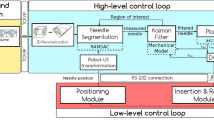
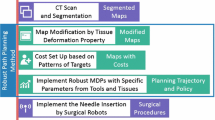
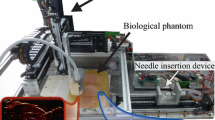
Abstract
Image-guided robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery is an important medicine procedure used for biopsy or local target therapy. In order to reach the target region not accessible using traditional techniques, long and thin flexible needles are inserted into the soft tissue which has large deformation and nonlinear characteristics. However, the detection results and therapeutic effect are directly influenced by the targeting accuracy of needle steering. For this reason, the needle-tissue interactive mechanism, path planning, and steering control are investigated in this review by searching literatures in the last 10 years, which results in a comprehensive overview of the existing techniques with the main accomplishments, limitations, and recommendations. Through comprehensive analyses, surgical simulation for insertion into multi-layer inhomogeneous tissue is verified as a primary and propositional aspect to be explored, which accurately predicts the nonlinear needle deflection and tissue deformation. Investigation of the path planning of flexible needles is recommended to an anatomical or a deformable environment which has characteristics of the tissue deformation. Nonholonomic modeling combined with duty-cycled spinning for needle steering, which tracks the tip position in real time and compensates for the deviation error, is recommended as a future research focus in the steering control in anatomical and deformable environments.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abayazid M, Moreira P, Shahriari N, Patil S, Alterovitz R, Misra S (2015) Ultrasound-guided three-dimensional needle steering in biological tissue with curved surfaces. Med Eng Phys 37:145–150
Abayazid M, Roesthuis RJ, Reilink R, Misra S (2013) Integrating deflection models and image feedback for real-time flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Robot 29:542–553
Abayazid M, Vrooijink GJ, Patil S, Alterovitz R, Misra S (2014) Experimental evaluation of ultrasound-guided 3D needle steering in biological tissue. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 9:931–939
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Moallem M (2007) Needle insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Med Eng Phys 29:413–431
Abolhassani N, Patel R (2006) Deflection of a flexible needle during insertion into soft tissue. Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, pp 3858–3861
Abolhassani N, Patel RV, Ayazi F (2007) Minimization of needle deflection in robot-assisted prostate brachytherapy. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg 3:140–148
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Moallem M (2006) Control of soft tissue deformation during robotic needle insertion. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 15:165–176
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Moallem M (2004) Experimental study of robotic needle insertion in soft tissue. Int Congr 1268:797–802
Abolmaesumi P, Salcudean SE, Zhu WH et al (2002) Image-guided control of a robot for medical ultrasound. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 18:11–23
Adebar TK, Fletcher AE, Okamura AM (2014) 3-D ultrasound-guided robotic needle steering in biological tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61:2899–2910
Adebar TK, Greer JD, Laeseke PF, Hwang GL, Okamura AM (2016) Methods for improving the curvature of steerable needles in biological tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63:1167–1177
Adhami L, Coste-Manière È (2003) Optimal planning for minimally invasive surgical robots. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 19:854–863
Ahn B, Kim J (2009) Efficient soft tissue characterization under large deformations in medical simulations. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 10:115–121
Alterovitz R, Branicky M, Goldberg K (2008) Motion planning under uncertainty for image-guided medical needle steering. Int J Robot Res 27:1361–1374
Alterovitz R, Lim A, Goldberg K et al (2005) Steering flexible needles under Markov motion uncertainty. IEEE/RSJ International conference on intelligent robots and systems, pp 1570–1575
Alterovitz R, Goldberg K, Okamura A (2005) Planning for steerable bevel-tip needle insertion through 2D soft tissue with obstacles. IEEE International conference on robotics and automation, pp 1640–1645
Asadian A, Kermani MR, Patel RV (2012) A novel force modeling scheme for needle insertion using multiple Kalman filters. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 61:429–438
Asadian A, Kermani MR, Patel RV (2010) A compact dynamic force model for needle-tissue interaction. Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, pp 2292–2295
Azar T, Hayward V (2008) Estimation of the fracture toughness of soft tissue from needle insertion. International Symposium on Biomedical Simulation, pp 166–175
Barbe L, Bayle B, Mathelin MD, Gangi A (2007) Needle insertions modeling: identifiability and limitations. Biomed Signal Process Control 2:191–198
Basafa E, Farahmand F (2011) Real-time simulation of the nonlinear visco-elastic deformations of soft tissues. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 6:297–307
Bax JS, Waring CS, Sherebrin S et al (2013) 3D image-guided robotic needle positioning system for small animal interventions. Med Phys 40:113–132
Bax J, Smith D, Bartha L, Montreuil J, Sherebrin S, Gardi L, Edirisinghe C, Fenster A (2011) A compact mechatronic system for 3D ultrasound guided prostate interventions. Med Phys 38:1055–1069
Bernardes MC, Adorno BV, Poignet P, Borges GA (2013) Robot-assisted automatic insertion of steerable needles with closed-loop imaging feedback and intraoperative trajectory replanning. Mechatronics 23:630–645
Bickel B, Bächer M, Otaduy MA, Matusik W, Pfister H, Gross M (2009) Capture and modeling of non-linear heterogeneous soft tissue. ACM Trans Graph 28:341–352
Biot MA (1937) Bending of an infinite beam on an elastic foundation. J Appl Mech 59:A1–A7
Butz KD, Griebel AJ, Novak T, Harris K, Kornokovich A, Chiappetta MF, Neu CP (2012) Prestress as an optimal biomechanical parameter for needle penetration. J Biomech 45:1176–1179
Cadiere GB, Himpens J, Germay O et al (2001) Feasibility of robotic laparoscopic surgery: 146 cases. World J Surg 25:1467–1477
Carra A, Avila-Vilchis JC (2010) Needle insertion modeling through several tissue layers. International Asia Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pp 237–240
Chae Y, Um SI, Yi SH, Lee H, Chang DS, Yin CS, Park HJ (2011) Comparison of biomechanical properties between acupuncture and non-penetrating sham needle. Complement Ther Med 19:S8–S12
Chentanez N, Alterovitz R, Ritchie D et al (2009) Interactive simulation of surgical needle insertion and steering. ACM Trans Graph 28:88(1)–88(10)
Cleary K, Peters TM (2010) Image-guided interventions: technology review and clinical applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 12:119–142
Cowan NJ, Goldberg K, Chirikjian GS, Fichtinger G, Alterovitz R, Reed KB, Kallem V, Park W, Misra S, Okamura AM (2011) Robotic needle steering: design, modeling, planning, and image guidance. In: Rosen J, Hannaford B, Satava RM (eds) Surgical robotics. Springer US, New York, pp 557–582
Dehghan E, Salcudean SE (2009) Needle insertion parameter optimization for brachytherapy. IEEE Trans Robot 25:303–315
Dehghan E, Salcudean SE (2007) Needle insertion point and orientation optimization in non-linear tissue with application to brachytherapy. IEEE International conference on robotics and automation, pp 2267–2272
Dimaio SP, Salcudean SE (2005) Interactive simulation of needle insertion models. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52:1167–1179
Dimaio SP, Salcudean SE (2005) Needle steering and motion planning in soft tissues. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52:965–974
Dimaio SP, Salcudean SE (2003) Needle insertion modeling and simulation. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 19:864–875
Duindam V, Xu JJ, Alterovitz R, Sastry S, Goldberg K (2009) 3D motion planning algorithms for steerable needles using inverse kinematics. Int J Robot Res 57:535–549
Duindam V, Alterovitz R, Sastry S et al (2008) Screw-based motion planning for bevel-tip flexible needles in 3D environments with obstacles. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 2483–2488
Engh JA, Podnar G, Kondziolka D et al (2006) Toward effective needle steering in brain tissue. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp 559–562
Fisher T, Hamed A, Vartholomeos P, Masamune K, Tang G, Ren H, Tse ZTH (2014) Intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging-conditional robotic devices for therapy and diagnosis. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part H-J Eng Med 228:303–318
Gao DD, Lei Y, Zheng HJ (2012) Needle steering for robot-assisted insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Chin J Mech Eng 25:629–638
Glozman D, Shoham M (2007) Image-guided robotic flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Robot 23:459–467
Gokgol C, Basdogan C, Canadinc D (2012) Estimation of fracture toughness of liver tissue: experiments and validation. Med Eng Phys 34:882–891
Goksel O, Dehghan E, Salcudean SE (2009) Modeling and simulation of flexible needles. Med Eng Phys 31:1069–1078
Groves RB, Coulman SA, Birchall JC, Evans SL (2012) Quantifying the mechanical properties of human skin to optimize future microneedle device design. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 15:73–82
Haddadi A, Hashtrudizaad K (2011) Development of a dynamic model for bevel-tip flexible needle insertion into soft tissues. Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society, pp 7478–7482
Jahya A, Van Der Heijden F, Misra S (2012) Observations of three-dimensional needle deflection during insertion into soft tissue. IEEE International conference on biomedical robotics and biomechatronics, pp 1205–1210
Jee T, Komvopoulos K (2014) Skin viscoelasticity studied in vitro by microprobe-based techniques. J Biomech 47:553–559
Jiang S, Li P, Yu Y, Liu J, Yang ZY (2014) Experimental study of needle-tissue interaction forces: effect of needle geometries, insertion methods and tissue characteristics. J Biomech 47:3344–3353
Jiang S, Liu XY, Bai S, Yang Z (2010) The potential field-based trajectory planning of needle invasion in soft tissue. J Biomed Eng 27:790–794
Jiang S, Liu S, Feng WH (2011) PVA hydrogels properties for biomedical application. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4:1228–1233
Kataoka H, Washio T, Audette M et al (2001) A model for relations between needle deflection, force, and thickness on needle penetration. Proc Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 2208:966–974
Kim S, Chung J, Yi BJ, Kim YS (2010) An assistive image-guided surgical robot system using O-arm fluoroscopy for pedicle screw insertion: preliminary and cadaveric study. Neurosurgery 67:1757–1767
Kobayashi Y, Hamano R, Watanabe H, Hong J, Toyoda K, Hashizume M, Fujie MG (2013) Use of puncture force measurement to investigate the conditions of blood vessel needle insertion. Med Eng Phys 35:684–689
Lehmann T, Tavakoli M, Usmani N, Sloboda R (2013) Force-sensor-based estimation of needle tip deflection in brachytherapy. J Sens 2013:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/263153
Leyendeeker JR, Dodd GD (2001) Minimally invasive techniques for the treatment of liver tumors. Semin Liver Dis 21:283–291
Li P, Jiang S, Liang D, Yang ZY, Yu Y, Wang W (2017) Modeling of path planning and needle steering with path tracking in anatomical soft tissues for minimally invasive surgery. Med Eng Phys 41:35–45
Li P, Jiang S, Yang J et al (2014) A combination method of artificial potential field and improved conjugate gradient for trajectory planning for needle insertion into soft tissue. J Med Biol Eng 34:568–573
Li P, Jiang S, Yu Y, Yang J, Yang Z (2015) Biomaterial characteristics and application of silicone rubber and PVA hydrogels mimicked in organ groups for prostate brachytherapy. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 49:220–234
Mahvash M, Dupont PE (2010) Mechanics of dynamic needle insertion into a biological material. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57:934–943
Majewicz A, Marra SP, Van Vledder MG et al (2012) Behavior of tip-steerable needles in ex vivo and in vivo tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59:2705–2715
Majewicz A, Siegel JJ, Stanley AA et al (2014) Design and evaluation of duty-cycling steering algorithms for robotically-driven steerable needles. IEEE International conference on robotics and automation, pp 5883–5888
Maurin B, Barbe L, Bayle B et al (2004) In vivo study of forces during needle insertions. Scientific Workshop on Medical Robotics Navigation and Visualization, pp 14–21
Minhas D, Engh JA, Riviere CN (2009) Testing of neurosurgical needle steering via duty-cycled spinning in brain tissue in vitro. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp 258–261
Minhas DS, Engh JA, Fenske MM (2007) Modeling of needle steering via duty-cycled spinning. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp 2756–2759
Misra S, Reed KB, Schafer BW, Ramesh KT, Okamura AM (2010) Mechanics of flexible needles robotically steered through soft tissue. Int J Robot Res 29:1640–1660
Misra S, Reed KB, Schafer BW et al (2009) Observations and models for needle-tissue interactions. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 2687–2692
Misra S, Macura KJ, Ramesh KT, Okamura AM (2009) The importance of organ geometry and boundary constraints for planning of medical interventions. Med Eng Phys 31:195–206
Misra S, Ramesh KT, Okamura AM (2008) Modeling of tool-tissue interactions for computer-based surgical simulation: a literature review. Presence Teleop Virt Environ 17:463–491
Misra S, Reed KB, Douglas AS et al (2008) Needle-tissue interaction forces for bevel-tip steerable needles. IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp 224–231
Mousavi SR, Khalaji I, Naini AS et al (2012) Statistical finite element method for real-time tissue mechanics analysis. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng 15:595–608
Neubach Z, Shoham M (2010) Ultrasound-guided robot for flexible needle steering. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57:799–805
Okamura AM, Simone C, O'Leary MD (2004) Force modeling for needle insertion into soft tissue. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 51:1707–1716
Oldfield MJ, Dini D, Jaiswal T, Baena FRY (2013) The significance of rate dependency in blade insertions into a gelatin soft tissue phantom. Tribol Int 63:226–234
Park YL, Elayaperumal S, Daniel B, Ryu SC, Shin M, Savall J, Black RJ, Moslehi B, Cutkosky MR (2010) Real-time estimation of 3-D needle shape and deflection for MRI-guided interventions. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 15:906–915
Park W, Kim JS, Zhou Y et al (2005) Diffusion-based motion planning for a nonholonomic flexible needle model. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 4600–4605
Patil S, Burgner J, Webster RJ, Alterovitz R (2014) Needle steering in 3-D via rapid replanning. IEEE Trans Robot 30:853–864
Patil S, Alterovitz R (2010) Interactive motion planning for steerable needles in 3D environments with obstacles. IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp 893–899
Podder TK, Sherman J, Clark DP et al (2005) Evaluation of robotic needle insertion in conjunction with in vivo manual insertion in the operating room. IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Interactive Communication, pp 66–72
Qin XF (2015) Deep insertion of long slender needle into deformable tissue and the application for prostate brachytherapy. North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Qin J, Pang WM, Chui YP, Wong TT, Heng PA (2010) A novel modeling framework for multilayered soft tissue deformation in virtual orthopedic surgery. J Med Syst 34:261–271
Reed KB, Majewicz A, Kallem V, Alterovitz R, Goldberg K, Cowan N, Okamura A (2011) Robot-assisted needle steering. IEEE Robot Autom Mag 18:35–46
Roesthuis RJ, Kemp M, Van Den Dobbelsteen JJ et al (2014) Three-dimensional needle shape reconstruction using an array of fiber bragg grating sensors. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 19:1115–1126
Roesthuis RJ, Abayazid M, Misra S (2012) Mechanics-based model for predicting in-plane needle deflection with multiple bends. IEEE International Conference on Biomedical Robotics and Biomechatronics, pp 69–74
Roesthuis RJ, Van Veen YRJ, Jahya A et al (2011) Mechanics of needle-tissue interaction. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp 2557–2563
Seitel A, Engel M, Sommer CM, Radeleff BA, Essert-Villard C, Baegert C, Fangerau M, Fritzsche KH, Yung K, Meinzer HP, Maier-Hein L (2011) Computer-assisted trajectory planning for percutaneous needle insertions. Med Phys 38:3246–3259
Sergi PN, Jensen W, Micera S, Yoshida K (2012) In vivo interactions between tungsten microneedles and peripheral nerves. Med Eng Phys 34:747–755
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA-Cancer J Clin 66:10–29
Simone C, Okamura AM (2003) Modeling of needle insertion forces for robot-assisted percutaneous therapy. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 2085–2091
Sun W, Alterovitz R (2014) Motion planning under uncertainty for medical needle steering using optimization in belief space. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp 1775–1781
Swaney PJ, Burgner J, Gilbert HB, Webster RJ (2013) A flexure-based steerable needle: high curvature with reduced tissue damage. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 60:906–909
Van Den Berg NJ, Van Gerwen DJ, Dankelman J, Van Den Dobbelsteen JJ (2014) Design choices in needle steering—a review. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 20:2172–2183
Van Gerwen DJ, Dankelman J, Van Den Dobbelsteen JJ (2012) Needle-tissue interaction forces—a survey of experimental data. Med Eng Phys 34:665–680
Van Veen YR, Jahya A, Misra S (2012) Macroscopic and microscopic observations of needle insertion into gels. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part H-J Eng Med 226:441–449
Vrooijink GJ, Abayazid M, Patil S, Alterovitz R, Misra S (2014) Needle path planning and steering in a three-dimensional non-static environment using two-dimensional ultrasound images. Int J Robot Res 33:1361–1374
Wang JJ, Li XP, Zheng JJ, Sun D (2014) Dynamic path planning for inserting a steerable needle into a soft tissue. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 19:549–558
Webster RJ, Jones BA (2010) Design and kinematic modeling of constant curvature continuum robots: a review. Int J Robot Res 29:1661–1683
Webster RJ, Kim JS, Cowan NJ et al (2006) Nonholonomic modeling of needle steering. Int J Robot Res 25:509–525
Wood NA, Shahrour K, Ost MC, Riviere CN (2010) Needle steering system using duty-cycled rotation for percutaneous kidney access. Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, pp 5432–5435
Wood NA, Lehocky CA, Riviere CN (2013) Algorithm for three-dimensional control of needle steering via duty-cycled rotation. IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics, pp 237–241
Xie Y, Sun D, Tse HYG, Liu C, Cheng SH (2011) Force sensing and manipulation strategy in robot-assisted microinjection on zebrafish embryos. IEEE-ASME Trans Mechatron 16:1002–1010
Xie Y, Sun D, Liu C et al (2009) A force control approach to a robot-assisted cell microinjection system. Int J Robot Res 29:1222–1232
Xu J, Duindam V, Alterovitz R et al (2009) Planning fireworks trajectories for steerable medical needles to reduce patient trauma. IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, pp 4517–4522
Yamaguchi S, Tsutsui K, Satake K, Morikawa S, Shirai Y, Tanaka HT (2014) Dynamic analysis of a needle insertion for soft materials: arbitrary Lagrangian-Eulerian-based three-dimensional finite element analysis. Comput Biol Med 53:42–47
Yan K, Podder T, Li L, Joseph J, Rubens DR, Messing EM, Liao L, Yu Y (2009) A real-time prostate cancer detection technique using needle insertion force and patient-specific criteria during percutaneous intervention. Med Phys 36:3356–3362
Yoshida K, Lewinsky I, Nielsen M, Hylleberg M (2007) Implantation mechanics of tungsten microneedles into peripheral nerve trunks. Med Biol Eng Comput 45:413–420
Zhang YD, Zhao YJ, Tu F et al (2011) A review on path planning of flexible needle. J Harbin Univ Sci Technol 16:7–11
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of the People’s Republic of China (No. 51775368), Key Technology and Development Program of Tianjin Municipal Science and Technology Commission (No. 14ZCDZGX00490).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
For this type of study, formal consent is not required.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 64 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Yang, Z. & Jiang, S. Needle-tissue interactive mechanism and steering control in image-guided robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery: a review. Med Biol Eng Comput 56, 931–949 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1825-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1825-0