Abstract
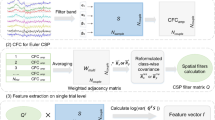
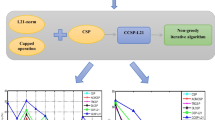
The technique of common spatial patterns (CSP) is a widely used method in the field of feature extraction of electroencephalogram (EEG) signals. Motivated by the fact that a cosine distance can enlarge the distance between samples of different classes, we propose the Euler CSP (e-CSP) for the feature extraction of EEG signals, and it is then used for EEG classification. The e-CSP is essentially the conventional CSP with the Euler representation. It includes the following two stages: each sample value is first mapped into a complex space by using the Euler representation, and then the conventional CSP is performed in the Euler space. Thus, the e-CSP is equivalent to applying the Euler representation as a kernel function to the input of the CSP. It is computationally as straightforward as the CSP. However, it extracts more discriminative features from the EEG signals. Extensive experimental results illustrate the discrimination ability of the e-CSP.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wolpaw JR, Birbaumer N, McFarland DJ, Pfurtscheller G, Vaughan TM (2002) Brain-computer interfaces for communication and control. Clin Neurophysiol 113(6):767–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1388-2457(02)00057-3
Daly JJ, Wolpaw JR (2008) Brain-computer interfaces in neurological rehabilitation. The Lancet Neurol 7(11):1032–1043. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1474-4422(08)70223-0
Kathner I, Wriessnegger SC, Müller-Putz GR, Kübler A, Halder S (2014) Effects of mental workload and fatigue on the P300, alpha and theta band power during operation of an ERP (P300) brain-computer interface. Biol Psychol 102:118–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsycho.2014.07.014
Reza MF, Ikoma K, Ito T, Ogawa T, Mano Y (2007) N200 latency and P300 amplitude in depressed mood post-traumatic brain injury patients. Neuropsychol Rehabil 17(6):723–734. https://doi.org/10.1080/09602010601082441
Zhang N, Tang J, Liu Y, Zhou Z (2016) A novel P300-BCI with virtual stimulus continuous motion. The 8th International Conference on Intelligent Human-Machine Systems and Cybernetics (IHMSC), pp. 415–417. https://doi.org/10.1109/IHMSC.2016.222
Wang L, Liu X, Liang Z, Yang Z, Hu X (2019) Analysis and classification of hybrid BCI based on motor imagery and speech imagery. Measurement 147:106842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.07.070
Hernán D, Fernando M, Elizabeth F, Córdova F (2018) Intra and inter-hemispheric correlations of the order/chaos fluctuation in the brain activity during a motor imagination task. Procedia Computer Science 139:456–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2018.10.250
Florin P, Fazli S, Badower Y, Blankertz B, Müller K-R (2007) Single trial classification of motor imagination using 6 dry EEG electrodes. PLoS One 2(7):e637. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000637
Lee S-B, Kim H-J, Kim H, Jeong J-H, Lee S-W, Kim D-J (2019) Comparative analysis of features extracted from EEG spatial, spectral and temporal domains for binary and multiclass motor imagery classification. Inf Sci 502:190–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ins.2019.06.008
Sözer AT, Fidan CB (2018) Novel spatial filter for SSVEP-based BCI: a generated reference filter approach. Comput Biol Med 96:98–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2018.02.019
Pfurtscheller G, Lopes da Silva FH (1999) Event related EEG/MEG synchronization and desynchronization: basic principles. Clin Neurophysiol 110(11):1842–1857. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1388-2457(99)00141-8
Hatamikia S, Nasrabadi AM (2015) Subject transfer BCI based on composite local temporal correlation common spatial pattern. Comput Biol Med 64:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2015.06.001
Blankertz B, Tomioka R, Lemm S, Kawanabe M, Müller K-R (2008) Optimizing spatial filters for robust EEG single-trial analysis. IEEE Signal Process Mag 25(1):41–56. https://doi.org/10.1109/msp.2008.4408441
Vuckovic A, Sepulveda F (2008) A four-class BCI based on motor imagination of the right and the left-hand wrist. International Symposium on Applied Sciences on Biomedical and Communication Technologies, pp. 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISABEL.2008.4712628
Hong K-S, Khan MJ (2017) Hybrid brain–computer interface techniques for improved classification accuracy and increased number of commands: a review. Front Neurorobotics 11:35. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbot.2017.00035
Wang H, Zheng W (2008) Local temporal common spatial patterns for robust single-trial EEG classification. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 16(2):131–139. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2007.914468
Dong J, Chen B, Lu N, Zheng N, Wang H (2017) Correntropy induced metric based common spatial pattern. The 27th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP), pp.1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/MLSP.2017.8168132
Park Y, Chung W (2019) Frequency-optimized local region common spatial pattern approach for motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 27(7):1378–1388. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2922713
Park Y, Chung W (2020) Optimal channel selection using correlation coefficient for CSP based EEG classification. IEEE Access 8:111514–111521. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3003056
Park Y, Chung W (2018) BCI classification using locally generated CSP features. The 6th International Conference on Brain–Computer Interface (BCI), pp.1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/IWW-BCI.2018.8311492
Yu Z, Ma T, Fang N, Wang H, Li Z, Fan H (2020) Local temporal common spatial patterns modulated with phase locking value. Biomed Signal Process Control 59:101882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2020.101882
Lachaux JP, Rodriguez E, Martinerie J, Varela FJ (1999) Measuring phase synchrony in brain signals. Hum Brain Mapp 8(4):194–208. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-0193(1999)8:4%3c194::AID-HBM4%3e3.0.CO;2-C
Chakraborty B, Ghosal S, Ghosh L, Konar A, Nagar AK (2019) Phase-sensitive common spatial pattern for EEG classification. IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics (SMC), pp. 3654–3659. https://doi.org/10.1109/SMC.2019.8914070
Geirnaert S, Francart T, Bertrand A (2021) Fast EEG-based decoding of the directional focus of auditory attention using common spatial patterns. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 68(5):1557–1568. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2020.3033446
Miao Y, Jin J, Daly I, Zuo C, Wang X, Cichocki A, Jung T (2021) Learning common time-frequency-spatial patterns for motor imagery classification. IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 29:699–707. https://doi.org/10.1109/TNSRE.2021.3071140
Fu R, Han M, Tian Y, Shi P (2020) Improvement motor imagery EEG classification based on sparse common spatial pattern and regularized discriminant analysis. J Neurosci Methods 343:108833. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108833
Tan H, Zhang X, Guan N, Tao D, Huang X, Luo Z (2015) Two-dimensional Euler PCA for face recognition. International Conference on Multimedia Modeling, pp. 548–559. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-14442-9_59
Liwicki S, Tzimiropoulos G, Zafeiriou S, Pantic M (2013) Euler principal component analysis. Int J Comput Vis 101(3):498–518. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-012-0558-z
Liao S, Gao Q, Yang Z, Chen F, Nie F, Han J (2018) Discriminant analysis via joint Euler transform and L2,1-norm. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(11):5668–5682. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2859589
Liu Y, Gao Q, Han J, Wang S (2018) Euler sparse representation for image classification. The 32th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-18), pp. 3691–3697. https://aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI18/paper/view/16524
Talukdar U, Hazarika SM, Gan JQ (2020) Adaptation of common spatial patterns based on mental fatigue for motor-imagery BCI. Biomed Signal Process Control 58:101829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bspc.2019.101829
Ghaheri H, Ahmadyfard AR (2013) Extracting common spatial patterns from EEG time segments for classifying motor imagery classes in a brain computer interface (BCI). Sci Iran 20(6):2061–2072
Koren Y, Carmel L (2004) Robust linear dimensionality reduction. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Graph 10(4):459–470. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVCG.2004.17
Tu W, Sun S (2012) A subject transfer framework for EEG classification. Neurocomputing 82:109–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2011.10.024
Fitch AJ, Kadyrov A, Christmas WJ, Kittler J (2005) Fast robust correlation. IEEE Trans Image Process 14(8):1063–1073. https://doi.org/10.1109/tip.2005.849767
Cho H, Ahn M, Ahn S, Kwon M, Jun SC (2017) EEG datasets for motor imagery brain–computer interface. GigaScience 6(7):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/gigascience/gix034
Fang N (2018) Lp-norm-based local temporal common spatial patterns. Southeast University, Master's Thesis
Lotte F, Guan C (2011) Regularizing common spatial patterns to improve BCI designs: unified theory and new algorithms. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 58(2):355–362. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2010.2082539
Chicco D, Jurman G (2020) The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genomics 21:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6413-7
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 62176054 and the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province under Grant GXXT-2020-015. The authors would like to thank the anonymous reviewers for their thoughtful comments and suggestions.
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China, 62176054, Haixian Wang, the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province, GXXT-2020–015, Haixian Wang
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Wei, M., Luo, N. et al. Euler common spatial patterns for EEG classification. Med Biol Eng Comput 60, 753–767 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02488-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02488-7