of four brain extraction algorithms. NeuroImage 22(3):1255–1261
Funding
The author would like to thank Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Cientifico e Tecnologico (CNPq) grant 201871/2015-7/SWE for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Silva Senra Filho, A.C. A hybrid approach based on logistic classification and iterative contrast enhancement algorithm for hyperintense multiple sclerosis lesion segmentation. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 1063–1076 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1747-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-017-1747-2