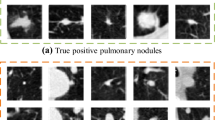
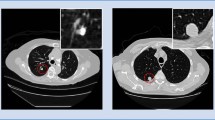
Abstract
With the advancement of artificial intelligence, CNNs have been successfully introduced into the discipline of medical data analyzing. Clinically, automatic pulmonary nodules detection remains an intractable issue since those nodules existing in the lung parenchyma or on the chest wall are tough to be visually distinguished from shadows, background noises, blood vessels, and bones. Thus, when making medical diagnosis, clinical doctors need to first pay attention to the intensity cue and contour characteristic of pulmonary nodules, so as to locate the specific spatial locations of nodules. To automate the detection process, we propose an efficient architecture of multi-task and dual-branch 3D convolution neural networks, called DBPNDNet, for automatic pulmonary nodule detection and segmentation. Among the dual-branch structure, one branch is designed for candidate region extraction of pulmonary nodule detection, while the other incorporated branch is exploited for lesion region semantic segmentation of pulmonary nodules. In addition, we develop a 3D attention weighted feature fusion module according to the doctor’s diagnosis perspective, so that the captured information obtained by the designed segmentation branch can further promote the effect of the adopted detection branch mutually. The experiment has been implemented and assessed on the commonly used dataset for medical image analysis to evaluate our designed framework. On average, our framework achieved a sensitivity of 91.33% false positives per CT scan and reached 97.14% sensitivity with 8 FPs per scan. The results of the experiments indicate that our framework outperforms other mainstream approaches.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [46].
References
Zhang J, Sun Y, Li G, Wang Y, Sun J, Li J (2022) Machine-learning-assisted shear strength prediction of reinforced concrete beams with and without stirrups. Eng Comput 38:1293–1307
Mai HT, Lieu QX, Kang J, Lee J (2022) A novel deep unsupervised learning-based framework for optimization of truss structures. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-022-01636-3
Lee SY, Park C-S, Park K, Lee HJ, Lee S (2022) A Physics-informed and data-driven deep learning approach for wave propagation and its scattering characteristics. Eng Comput. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-022-01640-7
Shoeibi A, Khodatars M, Alizadehsani R et al (2020) Automated detection and forecasting of covid- 19 using deep learning techniques: a review. 47(11):2533–2548. arXiv preprint arXiv:2007.10785
Ba AF, Huang H, Wang M, Ye X, Gu Z, Chen H, Cai X (2022) Levy-based antlion-inspired optimizers with orthogonal learning scheme. Eng Comput 38:397–418
Liu W, Dragomir A, Dumitru E, Christian S, Scott R et al (2016) Ssd: single shot multibox detector, in Eur. Conf. Comput. Vis. Springer, pp 21–37
Redmon J, Farhadi A (2017) Yolo9000: better, faster, stronger. In: IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recog, pp 7263–7271
Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A (2016) You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recog, pp 779–788
Dou Q, Chen H, Yu L, Qin J, Heng P-A (2016) Multilevel contextual 3-d cnns for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(7):1558–1567
Li Y, Fan Y (2020) Deepseed: 3d squeeze-and-excitation encoder-decoder convolutional neural networks for pulmonary nodule detection. IEEE Int Symp Biomed Imaging (ISBI) 2020:1866–1869
Yan X, Pang J, Qi H, Zhu Y, Bai C, Geng X, Liu M, Terzopoulos D, Ding X (2016) Classification of lung nodule malignancy risk on computed tomography images using convolutional neural network: a comparison between 2d and 3d strategies, in Asian Conf. Comput. Vis. Springer, pp 91–101
Tang H, Zhang C, Xie X (2019) Nodulenet: Decoupled false positive reduction for pulmonary nodule detection and segmentation, in International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, pp 266–274
Manickavasagam R, Selvan S, Selvan M (2022) CAD system for lung nodule detection using deep learning with CNN. Med Biol Eng Compu 60(1):221–228
Mahmood SA, Ahmed HA (2022) An improved CNN-based architecture for automatic lung nodule classification. Med Biol Eng Comput 60(7):1–10
Sherwani MK, Marzullo A, De Momi E, Calimeri F (2022) Lesion segmentation in lung CT scans using unsupervised adversarial learning. Med Biol Eng Comput 60(11):1–13
Yu N, Yang R, Huang M (2022) Deep common spatial pattern based motor imagery classification with improved objective function. Int J Netw Dyn Intell 1(1):73–84
Zhang Q, Zhou Y (2022) Recent advances in non-Gaussian stochastic systems control theory and its applications. Int J Netw Dyn Intell 1(1):111–119
Wang X, Sun Y, Ding D (2022) Adaptive dynamic programming for networked control systems under communication constraints: a survey of trends and techniques. Int J Netw Dyn Intell 1(1):85–98
Akhavanallaf A, Shiri I, Arabi H, Zaidi H (2020) Whole-body voxel-based internal dosimetry using deep learning. European J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 48:670–682
Arabi H, Akhavanallaf A et al (2021) The promise of artificial intelligence and deep learning in PET and SPECT imaging. Phys Med 83:122–137
Arabi H, Zaidi H (2021) Applications of artificial intelligence and deep learning in molecular imaging and radiotherapy. European J Hybrid Imaging 4(1):17
Shiri I, Arabi H, Geramifar P et al (2020) Deep-JASC: joint attenuation and scatter correction in whole-body 18 F-FDG PET using a deep residual network. European J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 47:2533–2548
Messay T, Hardie RC, Rogers SK (2010) A new computationally efficient cad system for pulmonary nodule detection in ct imagery. Med Image Anal 14(3):390–406
Duggan N, Bae E, Shen S, Hsu W, Bui A, Jones E, Glavin M, Vese L (2015) A technique for lung nodule candidate detection in ct using global minimization methods. In: Int. Worksh. Energy Minimization Methods in Comput. Vis. Pattern Recog. Springer, pp 478–491
Jacobs C, Rikxoort EM, Twellmann T et al (2014) Automatic detection of subsolid pulmonary nodules in thoracic computed tomography images. Med Image Anal 18(2):374–384
Fu C, Liu W, Ranga A, Tyagi A (2017) Dssd: deconvolutional single shot detector. arXiv preprint arXiv:1701.06659
Lin T, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection. Int Conf Comput Vis 2017:2980–2988
Setio A, Ciompi F, Litjens G, Gerke P, Jacobs C et al (2016) Pulmonary nodule detection in ct images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1160–1169
Liao F, Liang M, Li Z, Hu X, Song S (2019) Evaluate the malignancy of pulmonary nodules using the 3-d deep leaky noisy-or network. IEEE Tran Neural Netw Learn Syst 30(11):3484–3495
Luo X, Song T et al (2022) Scpm-net: an anchor-free 3d lung nodule detection network using sphere representation and center points matching. Med Image Anal 75:102287
Farhangi MM, Sahiner B, Petrick N, Pezehsk A (2021) Automatic lung nodule detection in thoracic CT scans using dilated slice-wise convolutions. Med Phys 48(7):3741–3751
Song T et al (2020) CPM-Net: A 3D center-points matching network for pulmonary nodule detection in CT scans. In: International Conference on MICCAI. Springer, vol 12266, pp 550–559
Zhou Z et al (2020) UNet++: redesigning skip connections to exploit multiscale features in image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(6):1856–1867
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi SA (2016) V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. Proceedings of 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), pp 565–571
Oktay O et al (2018) Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas. Comput Vision Pattern Recog 3
Kamal U et al (2020) Lung cancer tumor region segmentation using recurrent 3D-DenseUNet. MICCAI 2020 Thoracic Image Analysis (TIA) Workshop 2020, 12502:36–47
Liang X et al (2021) Incorporating the hybrid deformable model for improving the performance of abdominal CT segmentation via multi-scale feature fusion network. Med Image Anal 73:102156
Shi C et al (2021) Multi-slice low-rank tensor decomposition based multi-atlas segmentation: application to automatic pathological liver CT segmentation. Med Image Anal 73:102152
Jian MW, Wang J, Yu H, Wang GD, Meng XJ, Yang L, Dong JY, Yin YL (2021) Visual saliency detection by integrating spatial position prior of object with background cues. Exp Syst Appl 168:114219
Jian MW, Wang JJ, Yu H, Wang GG (2021) Integrating object proposal with attention networks for video saliency detection. Inf Sci 576:819–830
Jian MW, Wang J, Dong JY, Cui CR, Nie XS, Yin YL (2020) Saliency detection using multiple low-level priors and a propagation mechanism. Multimed Tools Appl 79(45):33465–33482
Lu XW, Jian MW, Wang X, Yu H, Dong JY, Lam KM (2020) Visual saliency detection via combining center prior and U-Net. Multimed Systs 28(5):1689–1698
Zhu W, Liu C, Fan W, Xie X (2018) Deeplung: deep 3d dual path nets for automated pulmonary nodule detection and classification. In: 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 673–681
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2015) Faster r-cnn: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(6):1137–1149
Mei J, Cheng MM, Xu G, Wan LR, Zhang H (2021) Sanet: a slice aware network for pulmonary nodule detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell pp 1–19
Armato SG, McLennan G et al (2011) The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on ct scans. Med Phys 38(2):915–931
Setio A et al (2017) Validation, comparison, and combination of algorithms for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules in computed tomography images: the luna16 challenge. Med Image Anal 42:1–13
Zuo W, Zhou F, He Y (2020) An embedded multi-branch 3d convolution neural network for false positive reduction in lung nodule detection. J Digit Imaging 33:(4)
Yuan H et al (2021) Pulmonary nodule detection using 3-d residual u-net oriented context-guided attention and multi-branch classification network. IEEE Access 99:1–1
Zheng S et al (2020) Automatic pulmonary nodule detection in ct scans using convolutional neural networks based on maximum intensity projection. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(5):797–805
Ozdemir O, Russell RL, Berlin AA (2020) A 3D probabilistic deep learning system for detection and diagnosis of lung cancer using low-dose CT scans. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(5):1419–1429
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (61976123, 61601427); Taishan Young Scholars Program of Shandong Province; and Key Development Program for Basic Research of Shandong Province (ZR2020ZD44).
Funding
National Natural Science Foundation of China,61976123,Muwei Jian
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Muwei Jian: writing—conceptualization, methodology, writing—review and editing, supervision; Haodong Jin: software, validation, software, visualization, methodology; Linsong Zhang: formal analysis, data curation; Benzheng Wei: validation, data curation, visualization; Hui Yu: supervision, writing—review and editing, methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Research involving Human Participants and/or Animals
The authors declared that they have no involving Human Participants and/or Animals to this work.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jian, M., Jin, H., Zhang, L. et al. DBPNDNet: dual-branch networks using 3DCNN toward pulmonary nodule detection. Med Biol Eng Comput 62, 563–573 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02957-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02957-1