Abstract
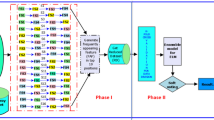
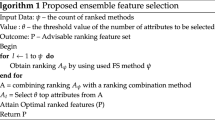
Computational classification of cancers is an important research problem. Gene expression data has 1000s of features, very few samples, and a class imbalance problem. In this paper, we have proposed a framework for the classification of cancer gene expression profiles. The framework consists of a pipeline of methods for data pre-processing, feature selection, and classification. Data pre-processing is done by standard scaling and normalization of the features. The feature selection is performed in two steps. First, recursive feature elimination (RFE) is used; then, a genetic algorithm is applied only in case RFE results in a feature subset of size more than a specific threshold. Next, is a meta-pool of diverse, individual as well as ensemble classifiers. Hyper-parameters of each member in the meta-pool are optimized using Bayesian Optimization. An algorithm is developed to select the best classifier from the meta-pool based on classification accuracy and computation time taken. We evaluated the framework on 6 publicly available microarray datasets and the PAN-Cancer RNA Sequencing dataset. We found that the classifier selected by the proposed framework produced significant improvement in classification accuracy and computation time required to predict labels for test datasets. A detailed comparison with the state-of-the-art methods shows that the proposed framework outperforms all of them.
Graphic Abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoadley KA, Yau C, Hinoue T, Wolf DM, Lazar AJ, Drill E et al (2018) Cell-of-origin patterns dominate the molecular classification of 10,000 tumors from 33 types of cancer. Cell 173(2):291–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.03.022
TCGA dataset https://gdc.cancer.gov/about-data/publications/pancanatlas. Accessed 12 Jul 2021
Golub GTR, Slonim DK, Tamayo P, Gaasenbeek M, Huard C, Mesirov JP, Coller H, LoH M, Downing JR, Caligiuri MA, Bloomfield CD, Lander ES (1999) Molecular classification of cancer: class discovery and class prediction by gene expression monitoring. Science 286(5439):531–537
Alizadeh A et al (2000) Different types of diffuse large b-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 403:503–511
Chiesa M, Maioli G, Colombo GI et al (2020) GARS: genetic algorithm for the identification of a Robust Subset of features in high-dimensional datasets. BMC Bioinform 21:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-020-3400-6
Guyon I, Weston J, Barnhill S, Vapnik V (2002) Gene selection for cancer classification using support vector machines. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng 25(1):1–14
Jansi RM, Devaraj D (2019) Two-stage hybrid gene selection using mutual information and genetic algorithm for cancer data classification. J Med Syst 43:235
Khan J, Wei JS, Ringner M, Saal LH, Ladanyi M, Westermann F et al (2001) Classification and diagnostic prediction of cancers using gene expression profiling and artificial neural Networks. Nat Med 7:673–679
Pomeroy SL et al (2002) Prediction of central nervous system embryonal tumor outcome based on gene expression. Nature 415(6870):436–442
Singh D, Febbo P, Ross K, Jackson D, Manola J, Ladd C et al (2002) Gene expression correlates of clinical prostate cancer behavior. Cancer Cell 1(2):203–209
Fletcher S, Verma B, Jan ZM, Zhang M (2018) The optimized selection of base-classifiers for ensemble classification using a multi-objective genetic algorithm. In: Proceedings of International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro. 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1109/ijcnn.2018.8489467.
Efron B (1979) Bootstrap methods: another look at the Jackknife. Ann Stat 7(1):1–26
Chawla N, Bowyer KW, Hall LO, Kegelmeyer WP (2002) SMOTE: synthetic minority over-sampling technique. J Artif Intell Res 16:321–357
Bergstra J, Bardenet R, Bengio Y, Kégl B (2011) Algorithms for hyper-parameter optimization. In Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, NIPS 2011, 24:2546–2554
Pedregosa et al (2011) Scikit-learn: machine learning in Python. JMLR 12:2825–2830
Rana M, Ahmed K (2020) Feature selection and biomedical signal classification using minimum redundancy maximum relevance and artificial neural network. Proceedings of international joint conference on computational intelligence algorithms for intelligent systems. Springer, Singapore
Nancy SG, Saranya K, Rajasekar S (2020) Neuro-fuzzy ant bee colony based feature selection for cancer classification. Springer innovations in communication and computing. Springer, Cham
Shukla AK, Tripathi D (2020) Detecting biomarkers from microarray data using distributed correlation-based gene selection. Genes & Genom 42:449–465
Kourou K, Rigas G, Papaloukas C, Mitsis M, Fotiadis DI (2020) Cancer classification from time-series microarray data through regulatory Dynamic Bayesian Networks. Comput Biol Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103577
Yanhao H, Lihui X, Chuanze K, Minghui W, Qin M, Bin Y (2020) SGL-SVM: a novel method for tumor classification via support vector machine with sparse group Lasso. J Theor Biol 486:110098. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtbi.2019.110098
Xiaohong H, Dengao L, Ping L, Li W (2020) Feature selection by recursive binary gravitational search algorithm optimization for cancer classification. Soft Comput 24(6):4407–4425
Morais-Rodrigues F, Silverio-Machado R, Kato RB, Rodrigues DLN, Valdez- BJ, Fonseca V (2019) Analysis of the microarray gene expression for breast cancer progression after the application modified logistic regression. Gene. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.144168
Loey M, Wajeeh JM, Hazem E-B, Hamed N, Taha M, Eldeen M, Khalifa M (2020) Breast and colon cancer classification from gene expression profiles using data mining techniques. Symmetry 12:408
Akhand MAH, Asaduzzaman MM, Mir HK, Hafizur Rahman MM (2019) Cancer classification from DNA microarray data using mRMR and artificial neural network. Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 10:7
Zakariyal YA, Hisyam LM (2019) A two-stage sparse logistic regression for optimal gene selection in high-dimensional microarray data classification. Adv Data Anal Classif 13:753–771
Sarah AM, Saleh AI, Labib M (2019) Gene expression cancer classification using modified K-nearest neighbors technique. BioSystems 176:41–51
Russul A, Jingyu H, Azzawi H, Yong X (2019) A novel gene selection algorithm for cancer classification using microarray datasets. BMC Med Genom 12:10
Mignone P, Pio G, Džeroski S et al (2020) Multi- task learning for the simultaneous reconstruction of the human and mouse gene regulatory networks. Sci Rep 10:22295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-78033-7
Ziba K, Marjan N, Mohammad JR (2020) Detection and classification of breast cancer using logistic regression feature selection and GMDH classifier. J Biomed Inform 111:103591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbi.2020.103591
Bong-Hyun K, Kijin Y, Peter CWL (2020) Cancer classification of single-cell gene expression data by neural network. Bioinformatics 36(5):1360–1366. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz772
Way GP, Sanchez-Vega F, La K, Armenia J, Chatila WK, Luna A, Sander C, Cherniack AD, Mina M, Ciriello G, Schultz N, Sanchez Y, Greene CS (2018) Machine learning detects pan-cancer Ras pathway activation in the cancer genome atlas. Cell Rep 23(1):172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.046
Eraslan G et al (2019) Single-cell RNA-seq denoising using a deep count autoencoder. Nat Commun 10:390
Dhahri H, Rahmany I, Mahmood A, Al Maghayreh E, Elkilani W (2020) Tabu search and machine-learning classification of benign and malignant proliferative breast lesions. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4671349
Liu X, Zhang Y, Fu C, Zhang R, Zhou F (2021) EnRank: an ensemble method to detect pulmonary hypertension biomarkers based on feature selection and machine learning models. Front Genet 12:636429. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.636429
Lee K, Jeong Ho, Lee S et al (2019) CPEM: Accurate cancer type classification based on somatic alterations using an ensemble of a random forest and a deep neural network. Sci Rep 9:16927. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-53034-3
Tang X, Shi Z, Jin M (2021) Multi-category multi-state information ensemble-based classification method for precise diagnosis of three cancers. Neural Comput & Applic. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00521-021-06211-3
Ilyas QM, Ahmad M (2021) An enhanced ensemble diagnosis of cervical cancer: a pursuit of machine intelligence towards sustainable health. IEEE Access 9:12374–12388. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3049165
Francesconi M, Remondini D, Neretti N et al (2008) Reconstructing networks of pathways via significance analysis of their intersections. BMC Bioinform 9:S9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-9-S4-S9
Zura K, Willie Y (2017) K-means and cluster models for cancer signatures. Biomol Detect Quantif 13:7–31
Yu G, Yu X, Wang J (2017) Network-aided Bi-clustering for discovering cancer subtypes. Sci Rep 7:1046. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01064-0
Leukemia Dataset https://web.stanford.edu/~hastie/CASI_files/DATA/leukemia.html. Accessed 25 Dec 2020
SRBCT Dataset https://research.nhgri.nih.gov/microarray/Supplement/. Accessed 25 Dec 2020
Colon Dataset http://genomics-pubs.princeton.edu/oncology/. Accessed 25 Dec 2020
Microarray Data Sets ftp://stat.ethz.ch/Manuscripts/dettling. Accessed 25 Dec 2020
Prostate Dataset https://leo.ugr.es/elvira/DBCRepository/ProstateCancer/ProstateCancer.zip
Lymphoma Dataset https://llmpp.nih.gov/lymphoma/, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/query/acc.cgi?acc=GSE60
Alon U, Barkai N, Notterman DA et al (1999) Broad patterns of gene expression revealed by clustering analysis of tumor and normal colon tissues probed by oligonucleotide array. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6745–6750
Snoek J, Larochelle H, Adams RP (2012) Practical Bayesian optimization of machine learning algorithms. In: NIPS’12: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. 2:2951–2959
Bergstra J, Yamins D, Cox DD (2013) Making a science of model search: hyperparameter optimization in hundreds of dimensions for vision architectures. In ICML’13: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning, 28:115–123
Wu J, Chen X, Zhang H, Xiong L, Lei H, Deng S (2019) Hyperparameter optimization for machine learning models based on bayesian optimization. J Electron Sci Technol 17(1):26–40
Bergstra J, Bengio Y (2012) Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. J Mach Learn Res 13(1):281–305
Acknowledgements
Authors are thankful to the reviewers for very useful comments and suggestions which greatly improved this work and its presentation.
Funding
This research work is funded by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, under the scheme DST ICPS 2018.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koul, N., Manvi, S.S. Framework for classification of cancer gene expression data using Bayesian hyper-parameter optimization. Med Biol Eng Comput 59, 2353–2371 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02442-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02442-7