Abstract
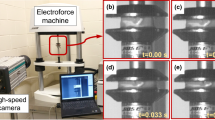
To fully understand the brain injury mechanism and develop effective protective approaches, an accurate constitutive model of brain tissue is firstly required. Generally, the brain tissue is regarded as a kind of viscoelastic material and is simply used in the simulation of brain injury. In fact, the brain tissue has the behavior of the visco-hyperelastic property. Therefore, this paper presents an effective computational inverse method to determine the material parameters of visco-hyperelastic constitutive model of brain white matter through compression experiments. First, with the help of 3D hand scanner, 3D geometries of brain white matter specimens are obtained to make it possible to establish the accurate simulation models of the specific specimens. Then, the global sensitivity analysis is adopted to evaluate the importance of the material parameters and further determine the parameters which may be identified. Subsequently, based on the genetic algorithm, the optimal material parameters of brain white matter can be identified by minimizing the match error between the experimental and simulated responses. Finally, by comparing the experiment and simulation results on the other specific specimen, and the simulation results with the material parameters from the references, respectively, the accuracy and reliability of the constitutive model parameters of brain white matter are demonstrated.

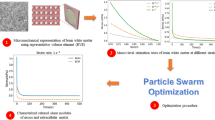
The main flowchart of the computational inverse technique for determining the material parameters of specimen-specific on brain white matter. Generalization: Combining the computational inverse method and unconfined uniaxial compression experiment of the specific specimen, an effective identification method is presented to accurately determine the hyperelastic and viscoelastic parameters of brain white matter in this paper.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2015) Global status report on road safety 2015. World Health Organization
Golman AJ, Danelson KA, Miller LE, Stitzel JD (2014) Injury prediction in a side impact crash using human body model simulation. Accid Anal Prev 64(2):1–8
Gabler LF, Crandall JR, Panzer MB (2016) Assessment of kinematic brain injury metrics for predicting strain responses in diverse automotive impact conditions. Ann Biomed Eng 44(12):3705–3718
Candefjord S, Winges J, Malik AA, Yu YN, Rylander T, McKelvey T, Fhager A, Elam M, Persson M (2016) Microwave technology for detecting traumatic intracranial bleedings: tests on phantom of subdural hematoma and numerical simulations. Med Biol Eng Comput 55(8):1–12
Cui S, Li H, Li X, Ruan J (2015) Effects of the variation in brain tissue mechanical properties on the intracranial response of a 6-year-old child. Comput Math Method M. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/529729
Chatelin S, Deck C, Renard F, Kremer S, Heinrich C, Armspach JP, Willinger R (2011) Computation of axonal elongation in head trauma finite element simulation. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater 4(8):1905–1919
Chatelin S, Deck C, Willinger R (2013) An anisotropic viscous hyperelastic constitutive law for brain material finite-element modeling. J Biorheol 27(1):26–37
Miller K, Chinzei K (1997) Constitutive modelling of brain tissue: experiment and theory. J Biomech 30(11–12):1115–1121
Miller K, Chinzei K, Orssengo G, Bednarz P (2000) Mechanical properties of brain tissue in-vivo: experiment and computer simulation. J Biomech 33(11):1369–1376
Li Y, Deng J, Zhou J, Li X (2016) Elastic and viscoelastic mechanical properties of brain tissues on the implanting trajectory of sub-thalamic nucleus stimulation. J Mater Sci Mater Med 27(11):163
Bilston LE, Liu Z, Phan-Thien N (2001) Large strain behaviour of brain tissue in shear: some experimental data and differential constitutive model. Biorheology 38(4):335–345
Tamura A, Hayashi S, Nagayama K, Matsumoto T (2008) Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in high-rate extension. J Biomech Sci Eng 3(2):263–274
Wu JZ, Dong RG, Schopper AW (2004) Analysis of effects of friction on the deformation behavior of soft tissues in unconfined compression tests. J Biomech 37(1):147–155
Hrapko M, Van Dommelen JAW, Peters GWM, Wismans JSHM (2006) The mechanical behaviour of brain tissue: large strain response and constitutive modelling. Biorheology 43(5):623–636
Hrapko M, Van Dommelen JAAW, Peters GWM, Wismans JSHM (2008) The influence of test conditions on characterization of the mechanical properties of brain tissue. J Biomech Eng 130(3):031003
Pervin F, Chen WW (2011) Effect of inter-species, gender, and breeding on the mechanical behavior of brain tissue. NeuroImage 54:S98–S102
Antona-Makoshi J, Davidsson J, Ejima S, Ono K, Brolin K, Anata K (2013) Correlation of global head and brain tissue injury criteria to experimental concussion derived from monkey head trauma experiments. In IRCOBI Conference (No. IRC-13-55, pp. 509–522)
Yue H, Deng J, Zhou J, Li Y, Chen F, Li L (2017) Biomechanics of porcine brain tissue under finite compression. J Mech Med Biol 17(01):1750001
Parkinson CM, O'Brien A, Albers TM, Simon MA, Clifford CB, Pritchett-Corning KR (2011) Diagnostic necropsy and selected tissue and sample collection in rats and mice. J Vis Exp 54:e2966
Laksari K, Shafieian M, Darvish K (2012) Constitutive model for brain tissue under finite compression. J Biomech 45(4):642–646
Ruan JS, Khalil T, King AI (1991) Human head dynamic response to side impact by finite element modeling. J Biomech Eng 113(3):276–283
Claessens MHA (1997) Finite element modeling of the human head under impact conditions. Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven
Takhounts EG, Crandall JR, Darvish K (2003) On the importance of nonlinearity of brain tissue under large deformations (No. 2003-22-0005). SAE Technical Paper
Takhounts EG, Eppinger RH, Campbell JQ, Tannous RE, Power ED, Shook LS (2003) On the development of the SIMon finite element head model. In Sae Conference Proceedings P (pp. 107-134). SAE; 1999
Kleiven S, Hardy WN (2002) Correlation of an FE model of the human head with local brain motion—consequences for injury prediction. Stapp Car Crash J 46(2):123–144
Ho J, Holst H, Kleiven S (2009) Automatic generation and validation of patient-specific finite element head models suitable for crashworthiness analysis. Int J Crashworthiness 14(6):555–563
Shafiee A, Ahmadian MT, & Hoviattalab M (2016) Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in compression. In ASME 2016 International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference
Kim B, Lee SB, Lee J, Sehyun C, Hyungmin P, Sanghoon Y, Sung HP (2012) A comparison among neo-Hookean model, Mooney-Rivlin model, and Ogden model for chloroprene rubber. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 13(5):759–764
Ahsanizadeh S, Li L (2015) Visco-hyperelastic constitutive modeling of soft tissues based on short and long-term internal variables. Biomed Eng Online 14(1):29
Budday S, Sommer G, Birkl C, Langkammer C, Haybaeck J, Kohnert J, Bauer M, Paulsen F, Steinmann P, Kuhl E, Holzapfel GA (2017) Mechanical characterization of human brain tissue. Acta Biomater 48:319–340
de Rooij R, Kuhl E (2016) Constitutive modeling of brain tissue: current perspectives. Appl Mech Rev 68(1):010801
Velardi F, Fraternali F, Angelillo M (2006) Anisotropic constitutive equations and experimental tensile behavior of brain tissue. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 5(1):53–61
Rashid B, Destrade M, Gilchrist MD (2012) Mechanical characterization of brain tissue in compression at dynamic strain rates. J Mech Behav Biomed 10:23–38
Brands DWA, Peters GWM, Bovendeerd PHM (2004) Design and numerical implementation of a 3-D non-linear viscoelastic constitutive model for brain tissue during impact. J Biomech 37(1):127–134
Finan JD, Sundaresh SN, Elkin BS, McKhann GM II, Morrison B III (2017) Regional mechanical properties of human brain tissue for computational models of traumatic brain injury. Acta Biomater 55:333–339
Jiang Y, Li G, Qian LX, Destrade M, Cao Y (2015) Measuring the linear and nonlinear elastic properties of brain tissue with shear waves and inverse analysis. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 14(5):1119–1128
Harb N, Labed N, Domaszewski M, Peyraut F (2014) Optimization of material parameter identification in biomechanics. Struct Multidiscip Optim 49(2):337–349
Zhang W, Liu J, Cho C, Han X (2015) A hybrid parameter identification method based on Bayesian approach and interval analysis for uncertain structures. Mech Syst Signal Process 60-61:853–865
Liu J, Hu Y, Xu C, Jiang C, Han X (2016) Probability assessments of identified parameters for stochastic structures using point estimation method. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 156:51–58
Liu J, Cai H, Jiang C, Han X, Zhang Z (2018) An interval inverse method based on high dimensional model representation and affine arithmetic. Appl Math Model 63:732–743
Ahn B, Kim Y, Kim J (2008) Biomechanical characterization with inverse FE model parameter estimation. Trans Korean Soc Mech Eng A 33(11):1202–1208
Chawla A, Mukherjee S, Karthikeyan B (2009) Characterization of human passive muscles for impact loads using genetic algorithm and inverse finite element methods. Biomech Model Mechanobiol 8(1):67–76
Guan F, Zhang G, Liu J, Wang S, Luo X, Zhu F (2017) Study on material parameters identification of brain tissue considering uncertainty of friction coefficient. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol. 250, No. 1, p. 012049). IOP Publishing
Nicolle S, Lounis M, Willinger R (2004) Shear properties of brain tissue over a frequency range relevant for automotive impact situations: new experimental results (No. 2004-22-0011). SAE Technical Paper
Mooney M (1940) A theory of large elastic deformation. J Appl Phys 11(9):582–592
Rivlin RS (1948) Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials IV. Further developments of the general theory. Phil Trans R Soc Lond A 241(835):379–397
Mendis KK, Stalnaker RL, Advani SH (1995) A constitutive relationship for large deformation finite element modeling of brain tissue. J Biomech Eng 117(3):279–285
Elhage H, Mallick PK, Zamani N (2004) Numerical modeling of quasi-static axial crush of square aluminium-composite hybrid tubes. Int J Crashworthiness 9(6):653–664
Sobol IM (1993) Sensitivity estimates for nonlinear mathematical models. Math Model Comput Exp 1(4):407–414
Liu J, Tu L, Liu G, Jiang C, Zhang Z (2018) An analytical structural global sensitivity analysis method based on direct integral. Inverse Probl Sci En. https://doi.org/10.1080/17415977.2018.1531856
Funding
This work is supported by the National Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51621004 and 11572115) and an independent research project of the State Key Laboratory of Reliability and Intelligence Electrical Equipment, Hebei University of Technology (EERIZZ2018001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution or practice at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Liu, J., Guan, F. et al. Identification of the visco-hyperelastic properties of brain white matter based on the combination of inverse method and experiment . Med Biol Eng Comput 57, 1109–1120 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1944-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-018-1944-7