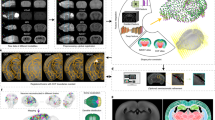
Abstract
An important step in brain image analysis is to divide specific brain regions by matching brain slices to standard brain reference atlases, and perform statistical analysis on the labeled neurons in each brain region. Taking mouse fluorescently labeled brain slices as an example, due to the noise and distortion introduced during the preparation of brain slices, and the modal differences with standard brain atlas, the brain slices cannot directly establish an accurate one-to-one correspondence with the brain atlas, which in turn affects the accuracy of the number of labeled neurons in each brain region. This paper introduces the idea of image representation, uses neural networks to realize the registration of different modal mouse brain slices and brain atlas, completes the regional localization of the brain slices, and uses threshold segmentation to detect and count the labeled neurons in each brain region. The method proposed in this paper can effectively solve the problem of large deviation of neurons count caused by the inaccurate division of brain regions in large deformed brain slices, and can automatically realize accurate count of labeled neurons in each brain region of brain slices.
Graphical abstract

The whole framework of method for counting labeled neurons in mouse brain regions based on image representation and registration.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alom MZ, Taha TM, Yakopcic C, Westberg S, Asari VK (2018) The History Began from AlexNet: A Comprehensive Survey on Deep Learning Approaches.
Ambinder EP (2005) A history of the shift toward full computerization of medicine. J Oncol Pract 1(2):54–56. https://doi.org/10.1200/jop.1.2.54
Avants BB, Epstein CL, Grossman M, Gee JC (2008) Symmetric diffeomorphic image registration with cross-correlation: evaluating automated labeling of elderly and neurodegenerative brain. Med Image Anal 12(1):26–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2007.06.004
Dalca AV, Balakrishnan G, Guttag J, Sabuncu MR (2018) Unsupervised Learning for Fast Probabilistic Diffeomorphic Registration. In A. F. Frangi, J. A. Schnabel, C. Davatzikos, C. AlberolaLopez, & G. Fichtinger (Eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention - Miccai 2018, Pt I (Vol. 11070, pp. 729-738). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00928-1_82
Dalca AV, Balakrishnan G, Guttag J, Sabuncu MR (2019) Unsupervised learning of probabilistic diffeomorphic registration for images and surfaces. Med Image Anal 57:226–236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2019.07.006
Fu Y, Lei Y, Wang T, Curran WJ, Liu T, Yang X (2020) Deep learning in medical image registration: a review. Phys Med Biol 65(20):Article 20tr01. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/ab843e
Haskins G, Kruger U, Yan P (2020) Deep learning in medical image registration: a survey. Mach Vis Appl 31(1):Article 8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00138-020-01060-x
Heinrich MP, Jenkinson M, Bhushan M, Matin T, Gleeson FV, Brady SM, Schnabel JA (2012) MIND: modality independent neighbourhood descriptor for multi-modal deformable registration. Med Image Anal 16(7):1423–1435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2012.05.008
Hu Y, Modat M, Gibson E, Ghavami N, Bonmati E, Moore CM, Emberton M, Noble JA, Barratt DC, Vercauteren T, Ieee (2018) Label-driven weakly-supervised learning for multimodal deformable image registration. In 2018 IEEE 15th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (pp. 1070-1074). <Go to ISI>://WOS: 000455045600245
Jia F, Zhu X, Xu F (2016) A single adaptive point mutation in Japanese encephalitis virus capsid is sufficient to render the virus as a stable vector for gene delivery. Virology 490:109–118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2016.01.001
Kaiming H, Xiangyu Z, Shaoqing R, Jian S (2016) Deep residual learning for image recognition. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), 770-778. 10.1109/cvpr.2016.90
Maes F, Collignon A, Vandermeulen D, Marchal G, Suetens P (1997) Multimodality image registration by maximization of mutual information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 16(2):187–198. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.563664
Mok TCW, Chung ACS (2020) Large Deformation Diffeomorphic Image Registration with Laplacian Pyramid Networks. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-59716-0_21
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(6):1137–1149. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2016.2577031
Renier N, Adams EL, Kirst C, Wu Z, Azevedo R, Kohl J, Autry AE, Kadiri L, Venkataraju KU, Zhou Y, Wang VX, Tang CY, Olsen O, Dulac C, Osten P, Tessier-Lavigne M (2016) Mapping of brain activity by automated volume analysis of immediate early genes. Cell 165(7):1789–1802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.007
Roche A, Pennec X, Malandain G, Ayache N (2001) Rigid registration of 3-D ultrasound with MR images: a new approach combining intensity and gradient information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(10):1038–1049. https://doi.org/10.1109/42.959301
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In N. Navab, J. Hornegger, W. M. Wells, & A. F. Frangi (Eds.), Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Pt Iii (Vol. 9351, pp. 234-241). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28
Shen Q, Xiao G, Zheng Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Zhu X, Jia F, Su P, Nie B, Xu F, Zhang B (2019) ARMBIS: accurate and robust matching of brain image sequences from multiple modal imaging techniques. Bioinformatics 35(24):5281–5289. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz404
Viola P, Wells WM III (1995). Alignment by maximization of mutual information. 10.1109/iccv.1995.466930
Wachinger C, Navab N (2012) Entropy and Laplacian images: structural representations for multi-modal registration. Med Image Anal 16(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2011.03.001
Wein W, Brunke S, Khamene A, Callstrom MR, Navab N (2008) Automatic CT-ultrasound registration for diagnostic imaging and image-guided intervention. Med Image Anal 12(5):577–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2008.06.006
Yao R, Ochoa M, Intes X, Yan P, IEEE (2018 2018 Apr 04-07). Deep Compressive Macroscopic Fluorescence Lifetime Imaging. IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging [2018 IEEE 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (isbi 2018)]. 15th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Washington, DC
Zhang Z, Sejdic E (2019) Radiological images and machine learning: Trends, perspectives, and prospects. Comput Biol Med 108:354–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.02.017
Zhang Z, Jin S, Zhu X, Jia F, Wang H, Liu Q, He X, Xu F (2014) Advancement in neurotropic virus-mediated trans-synaptic neural circuit tracing. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences 26(6):634–644. https://doi.org/10.13376/j.cbls/2014089
Zhou Z, Siddiquee MMR, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2018) UNet++: A Nested U-Net Architecture for Medical Image Segmentation. Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support : 4th International Workshop, DLMIA 2018, and 8th International Workshop, ML-CDS 2018, held in conjunction with MICCAI 2018, Granada, Spain, S... 11045, 3-11. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00889-5_1
Zhu X, He X, Liu Y, Wen P, Wang L, Zhang Z, Xu F (2018) A convenient semi-automatic method for analyzing brain sections: registration, segmentation and cell counting. Chinese Journal of Magnetic Resonance, 35(2), 133-140, Article 1000-4556(2018)35:2<133:Yzjydn> 2.0.Tx;2-d. <Go to ISI>://CSCD:6255585
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) General Program, grant number 61807031.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Niu, K., Chen, L. et al. Method for counting labeled neurons in mouse brain regions based on image representation and registration. Med Biol Eng Comput 60, 487–500 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02495-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-021-02495-8