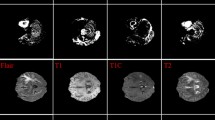
Abstract
Brain tumor segmentation is an important direction in medical image processing, and its main goal is to accurately mark the tumor part in brain MRI. This study proposes a brand new end-to-end model for brain tumor segmentation, which is a multi-scale deep residual convolutional neural network called mResU-Net. The semantic gap between the encoder and decoder is bridged by using skip connections in the U-Net structure. The residual structure is used to alleviate the vanishing gradient problem during training and ensure sufficient information in deep networks. On this basis, multi-scale convolution kernels are used to improve the segmentation accuracy of targets of different sizes. At the same time, we also integrate channel attention modules into the network to improve its accuracy. The proposed model has an average dice score of 0.9289, 0.9277, and 0.8965 for tumor core (TC), whole tumor (WT), and enhanced tumor (ET) on the BraTS 2021 dataset, respectively. Comparing the segmentation results of this method with existing techniques shows that mResU-Net can significantly improve the segmentation performance of brain tumor subregions.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets are provided by BraTS 2021 Challenge and are allowed for personal academic research. The specific link to the dataset is https://ipp.cbica.upenn.edu/.
References
Bakas S, Reyes M, Jakab A, Bauer S, Rempfler M, Crimi A et al (2018) Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS challenge. arXiv:1811.02629. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1811.02629
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg AC, Fei-Fei L (2015) ImageNet LargeScale Visual Recognition Challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision 115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y
Zeng T, Wu B, Ji S (2017) DeepEM3D, approaching human-level performance on 3D anisotropic EM image segmentation. Bioinformatics 33(16):2555–2562. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx188
Baid U et al (2021) The RSNA-ASNR-MICCAI BraTS 2021 benchmark on brain tumor segmentation and radio genomic classification. arXiv:2107.02314. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2107.02314
Menze BH, Jakab A, Bauer S, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Farahani K, Kirby J et al (2015) The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans Med Imaging 34(10):1993–2024. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2014.2377694
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J et al (2017) Advancing The Cancer Genome Atlas glioma MRI collections with ex-pert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci Data 4. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017.117
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J et al (2017) Segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-GBM collection. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2017.KLXWJJ1Q
Bakas S, Akbari H, Sotiras A, Bilello M, Rozycki M, Kirby J et al (2017) segmentation labels and radiomic features for the pre-operative scans of the TCGA-GBM collection. https://doi.org/10.7937/K9/TCIA.2017.GJQ7R0EF
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net, Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells WM, Frangi AF (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI2015. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 234–241
Myronenko A (2019) 3D MRI brain tumor segmentation using autoencoder regularization. In: Crimi A, Bakas S, Kuijf H, Keyvan F, Reyes M, van Walsum T (eds) Brain lesion, glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 311–320
Isensee F, Jaeger PF, Kohl SA, Petersen J, Maier-Hein K (2021) nnU-Net: a self-configuring method for deep learning-based biomedical image segmentation. Nature Methods 18(2):203–211. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41592-020-01008-z
Isensee F, Jäger PF, Full PM, Vollmuth P, Maier-Hein KH (2021) nnU-Net for brain tumor segmentation. In: Crimi A, Bakas S (eds) Brain lesion, glioma, multiple sclerosis, stroke and traumatic brain injuries. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 118–132
Razzak MI, Imran M, Xu G (2019) Efficient brain tumor segmentation with multiscale two-pathway-group conventional neural networks. IEEE J Biomed Heal Informatics 23(5):1911–1919. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2874033
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VF, Simpson JP, Kane AD, Menon DK, Rueckert D, Glocker B (2017) Efficient multiscale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 36(2):61–78
Oktay O, Schlemper J, Folgoc LL, Lee M, Heinrich M, Misawa K, Mori K, McDonagh S, Hammerla NY, Kainz B et al (2018) Attention u-net: learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv, arXiv:1804.03999
Wang W, Chen C, Ding M, Yu H, Zha S, Li J (2021) TransBTS: multimodal brain tumor segmentation using transformer. In: de Bruijne M et al (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2021. MICCAI 2021. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 12901. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-87193-2_11
Chen J, Lu Y, Yu Q, Luo X, Adeli E, Wang Y, Lu L, Yuille AL, Zhou Y (2021) TransUNet: transformers make strong encoders for medical image segmentation. arXiv:2102.04306. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2102.04306
Zhang Z, Liu Q, Wang Y (2018) Road extraction by deep residual u-net. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 15:749–753
Baid U, Talbar S, Rane S, Gupta S, Thakur MH, Moiyadi A, Sable N, Akolkar M, Mahajan A (2020) A novel approach for fully automatic intra-tumor segmentation with 3D U-Net architecture for gliomas. Front Comput Neurosci 14:1–11
Milletari F, Navab N, Ahmadi SA (2016) V-Net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In: 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV) pp 565-571. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/3DV.2016.79
Zhang J, Xie Y, Wang Y, Xia Y (2020) Inter-slice context residual learning for 3D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40:661–672
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: Ourselin S, Joskowicz L, Sabuncu M, Unal G, Wells W (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2016. MICCAI 2016. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 9901. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_49
Rehman MU, Cho S, Kim JH, Chong KT (2020) Bu-Net: brain tumor segmentation using modified U-Net architecture. Electronics (Switzerland) 9(12):1–12
Rehman MU, Cho S, Kim J, Chong KT (2021) BrainSegNet: brain tumor MR image segmentation via enhanced encoder–decoder network. Diagnostics 11(2):169
Zhang W, Yang G, Huang H, Yang W, Xu X, Liu Y, Lai X (2021) ME-Net: multi-encoder net framework for brain tumor segmentation. Int J Imaging Syst Technol 31(4):1834–1848
Guan X, Yang G, Ye J, Yang W, Xu X, Jiang W, Lai X (2022) 3D AGSE-VNet: An automatic brain tumor MRI data segmentation framework. BMC Med Imaging 22(1):6
Peiris H, Hayat M, Chen Z, Egan G, Harandi M (2022) A Robust Volumetric Transformer for Accurate 3D Tumor Segmentation. In: Wang L, Dou Q, Fletcher PT, Speidel S, Li S (eds) Medical Image Computing and Computer Assisted Intervention – MICCAI 2022. MICCAI 2022. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 13435. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9_16
Hatamizadeh A et al (2021) UNETR: transformers for 3D medical image segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). IEEE, pp 1748–1758. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2103.10504
Pham Q, Nguyen-Truong H, Phuong NN, Nguyen KN, Nguyen CD, Bui T, Truong SQ (2022) Segtransvae: hybrid CNN - Transformer with regularization for medical image segmentation. In: 2022 IEEE 19th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). IEEE, Kolkata, India, pp 1-5
Hatamizadeh A, Nath V, Tang Y, Yang D, Roth HR, Xu D (2022) Swin UNETR: swin transformers for semantic segmentation of brain tumors in MRI images. arXiv:2201.01266. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2201.01266
Hatamizadeh A, Xu Z, Yang D, Li W, Roth HR, Xu D (2022) UNetFormer: a unified vision transformer model and pre-training framework for 3D medical image segmentation. arXiv:2204.00631. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2204.00631
Lin Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K, Dollar P (2017) Focal loss for dense object detection. Proc IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis 2017:2999–3007. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCV.2017.324
Ibtehaz Nabil, Sohel Rahman M (2020) MultiResUNet: rethinking the U-Net architecture for multimodal biomedical image segmentation. Neural Netw 121:74–87
Funding
(1) FC (No.61972117); (2) the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China (ZD2019E007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Li, Z., Wang, Z. et al. mResU-Net: multi-scale residual U-Net-based brain tumor segmentation from multimodal MRI. Med Biol Eng Comput 62, 641–651 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02965-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-023-02965-1