Abstract
Microwave imaging is one of the rapidly developing frontier disciplines in the field of modern medical imaging. The development of microwave imaging algorithms for reconstructing stroke images is discussed in this paper. Compared with traditional stroke detection and diagnosis techniques, microwave imaging has the advantages of low price and no ionizing radiation hazards. The research hotspots of microwave imaging algorithms in the field of stroke are mainly reflected in the design and improvement of microwave tomography, radar imaging, and deep learning imaging. However, the current research lacks the analysis and combing of microwave imaging algorithms. In this paper, the development of common microwave imaging algorithms is reviewed. The concept, research status, current research hotspots and difficulties, and future development trends of microwave imaging algorithms are systematically expounded.
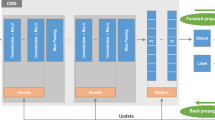
Graphical Abstract
The microwave antenna is used to collect scattered signals, and a series of microwave imaging algorithms are used to reconstruct the stroke image. The classification diagram and flow chart of the algorithms are shown in this Figure. (The classification diagram and flow chart are based on the microwave imaging algorithms.)






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lindsay MP, Norrving B, Sacco RL et al (2019) World Stroke Organization (WSO): global stroke fact sheet 2019. Int J Stroke 14(8):806–817
Katan M, Luft A (2018) Global burden of stroke. Semin Neurol 38(2):208–211
Murphy SJ, Werring DJ (2020) Stroke: causes and clinical features. Medicine (Abingdon) 48(9):561–566
Benjamin EJ, Muntner P, Alonso A et al (2019) Heart disease and stroke statistics-2019 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 139(10):e56–e528
Elameer M, Price CI, (2020) Neuroimaging methods for acute stroke diagnosis and treatment. In: Peplow, P.V., Martinez, B., Dambinova, S.A. (eds) Stroke biomarkers. Neuromethods 147: 297–333
Ramamurthy K, Menaka R, Johnson A et al (2020) Neuroimaging and deep learning for brain stroke detection — a review of recent advancements and future prospects. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 197:105728
Orel SG, Schnall MD (2001) MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology 220(1):13–30
Walsh KB (2019) Non-invasive sensor technology for prehospital stroke diagnosis: current status and future directions. Int J Stroke 14(6):592–602
Bevacqua MT, Bellizzi GG, Crocco L, et al. (2019) A method for quantitative imaging of electrical properties of human tissues from only amplitude electromagnetic data. Inverse Problems 35
Semenov SY, Svenson RH, Posukh VG et al (2002) Dielectrical spectroscopy of canine myocardium during acute ischemia and hypoxia at frequency spectrum from 100 kHz to 6 GHz. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21(6):703–707
Hopfer M, Planas R, Hamidipour A et al (2017) Electromagnetic tomography for detection, differentiation, and monitoring of brain stroke: a virtual data and human head phantom study. IEEE Antennas Propag Mag 59(5):86–97
Pagliari DJ, Pulimeno A, Vacca M, et al. (2015) A low-cost, fast, and accurate microwave imaging system for breast cancer detection. 2015 IEEE Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference (BioCAS)
Eesuola A, Chen Y, Tian GY (2011) Novel ultra-wideband directional antennas for microwave breast cancer detection. In: 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), 90–93
Qureshi AM, Mustansar Z (2017) Levels of detail analysis of microwave scattering from human head models for brain stroke detection. PeerJ 21(5):e4061
Mobashsher AT, Bialkowski KS, Abbosh AM (2016) Design of compact cross-fed three-dimensional slot-loaded antenna and its application in wideband head imaging system. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 15:1856–1860
Chew KM, Yong CY, Sudirman R, et al. (2018) Bio-signal processing and 2D representation for brain tumor detection using microwave signal analysis. 2018 IEEE Symposium on Computer Applications & Industrial Electronics (ISCAIE), 303–309
Jamlos MA, Mustafa WA, (2019) Improved confocal microwave imaging algorithm for tumor detection
Chaudhary SS, Mishra RK, Swarup A et al (1984) Dielectric properties of normal & malignant human breast tissues at radiowave & microwave frequencies. Indian J Biochem Biophys 21(1):76–79
Halter RJ, Zhou T, Meaney PM et al (2009) The correlation of in vivo and ex vivo tissue dielectric properties to validate electromagnetic breast imaging: initial clinical experience. Physiol Meas 30:S121–S136
Bindu GN, Abraham S, Lonappan A et al (2006) Active microwave imaging for breast cancer detection. Progress In Electromagnetics Res 58:149–169
Aldhaeebi MA, Alzoubi K, Almoneef TS et al (2020) Review of microwaves techniques for breast cancer detection. Sensors (Basel) 20(8):E2390
Mouty S, Bocquet B, Ringot R, et al. (2000) Microwave radiometric imaging (MWI) for the characterisation of breast tumours. Eur Phys J-appl Phys 10:73–78
Wang X, Xin H, Bauer D, et al. (2011) Microwave induced thermal acoustic imaging modeling for potential breast cancer detection. In: 2011 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation (APSURSI), 722–725
Pichot C, Jofre L, Peronnet G et al (1985) Active microwave imaging of inhomogeneous bodies. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat 33:416–425
Meaney PM, Fanning MW, Li D et al (2000) A clinical prototype for active microwave imaging of the breast. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 48:1841–1853
Yago Ruiz Á, Cavagnaro M, Crocco L (2023) An effective framework for deep-learning-enhanced quantitative microwave imaging and its potential for medical applications. Sensors 23(2):643
Semenov SY, Corfield DR (2008) Microwave tomography for brain imaging: feasibility assessment for stroke detection. Int J Antennas Propagation 2008:1–8
Fear EC, Li X, Hagness SC et al (2002) Confocal microwave imaging for breast cancer detection: localization of tumors in three dimensions. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 49(8):812–822
Ambrosanio M, Franceschini S, Baselice F, et al. (2020). Machine learning for microwave imaging. 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 1–4
Chew W (1998) Imaging and inverse problems in electromagnetics. Advances in computational electrodynamics: the finite-difference time-domain method; Artech House: Norwood. MA, USA, pp 653–702
Semenov SY, Seiser B, Stoegmann E, et al. (2014). Electromagnetic tomography for brain imaging: from virtual to human brain. 2014 IEEE Conference on Antenna Measurements & Applications (CAMA), 1–4
Mackay DJC. (1998). Introduction to Monte Carlo methods. In: Jordan, M.I. (eds) Learning in graphical models. NATO ASI Series, Springer, Dordrecht 89:175–204
Ambrosanio M, Franceschini S, Pascazio V, et al. (2021). Microwave breast imaging via neural networks for almost real-time applications
Holland JH (1975) Adaptation in natural and artificial systems 6(2):126–137
Hwang CR (1988) Simulated annealing: theory and applications. Acta Appl Math 12:108–111
Meza JC. (2010) Steepest descent. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics
Bisio I, Fedeli A, Lavagetto F et al (2018) A numerical study concerning brain stroke detection by microwave imaging systems. Multimed Tools Appl 77(8):9341–9363
Abubakar A, van den Berg P, Kooij B (2000) A conjugate gradient contrast source technique for 3D profile inversion. IEICE Trans Electron 83(12):1864–1874
Ireland D, Bialkowski K, Abbosh A (2013) Microwave imaging for brain stroke detection using Born iterative method. IET Microwaves Antennas Propag 7(11):909–915
Gilmore C, Abubakar A, Hu W et al (2009) Microwave biomedical data inversion using the finite-difference contrast source inversion method. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 57(5):1528–1538
Ireland D, Bialkowski M (2010) Feasibility study on microwave stroke detection using a realistic phantom and the FDTD method. Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference Proceedings, APMC :1360–1363
Zakaria A, Gilmore C, LoVetri J (2010) Finite-element contrast source inversion method for microwave imaging. Inverse Prob 26:115010–115021
Scapaticci R, Tobon J, Bellizzi G et al (2018) Design and numerical characterization of a low-complexity microwave device for brain stroke monitoring. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 66(12):7328–7338
Merunka I, Massa A, Vrba D et al (2019) Microwave tomography system for methodical testing of human brain stroke detection approaches. Int J Antennas Propag 2019:e4074862
Coli VL, Tournier PH, Dolean V et al (2019) Detection of simulated brain strokes using microwave tomography. IEEE J Electromagn RF Microw Med Biol 3(4):254–260
Estatico C, Pastorino M, Randazzo A (2012) A novel microwave imaging approach based on regularization in L(p) Banach spaces. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 60:3373–3381
Bisio I, Estatico C, Fedeli A et al (2018) Brain stroke microwave imaging by means of a Newton-conjugate-gradient method in $L^{p}$ Banach spaces. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techn 66(8):3668–3682
Estatico C, Fedeli A, Pastorino M et al (2015) A multifrequency inexact-Newton method in $L^p$ Banach spaces for buried objects detection. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 63(9):4198–4204
Estatico C, Fedeli A, Pastorino M et al (2018) Quantitative microwave imaging method in Lebesgue spaces with nonconstant exponents. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat 66(12):7282–7294
Estatico C, Fedeli A, Pastorino M et al (2020) A phaseless microwave imaging approach based on a Lebesgue-space inversion algorithm. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat 68(12):8091–8103
Bisio I, Estatico C, Fedeli A et al (2020) Variable-exponent Lebesgue-space inversion for brain stroke microwave imaging. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techn 68(5):1882–1895
Fedeli A, Randazzo A, Sciarrone A et al (2020) A microwave diagnostic technique for early-stage brain stroke characterization. 2020 XXXIIIrd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science. IEEE, Rome, pp 1–3
Fedeli A, Estatico C, Pastorino M et al (2020) Microwave detection of brain injuries by means of a hybrid imaging method. IEEE Open J Antennas and Propag 1:513–523
Fedeli A, Schenone V, Randazzo A et al (2021) Nonlinear S-parameters inversion for stroke imaging. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techn 69(3):1760–1771
Bisio I, Fedeli A, Garibotto C et al (2021) Two ways for early detection of a stroke through a wearable smart helmet: signal processing vs. electromagnetism. IEEE Wireless Commun 28(3):22–27
Afsari A, Abbosh AM, Rahmat-Samii Y (2019) Modified born iterative method in medical electromagnetic tomography using magnetic field fluctuation contrast source operator. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 67(1):454–463
Vasquez J, Scapaticci R, Turvani G et al (2019) Design and experimental assessment of a 2D microwave imaging system for brain stroke monitoring. Int J Antennas Propag 2019:e8065036
Vasquez J, Scapaticci R, Turvani G et al (2020) A prototype microwave system for 3D brain stroke imaging. Sensors 20(9):2607
Duarte D O R, Vasquez J A T, Vipiana F (2020) Electromagnetic virtual prototyping of a realistic 3-D microwave scanner for brain stroke imaging. In: 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP) 1–4
Tesarik J, Vrba J (2020) Validation of multilevel 24-port microwave imaging system for brain stroke monitoring on synthetic numerical data. In: 2020 14th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP), 1–5
Ye X, Chen X (2017) Subspace-based distorted-born iterative method for solving inverse scattering problems. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 65(12):7224–7232
Karadima O, Rahman M, Sotiriou I et al (2020) Experimental validation of microwave tomography with the DBIM-TwIST algorithm for brain stroke detection and classification. Sensors 20(3):840
Mariano V, Vasquez J, Scapaticci R, et al. (2020) Comparison of reconstruction algorithms for brain stroke microwave imaging 1–3
Ghavami N, Razzicchia E, Karadima O et al (2021) The use of metasurfaces to enhance microwave imaging: experimental validation for tomographic and radar-based algorithms. IEEE Open J Antennas Propag 3:89–100
Karadima O, Ghavami N, Sotiriou I, et al. (2020) Performance assessment of microwave tomography and radar imaging using an anthropomorphic brain phantom. In: 2020 XXXIIIrd General Assembly and Scientific Symposium of the International Union of Radio Science, Rome.
Ghavami N, Sotiriou I, Kosmas P (2019) Preliminary experimental validation of radar imaging for stroke detection with phantoms. 2019 Photonics & Electromagnetics Research Symposium - Fall (PIERS - Fall)
Karadima O, Lu P, Sotiriou I et al (2022) Experimental validation of the DBIM-TwIST algorithm for brain stroke detection and differentiation using a multi-layered anatomically complex head phantom. IEEE Open J Antennas Propag 3:274–286
Lu P, Kosmas P (2022) Three-dimensional microwave head imaging with GPU-based FDTD and the DBIM method. Sensors 22:2691
Guo L, Khosravi-Farsani M, Stancombe A et al (2022) Adaptive clustering distorted born iterative method for microwave brain tomography with stroke detection and classification. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 69(4):1512–1523
Semenov S, Seiser B, Stoegmann E, et al. (2014) Electromagnetic tomography for brain imaging: from virtual to human brain. In: 2014 IEEE Conference on Antenna Measurements & Applications (CAMA), 1–4
Tournier PH, Bonazzoli M, Dolean V et al (2017) Numerical modeling and high-speed parallel computing: new perspectives on tomographic microwave imaging for brain stroke detection and monitoring. IEEE Antennas Propag Mag 59(5):98–110
Henriksson T, Sahebdivan S, Planas R, et al. (2022) Human brain imaging by electromagnetic tomography: a mobile brain scanner for clinical settings. In: 2022 16th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP) 1–5
Elahi MA, O’Loughlin D, Lavoie BR et al (2018) Evaluation of image reconstruction algorithms for confocal microwave imaging: application to patient data. Sensors (Basel) 18(6):1678
Zamani A, Abbosh A, Mobashsher A (2016) Fast frequency-based multistatic microwave imaging algorithm with application to brain injury detection. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 64:1–10
Ricci E , Domenico S D , Cianca E , et al. (2015) Artifact removal algorithms for stroke detection using a multistatic MIST beamforming algorithm. In: 2015 37th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC) 1930–1933
Klemm M, Craddock IJ, Leendertz JA, et al. (2008) Improved delay-and-sum beamforming algorithm for breast cancer detection. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation 761402–1–761402–9
Xie Y, Guo B, Xu L et al (2006) Multistatic adaptive microwave imaging for early breast cancer detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 53(8):1647–1657
Entezami M, Faraji-Dana R, Dehmollaian M (2017) Design and implementation of a head imaging system for trauma detection. In: 2017 Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), 1983–1986
Ireland D, Bialkowski M (2011) Microwave head imaging for stroke detection. Progress In Electromagn Res M 21:163–175
Ricci E, Colucciello A, Domenico SD, et al. (2015) Modified RAR and PLSR-based artifact removal for stroke detection in UWB radar imaging
Hagness S, Taflove A, Bridges J (1999) Three-dimensional FDTD analysis of a pulsed microwave confocal system for breast cancer detection: design of an antenna-array element. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 47(5):783–791
Xu L, Hagness S (2001) A confocal microwave imaging algorithm for breast cancer detection. Microwave Wireless Components Lett IEEE 11(3):130–132
Mohammed B J, Abbosh A M, Ireland D. Circular antenna array for brain imaging systems. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation
Mohammed BJ, Abbosh AM, Mustafa S et al (2014) Microwave system for head imaging. IEEE Trans Instrum Meas 63(1):117–123
Mustafa S, Mohammed B, Abbosh A (2013) Novel preprocessing techniques for accurate microwave imaging of human brain. IEEE Antennas Wirel Propag Lett 12:460–463
Mobashsher AT, Abbosh AM, Wang Y (2014) Microwave system to detect traumatic brain injuries using compact unidirectional antenna and wideband transceiver with verification on realistic head phantom. IEEE Trans Microw Theory Tech 62(9):1826–1836
Mohammed B, Bialkowski K, Mustafa S et al (2015) Investigation of noise effect on image quality in microwave head imaging systems. Microwaves, Antennas & Propagation, IET 9(3):200–205
Ricci E, Cianca E, Rossi T et al (2016) (2016) Beamforming algorithms for UWB radar-based stroke detection: trade-off performance-complexity. J Commun Navig Sens Serv (CONASENSE) 1:11–28
Ricci E, Domenico SD, Cianca E et al (2017) PCA-based artifact removal algorithm for stroke detection using UWB radar imaging. Med Biol Eng Compu 55(6):909–921
Ricci E, Cianca E, Rossi T et al (2017) Performance evaluation of novel microwave imaging algorithms for stroke detection using an accurate 3D head model. Wireless Pers Commun 96(3):3317–3331
Saied I, Arslan T (2019) Microwave imaging algorithm for detecting brain disorders. In: 2019 29th International Conference Radioelektronika (RADIOELEKTRONIKA), 1–5
Sohani B, Khalesi B, Ghavami N et al (2020) Detection of haemorrhagic stroke in simulation and realistic 3-D human head phantom using microwave imaging. Biomed Signal Process Control 61:102001
Sohani B, Puttock J, Khalesi B et al (2020) Developing artefact removal algorithms to process data from a microwave imaging device for haemorrhagic stroke detection [J]. Sensors 20(19):5545
Lucas A, Iliadis M, Molina R et al (2018) Using deep neural networks for inverse problems in imaging: beyond analytical methods. IEEE Signal Process Mag 35(1):20–36
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Support-vector networks. Machine Learn 20:273–297
Fhager A, Persson M (2011) A microwave measurement system for stroke detection. In: 2011 Loughborough Antennas Propagation Conference, 1–2
Persson M, Fhager A, Trefná HD et al (2014) Microwave-based stroke diagnosis making global prehospital thrombolytic treatment possible. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 61(11):2806–2817
Guo L, Abbosh AM (2015) Microwave imaging of nonsparse domains using born iterative method with wavelet transform and block sparse Bayesian learning. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 63(11):4877–4888
Guo L, Abbosh A (2018) Stroke localization and classification using microwave tomography with k-means clustering and support vector machine. Bioelectromagnetics 39(4):312–324
Qureshi A, Mustansar Z, Mustafa S (2018) Finite-element analysis of microwave scattering from a three-dimensional human head model for brain stroke detection. Royal Society Open Science 5(7):180319
Wu Y, Zhu M, Li D, et al. (2016) Brain stroke localization by using microwave-based signal classification. 2016 International Conference on Electromagnetics in Advanced Applications (ICEAA), 828–831
Fhager A, Candefjord S, Persson M (2018) FDTD based simulation study of a classification based hemorrhagic stroke detector. In: 12th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation (EuCAP 2018), 1–3
Zhu G, Bialkowski A, Guo L et al (2021) Stroke classification in simulated electromagnetic imaging using graph approaches [J]. IEEE J Electromagn RF Microwaves Med Biol 5(1):46–53
Al-Saffar A, Bialkowski A, Baktashmotlagh M et al (2021) Closing the gap of simulation to reality in electromagnetic imaging of brain strokes via deep neural networks. IEEE Trans Comput Imaging 7:13–21
Borgwardt KM, Gretton A, Rasch MJ et al (2006) Integrating structured biological data by kernel maximum mean discrepancy. Bioinformatics 22(14):e49–e57
Alon L, Dehkharghani S (2021) A stroke detection and discrimination framework using broadband microwave scattering on stochastic models with deep learning. Sci Rep 11(1):1–9
Al-Saffar A, Zamani A, Stancombe A et al (2022) Operational learning-based boundary estimation in electromagnetic medical imaging. IEEE Trans Antennas Propag 70(3):2234–2245
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Chen, L., Xiong, H. et al. Review of microwave imaging algorithms for stroke detection. Med Biol Eng Comput 61, 2497–2510 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02848-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02848-5