Abstract
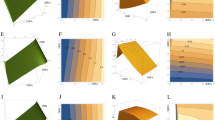
The objective of this study is to investigate the synergetic effect of the pelvic rotation and X-ray offset on the radiographic anteversion/inclination (RA/RI) angles of the acetabular cup using a mathematical model. A cone model for establishing the spatial relationship between a three-dimensional (3D) circle and its two-dimensional (2D) elliptical projection is utilized to quantify the relationship between the 3D RA/RI angles of the cup and their 2D counterparts with different types of pelvic rotations in pelvic/hip anteroposterior radiographs. The results reveal that the effect of inlet/outlet views on the 2D RA angle is similar to that of iliac/obturator views. The permissible ranges of pelvic rotation for the 2D RA angle with an acceptable bias are the 3D space formed by the limits of triple axial rotations. For a specified acceptable bias of the 2D RA angle, these ranges are almost equal between pelvic and hip radiographs. The combined inlet/obturator or outlet/iliac views can maintain the 2D RA angle of a pelvic radiograph within the same range of acceptable bias as that of a hip radiograph. For a 2D RA angle with an acceptable bias, the permissible range of pelvic rotation needs to be evaluated with equal attention in both radiographs.

The traditional methods for calculating the radiographic angles of the acetabular cup are based on the ellipse projection of the opening circle of the cup on radiographs. However, with varying locations of the X-ray source and pelvis rotations about different axes, the outline of this ellipse projection will change, and accordingly, the traditional method and calculating results will be inaccurate. In this study, a cone model for three-dimensional circle-to-two-dimensional ellipse projection is utilized to incorporate the effect of X-ray offset and quantify the relationships of the radiographic angles of the cup with the true orientation of the cup and pelvic rotations in either pelvic or hip anteroposterior radiographic situation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2D:
-
Two-dimensional
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- AP:
-
Anteroposterior
- RA:
-
Radiographic anteversion
- RI:
-
Radiographic inclination
- THA:
-
Total hip arthroplasty
- r :
-
The radius of the cup
- (o, p, q):
-
The coordinate of the X-ray beam source
- (x 0, y 0, z 0):
-
The coordinate of the center of the cup
- [k 1, i 1, j 1]:
-
The normal vector of the cup before rotation
- [k, i, j]:
-
The normal vector of the axis of the cup after rotation
- [l, m, n]:
-
The normal vector of the space line
- α :
-
The x-axial rotation of the cup
- β :
-
The y-axial rotation of the cup
- γ :
-
The z-axial rotation of the cup
References
Fujishiro T, Hiranaka T, Hashimoto S, Hayashi S, Kurosaka M, Kanno T, Masuda T (2016) The effect of acetabular and femoral component version on dislocation in primary total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 40:697–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2924-2
Grammatopoulos G, Alvand A, Monk AP, Mellon S, Pandit H, Rees J, Gill HS, Murray DW (2016) Surgeons’ accuracy in achieving their desired acetabular component orientation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 98:e72. https://doi.org/10.2106/jbjs.15.01080
Murray DW (1993) The definition and measurement of acetabular orientation. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 75:228–232
Ahn SJ, Warnecke HJ, Kotowski R (1999) Systematic geometric image measurement errors of circular object targets: mathematical formulation and correction. Photogramm Rec 16:485–502. https://doi.org/10.1111/0031-868X.00138
Forsyth D, Mundy JL, Zisserman A, Coelho C, Heller A, Rothwell C (1991) Invariant descriptors for 3-D object recognition and pose. IEEE T Pattern Anal 13:971–991
Seradge H, Nagle KR, Miller RJ (1982) Analysis of version in the acetabular cup. Clin Orthop Relat Res 166:152–157
Derbyshire B (2008) Correction of acetabular cup orientation measurements for X-ray beam offset. Med Eng Phys 30:1119–1126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2008.02.001
Derbyshire B, Diggle PJ, Ingham CJ, Macnair R, Wimhurst J, Jones HW (2014) A new technique for radiographic measurement of acetabular cup orientation. J Arthroplast 29:369–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2013.06.024
Amiri S, Masri BA, Garbuz D, Anglin C, Wilson DR (2012) A multiplanar radiography method for assessing cup orientation in total hip arthroplasty. J Biomech Eng 134:101008. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4007664
Malik A, Wan Z, Jaramaz B, Bowman G, Dorr LD (2010) A validation model for measurement of acetabular component position. J Arthroplast 25:812–819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2009.04.021
Wan Z, Malik A, Jaramaz B, Chao L, Dorr LD (2009) Imaging and navigation measurement of acetabular component position in THA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467:32–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0597-5
Schwarz TJ, Weber M, Dornia C, Worlicek M, Renkawitz T, Grifka J, Craiovan B (2017) Correction of pelvic tilt and pelvic rotation in cup measurement after THA - an experimental study. Rofo 189:864–873. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0043-110012
Schwarz T, Weber M, Worner M, Renkawitz T, Grifka J, Craiovan B (2017) Central X-ray beam correction of radiographic acetabular cup measurement after THA: an experimental study. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12:829–837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1489-x
Wang L, Thoreson AR, Trousdale RT, Morrey BF, Dai K, An KN (2017) Radiographic cup anteversion measurement corrected from pelvic tilt. Med Eng Phys 49:103–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2017.08.008
Tannast M, Zheng G, Anderegg C, Burckhardt K, Langlotz F, Ganz R, Siebenrock KA (2005) Tilt and rotation correction of acetabular version on pelvic radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res 438:182–190 &NA
Tannast M, Langlotz U, Siebenrock KA, Wiese M, Bernsmann K, Langlotz F (2005) Anatomic referencing of cup orientation in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 436:144–150 &NA
Wolf A, Digioia AM 3rd, Mor AB, Jaramaz B (2005) Cup alignment error model for total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 437:132–137 & NA
Wolf A, DiGioia AM 3rd, Mor AB, Jaramaz B (2005) A kinematic model for calculating cup alignment error during total hip arthroplasty. J Biomech 38:2257–2265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiomech.2004.09.033
Delagrammaticas DE, Alvi HM, Kaat AJ, Sullivan RR, Stover MD, Manning DW (2018) Quantitative effect of pelvic position on radiographic assessment of acetabular component position. J Arthroplast 33:608–614 e601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.09.033
Zhao JX, Su XY, Zhao Z, Xiao RX, Zhang LC, Tang PF (2018) Three-dimensional orientation and location-dependent varying rules of radiographic angles of the acetabular cup. Int Orthop 42:1819–1825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-3809-y
Zhao JX, Su XY, Xiao RX, Zhao Z, Zhang LH, Zhang LC, Tang PF (2016) A mathematical method for precisely calculating the radiographic angles of the cup after total hip arthroplasty. Med Eng Phys 38:1376–1381. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medengphy.2016.09.007
Lembeck B, Mueller O, Reize P, Wuelker N (2005) Pelvic tilt makes acetabular cup navigation inaccurate. Acta Orthop 76:517–523. https://doi.org/10.1080/17453670510041501
Widmer KH (2004) A simplified method to determine acetabular cup anteversion from plain radiographs. J Arthroplast 19:387–390
Eckman K, Hafez M, Ed F, Jaramaz B, Levison T, Digioia A (2006) Accuracy of pelvic flexion measurements from lateral radiographs. Clin Orthop Relat Res 451:154–160
Widmer D, Reising K, Kotter E, Helwig P (2018) Correct assessment of acetabular component orientation in total hip arthroplasty from plane radiographs. J Arthroplast 33:2652–2659.e2653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2018.02.023
Yun HH, Murphy WS, Ward DM, Zheng G, Hayden B, Murphy SB (2019) Effect of pelvic tilt and rotation on cup orientation in standing anteroposterior radiographs. Hip Int 1120700019831665. doi:https://doi.org/10.1177/1120700019831665
Yun H, Murphy WS, Ward DM, Zheng G, Hayden BL, Murphy SB (2018) Effect of pelvic tilt and rotation on cup orientation in both supine and standing positions. J Arthroplast 33:1442–1448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arth.2017.11.069
Acknowledgments
Anonymous reviewers are appreciated very much for their help to improve this manuscript.
Funding
This study was partially funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (FRF-TP-16-045A1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3502 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, JX., Su, XY., Zhao, Z. et al. The synergetic effect of pelvic rotation and X-ray offset on radiographic angles of the acetabular cup. Med Biol Eng Comput 57, 2359–2371 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02041-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-019-02041-7