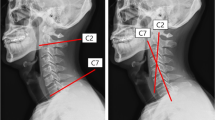
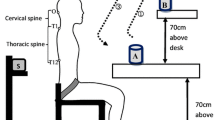
Abstract
The purposes of this study were to (1) examine the effects of different cervicothoracic postures on the stiffness of trapezius muscles and (2) compare the stiffness of the dominant and non-dominant trapezius muscles. Twenty-one healthy participants joined in this project. After maintaining different cervicothoracic postures for 2 min, MyotonPRO was used to measure the stiffness of the trapezius. The results showed that (1) the stiffness of trapezius muscles was significantly affected by different cervicothoracic postures. With the increase of neck flexion angle, the stiffness of the trapezius muscles increased (p < 0.05). The muscle stiffness of upper back relaxed was higher than that of upper back upright (p < 0.05). (2) The trapezius muscles on the non-dominant side were stiffer than that on the dominant side (p < 0.05). Poor cervicothoracic postures will increase the stiffness of upper, middle and lower trapezius muscles. Keeping the neck and upper back upright will keep the muscle stiffness at a low level, so as to reduce the occurrence of neck and shoulder fatigue and pain.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tas S, Korkusuz F, Erden Z (2018) Neck muscle stiffness in participants with and without chronic neck pain: a shear-wave elastography study. J Manipulative Physiol Ther 41(7):580–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmpt.2018.01.007
Namwongsa S, Puntumetakul R, Neubert MS, Boucaut R (2018) Factors associated with neck disorders among university student smartphone users. Work 61(3):367–378. https://doi.org/10.3233/WOR-182819
Ning X, Huang Y, Hu B, Nimbarte AD (2015) Neck kinematics and muscle activity during mobile device operations. Int J Ind Ergonom 48:10–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ergon.2015.03.003
Hansraj KK (2014) Assessment of stresses in the cervical spine caused by posture and position of the head. Surg Technol Int 25:277–279
Stephenson ML, Ostrander AG, Norasi H, Dorneich MC (2020) Shoulder muscular fatigue from static posture concurrently reduces cognitive attentional resources. Hum Factors 62(4):589–602. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720819852509
Kim S, Koo S (2016) Effect of duration of smartphone use on muscle fatigue and pain caused by forward head posture in adults. J Phys Ther Sci 28(6):1669–1672. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.1669
Kocur P, Lochynski D (2020) Female office workers with moderate neck pain have increased anterior positioning of the cervical spine and stiffness of upper trapezius myofascial tissue in sitting posture: response to letter to editor. PM R 12(10):1061. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmrj.12358
Yu M, Silvestre C, Mouton T et al (2013) Analysis of the cervical spine sagittal alignment in young idiopathic scoliosis: a morphological classification of 120 cases. Eur Spine J 22(11):2372–2381. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-013-2753-1
Dolan KJ, Green A (2006) Lumbar spine reposition sense: the effect of a ‘slouched’ posture. Manual Ther 11(3):202–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2006.03.003
Gaffney BM, Maluf KS, Curran-Everett D, Davidson BS (2014) Associations between cervical and scapular posture and the spatial distribution of trapezius muscle activity. J Electromyogr Kines 24(4):542–549. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelekin.2014.04.008
Eitivipart AC, Viriyarojanakul S, Redhead L (2019) Musculoskeletal disorder and pain associated with smartphone use: a systematic review of biomechanical evidence. Hong Kong Physiother J 38(02):77–90. https://doi.org/10.1142/S1013702518300010
Alsalameh A, Harisi M, Alduayji M, Almutham A, Mahmood F (2019) Evaluating the relationship between smartphone addiction/overuse and musculoskeletal pain among medical students at Qassim University. J Fam Med Prim Care 8(9):2953. https://doi.org/10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_665_19
Zhang J, Yu J, Liu C, Tang C, Zhang Z (2019) Modulation in elastic properties of upper trapezius with varying neck angle. Appl Bionics Biomech 2019:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6048562
Namwongsa S, Puntumetakul R, Neubert MS, Boucaut R (2019) Effect of neck flexion angles on neck muscle activity among smartphone users with and without neck pain. Ergonomics 62(12):1524–1533. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2019.1661525
Betsch M, Kalbhen K, Michalik R et al (2021) The influence of smartphone use on spinal posture – a laboratory study. Gait Posture 85:298–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2021.02.018
Malmström E, Olsson J, Baldetorp J, Fransson P (2015) A slouched body posture decreases arm mobility and changes muscle recruitment in the neck and shoulder region. Eur J Appl Physiol 115(12):2491–2503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3257-y
Kisilewicz A, Janusiak M, Szafraniec R et al (2018) Changes in muscle stiffness of the trapezius muscle after application of ischemic compression into myofascial trigger points in professional basketball players. J Hum Kinet 64(1):35–45. https://doi.org/10.2478/hukin-2018-0043
Jang H, Hughes LC, Oh D, Kim S (2019) Effects of corrective exercise for thoracic hyperkyphosis on posture, balance, and well-being in older women: a double-blind, group-matched design. J Geriatr Phys Ther 42(3):E17–E27. https://doi.org/10.1519/JPT.0000000000000146
Faramarzi KSY, Ghani ZHN (2020) Validity and reliability of smartphone-based Goniometer-Pro app for measuring the thoracic kyphosis. Musculoskelet Sci Pract 49:102216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msksp.2020.102216
Pourahmadi MR, Bagheri R, Taghipour M et al (2018) A new iPhone application for measuring active craniocervical range of motion in patients with non-specific neck pain: a reliability and validity study. Spine J 18(3):447–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spinee.2017.08.229
Choi J, Jung M, Yoo K (2016) An analysis of the activity and muscle fatigue of the muscles around the neck under the three most frequent postures while using a smartphone. J Phys Ther Sci 28(5):1660–1664. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.28.1660
Kozinc Ž, Šarabon N (2020) Shear-wave elastography for assessment of trapezius muscle stiffness: Reliability and association with low-level muscle activity. PLoS ONE 15(6):e0234359. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0234359
Lee ST, Moon J, Lee SH et al (2016) Changes in activation of serratus anterior, trapezius and Latissimus dorsi with slouched posture. Ann Rehabil Med 40(2):318. https://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2016.40.2.318
Schleip R, Naylor IL, Ursu D et al (2006) Passive muscle stiffness may be influenced by active contractility of intramuscular connective tissue. Med Hypotheses 66(1):66–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2005.08.025
Villanueva MBG, Jonai H, Sotoyama M et al (1997) Sitting posture and neck and shoulder muscle activities at different screen height settings of the visual display terminal. Ind Health 35(3):330–336. https://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.35.330
Sawada T, Okawara H, Nakashima D et al (2020) Reliability of trapezius muscle hardness measurement: a comparison between portable muscle hardness meter and ultrasound strain elastography. Sensors-Basel 20(24):7200. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20247200
Lee S, Choi Y, Kim J (2017) Effects of the cervical flexion angle during smartphone use on muscle fatigue and pain in the cervical erector spinae and upper trapezius in normal adults in their 20s. J Phys Ther Sci 29(5):921–923. https://doi.org/10.1589/jpts.29.921
Tomita Y, Suzuki Y, Tanaka Y et al (2021) Effects of sitting posture and jaw clenching on neck and trunk muscle activities during typing. J Oral Rehabil 48(5):568–574. https://doi.org/10.1111/joor.13152
Caneiro JP, O’Sullivan P, Burnett A et al (2010) The influence of different sitting postures on head/neck posture and muscle activity. Manual Ther 15(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2009.06.002
Imagama S, Hasegawa Y, Wakao N et al (2014) Impact of spinal alignment and back muscle strength on shoulder range of motion in middle-aged and elderly people in a prospective cohort study. Eur Spine J 23(7):1414–1419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00586-014-3251-9
Yoon W, Choi S, Han H, Shin G (2021) Neck muscular load when using a smartphone while sitting, standing, and walking. Hum Factors 63(5):868–879. https://doi.org/10.1177/0018720820904237
Escamilla RF, Yamashiro K, Paulos L, Andrews JR (2009) Shoulder muscle activity and function in common shoulder rehabilitation exercises. Sports Med 39(8):663–685. https://doi.org/10.2165/00007256-200939080-00004
Yan B, Lu X, Qiu Q, Nie G, Huang Y (2020) Predicting adolescent idiopathic scoliosis among Chinese children and adolescents. Biomed Res Int 2020:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1784360
Kleine BU, Schumann NP, Bradl I, Grieshaber R, Scholle HC (1999) Surface EMG of shoulder and back muscles and posture analysis in secretaries typing at visual display units. Int Arch Occ Env Hea 72(6):387–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200050390
Seghers J, Jochem A, Spaepen A (2010) Posture, muscle activity and muscle fatigue in prolonged VDT work at different screen height settings. Ergonomics 46(7):714–730. https://doi.org/10.1080/0014013031000090107
Farina D, Kallenberg LAC, Merletti R, Hermens HJ (2003) Effect of side dominance on myoelectric manifestations of muscle fatigue in the human upper trapezius muscle. Eur J Appl Physiol 90(5–6):480–488. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-003-0905-4
Elert JE, Rantapää-dahlqvist SB, Henriksson-larsén K, Lorentzon R, Gerdlé BUC (2009) Muscle performance, electromyography and fibre type composition in fibromyalgia and work-related myalgia. Scand J Rheumatol 21(1):28–34. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009749209095059
Kadi F, Ahlgren C, Waling K, Sundelin G, Thornell LE (2000) The effects of different training programs on the trapezius muscle of women with work-related neck and shoulder myalgia. Acta Neuropathol 100(3):253–258. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004019900174
Mannion AF, Meier M, Grob D, Müntener M (1998) Paraspinal muscle fibre type alterations associated with scoliosis: an old problem revisited with new evidence. Eur Spine J 7(4):289–293. https://doi.org/10.1007/s005860050077
Liu Y, Pan A, Hai Y et al (2019) Asymmetric biomechanical characteristics of the paravertebral muscle in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Clin Biomech 65:81–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2019.03.013
Horne JP, Flannery R, Usman S (2014) Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician 89(3):193–198
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Prof. Chunlong Liu and Prof. Zheng Zhang for technical support and review of this manuscript. We also thank Qiming Zhang for his help in providing suggestions for this paper. We are grateful to the students of the Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine for participating in the study as subjects.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, H., Yu, S., Hao, M. et al. Effects of cervicothoracic postures on the stiffness of trapezius muscles. Med Biol Eng Comput 60, 3009–3017 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-022-02655-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-022-02655-4