Abstract
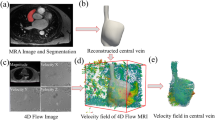
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of a notch at the distal end of a microcatheter on vein deformation in segmental adrenal venous sampling. A three-dimensional fluid–structure interaction simulation was performed using commercial finite element software. A computational model of a vein with a catheter inserted into it was constructed. The outer and inner diameters of the vein were 0.9 mm and 0.6 mm, respectively, whereas those of the catheter were 0.6 mm and 0.5 mm, respectively. The velocity of the blood flow at the outlet was 85 mm/s. The pressure at the inlet was 0 Pa. The mesh consisted of approximately 660,000 elements. The effect of the number (0–4) and shape (no notch, 1/4 circular, 1/3 circular, semicircular, 2/3 circlecircular, and 3/4 circular) of the notches at the distal end of the microcatheter on the vein deformation when a suction pressure was applied was evaluated. The venous wall displacement was the smallest with the one-notch catheter, followed by the four-notch catheter, and was the smallest with the catheter having 1/4-circular notches, followed by the one with 1/3-circular notches. In conclusion, microcatheters having one notch and 1/4-circular notches reduce vein deformation and lead to successful segmental adrenal venous sampling.

Comparing catheters having different notch shapes.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Funder JW, Carey RM, Fardella C, Gomez-Sanchez CE, Mantero F, Stowasser M, Young WF Jr, Montori VM (2008) Endocrine Society. Case detection, diagnosis, and treatment of patients with primary aldosteronism: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:3266–3281. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2008-0104
Fung YC (1996) Biomechanics: circulation. Springer-Verlag, New York, p 114.17
Hasegawa M (1983) Rheological properties and wall structures of large veins. Biorheology 20:531–545. https://doi.org/10.3233/BIR-1983-20510
Hasegawa M, Azuma T (1975) Rheological properties of the main vascular system: with special reference to the fine structure of walls. Proceedings of the 1975 Symposium on Biomaterials; 1–13
Jeschke K, Janetschek G, Peschel R, Schellander L, Bartsch G, Henning K (2003) Laparoscopic partial adrenalectomy in patients with aldosterone-producing adenomas: indications, technique, and results. Urology 61:69–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0090-4295(02)02240-9
Kawasaki Y, Ishidoya S, Kaiho Y, Ito A, Satoh F, Morimoto R, Nakagawa H, Arai Y (2011) Laparoscopic simultaneous bilateral adrenalectomy: assessment of feasibility and potential indications. Int J Urol 18:762–767. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-2042.2011.02846.x
Kaye DR, Storey BB, Pacak K, Pinto PA, Linehan WM, Bratslavsky G (2010) Partial adrenalectomy: underused first line therapy for small adrenal tumors. J Urol 184:18–25
Makita K (2013) Adrenal venous sampling for primary aldosteronism—tips and tricks for successful AVS procedure. Jpn J Intervent Radiol 28:204–210. https://doi.org/10.11407/ivr.28.204
Melby JC, Spark RF, Dale SL, Egdahl RH, Kahn PC (1967) Diagnosis and localization of aldosterone-producing adenomas by adrenal vein catheterization. N Engl J Med 277:1050–1056. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM196711162772002
Miyake Y, Tanaka K, Nishikawa T, Naruse M, Takayanagi R, Sasano H, Takeda Y, Shibata H, Sone M, Satoh F, Yamada M, Ueshiba H, Katabami T, Iwasaki Y, Tanaka H, Tanahashi Y, Suzuki S, Hasegawa T, Katsumata N, Tajima T, Yanase T (2014) Prognosis of primary aldosteronism in Japan: results from a nationwide epidemiological study. Endocr J 61:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ13-0353
Morimoto R, Satani N, Iwakura Y, Ono Y, Kudo M, Nezu M, Omata K, Tezuka Y, Seiji K, Ota H, Kawasaki Y, Ishidoya S, Nakamura Y, Arai Y, Takase K, Sasano H, Ito S, Satoh F (2016) A case of bilateral aldosterone-producing adenomas differentiated by segmental adrenal venous sampling for bilateral adrenal sparing surgery. J Hum Hypertens 30:379–385. https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2015.100
Nishikawa T, Omura M, Satoh F, Shibata H, Takahashi K, Tamura N, Tanabe A (2011) Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of primary aldosteronism—the Japan Endocrine Society 2009. Endocr J 58:711–721. https://doi.org/10.1507/endocrj.EJ11-0133
Omura M, Makita K, Yamaguchi K, Sasano H, Nishikawa T (2010) A new method of super-selective ACTH-stimulated adrenal venous sampling is revolutionarily useful for treatment of primary aldosteronism. J Hypertens 28:21–23. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.hjh.0000379105.76295.34
Omura M, Makita K (2010) Latest device of IVR part 1 Koshin medical: goldcrest microcatheter split tip (OM catheter). Rad Fan 8:51–53
Onozawa S, Yamaguchi H, Murata S, Makita K, Takase K, Tajima H, Kawamata H, Nishida N, Maeda H, Kanasaki S, Turusaki M, Tasumoto T, Ishiguchi T, Saito H (2015) Present status and strict analysis of adrenal venous sampling in Japan. Jpn J Intervent Radiol 30:42–47. https://doi.org/10.11407/ivr.30.42
Satani N, Ota H, Seiji K, Morimoto R, Kudo M, Iwakura Y, Ono Y, Nezu M, Omata K, Ito S, Satoh F, Takase K (2016) Intra-adrenal aldosterone secretion: segmental adrenal venous sampling for localization. Radiology 278:265–274. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015142159
Satoh F, Morimoto R, Seiji K, Satani N, Ota H, Iwakura Y, Ono Y, Kudo M, Nezu M, Omata K, Tezuka Y, Kawasaki Y, Ishidoya S, Arai Y, Takase K, Nakamura Y, McNamara K, Sasano H, Ito S (2015) Is there a role for segmental adrenal venous sampling and adrenal sparing surgery in patients with primary aldosteronism? Eur J Endocrinol 173:465–477. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-14-1161
Vonend O, Ockenfels N, Gao X, Allolio B, Lang K, Mai K, Quack I, Saleh A, Degenhart C, Seufert J, Seiler L, Beuschlein F, Quinkler M, Podrabsky P, Bidlingmaier M, Lorenz R, Reincke M, Rump LC (2011) Adrenal venous sampling evaluation of the German Conn’s registry. Hypertension 57:990–995. https://doi.org/10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.168484
Vuokko K, Harri S, Eino H (1983) Mechanical properties of fast and slow skeletal muscle with special reference to collagen and endurance training. J Biomech 17:725–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/0021-9290(84)90103-9
Wu VC, Chueh SC, Chang HW, Lin WC, Liu KL, Li HY, Lin YH, Wu KD, Hsieh BS (2008) Bilateral aldosterone-producing adenomas: differentiation from bilateral adrenal hyperplasia. QJM 101:13–22. https://doi.org/10.1093/qjmed/hcm101
Young WF (2007) Primary aldosteronism: renaissance of a syndrome. Clin Endocrinol 66:607–618. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2007.02775.x
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all individuals involved in this study for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinoshita, T., Seiji, K., Putra, N.K. et al. Effect of a notch at the distal end of a microcatheter on vein deformation in segmental adrenal venous sampling: a preliminary study using computational fluid dynamics. Med Biol Eng Comput 57, 1425–1436 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-01968-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-01968-1