Abstract
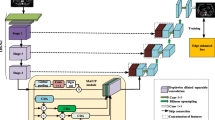
In the endoscopic images of bladder, accurate segmentation of different grade bladder tumor from blurred boundary regions and highly variable shapes is of great significance for doctors’ diagnosis and patients’ later treatment. We propose a nested attentional feature fusion segmentation network (NAFF-Net) based on the encoder-decoder structure formed by the combination of weighted pyramid pooling module (WPPM) and nested attentional feature fusion (NAFF). Among them, WPPM applies the cascade of atrous convolution to enhance the overall perceptual field while introducing adaptive weights to optimize multi-scale feature extraction, NAFF integrates deep semantic information into shallow feature maps, effectively focusing on edge and detail information in bladder tumor images. Additionally, a weighted mixed loss function is constructed to alleviate the impact of imbalance between positive and negative sample distribution on segmentation accuracy. Experiments illustrate the proposed NAFF-Net achieves better segmentation results compared to other mainstream models, with a MIoU of 84.05%, MPrecision of 91.52%, MRecall of 90.81%, and F1-score of 91.16%, and also achieves good results on the public datasets Kvasir-SEG and CVC-ClinicDB. Compared to other models, NAFF-Net has a smaller number of parameters, which is a significant advantage in model deployment.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jansen I, Lucas M, Bosschieter J, Boer OJ, Meijer SL, Leeuwen TG, Marquering HA, Nieuwenhuijzen JA, Bruin DM, Savci-Heijink CD (2020) Automated detection and grading of non-muscle-invasive urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Am J Pathol 190(7):1483–1490
Lenis AT, Lec PM, Chamie K (2020) Bladder cancer: a review. Jama 324(19):1980–1991
Hu X, Li G, Wu S (2022) Advances in diagnosis and therapy for bladder cancer. Cancers 14(13):3181
Sanghvi AB, Allen EZ, Callenberg KM, Pantanowitz L (2019) Performance of an artificial intelligence algorithm for reporting urine cytopathology. Cancer Cytopathology 127(10):658–666
Jansen I, Lucas M, Bosschieter J, Boer OJ, Meijer SL, Leeuwen TG, Marquering HA, Nieuwenhuijzen JA, Bruin DM, Savci-Heijink CD (2020) Automated detection and grading of non-muscle-invasive urothelial cell carcinoma of the bladder. Am J Pathol 190(7):1483–1490
Lin Z, He Z, Yao R, Wang X, Liu T, Deng Y, Xie S (2022) Deep dual attention network for precise diagnosis of COVID-19 from chest CT images. IEEE Trans Artif Intell 5(1):104–114
Lin Z, He Z, Wang X, Zhang B, Liu C, Su W, Tan J, Xie S (2023) DBGANet: dual-branch geometric attention network for accurate 3D tooth segmentation. IEEE Trans Circ Syst Video Technol 1–1
Liu M, Han Y, Wang J, Wang C, Wang Y, Meijering E (2023) LSKANet: Long strip kernel attention network for robotic surgical scene segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging, 1–1
Zhao C, Shuai R, Ma L, Liu W, Wu M (2021) Segmentation of dermoscopy images based on deformable 3D convolution and ResU-NeXt++. Medical and Biological Engineering and Computing, 59(9):1815–1832
Xun S, Li D, Zhu H, Chen M, Wang J, Li J, Chen M, Wu B, Zhang H, Chai X et al (2022) Generative adversarial networks in medical image segmentation: a review. Comput Biol Med 140:105063
Liu T, He Z, Lin Z, Cao G-Z, Su W, Xie S (2022) An adaptive image segmentation network for surface defect detection. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 1–14
Shi M, Shen J, Yi Q, Weng J, Huang Z, Luo A, Zhou Y (2022) LMFFNet: a well-balanced lightweight network for fast and accurate semantic segmentation. IEEE Trans Neural Netw Learn Syst 3205–3219
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: International conference on medical image computing computer-assisted intervention, Springer, pp 234–241
Chen L-C, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, Murphy K, Yuille AL (2017) DeepLab: semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 40(4):834–848
He K, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R (2017) Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision, pp 2961–2969
Shehab LH, Fahmy OM, Gasser SM, El-Mahallawy MS (2021) An efficient brain tumor image segmentation based on deep residual networks (ResNets). J King Saud Univ-Eng Sci 33(6):404–412
Deng Y, Hou Y, Yan J, Zeng D (2022) ELU-Net: an efficient and lightweight U-Net for medical image segmentation. IEEE Access 10:35932–35941
Ma X, Hadjiiski LM, Wei J, Chan H-P, Cha KH, Cohan RH, Caoili EM, Samala R, Zhou C, Lu Y (2019) U-Net based deep learning bladder segmentation in CT urography. Med Phys 46(4):1752–1765
Dolz J, Xu X, Rony J, Yuan J, Liu Y, Granger E, Desrosiers C, Zhang X, Ben Ayed I, Lu H (2018) Multiregion segmentation of bladder cancer structures in MRI with progressive dilated convolutional networks. Med Phys 45(12):5482–5493
Liu J, Liu L, Xu B, Hou X, Liu B, Chen X, Shen L, Qiu G (2019) Bladder cancer multi-class segmentation in MRI with pyramid-in-pyramid network. In: 2019 IEEE 16th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2019), IEEE, pp 28–31
Zhang B, Wang Y, Ding C, Deng Z, Li L, Qin Z, Ding Z, Bian L, Yang C (2023) Multi-scale feature pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 18(2):353–365
Wu Y, Shen H, Tan Y, Shi Y (2022) Automatic liver tumor segmentation used the cascade multi-scale attention architecture method based on 3D U-Net. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 17(10):1915–1922
Singh LK, Pooja Garg H, Khanna M (2022) Deep learning system applicability for rapid glaucoma prediction from fundus images across various data sets. Evolving Syst 13(6):807–836
Singh LK, Khanna M, Thawkar S, Singh R (2023) Deep-learning based system for effective and automatic blood vessel segmentation from retinal fundus images. Multimed Tools Appl 1–45
Niazi MKK, Yazgan E, Tavolara TE, Li W, Lee CT, Parwani A, Gurcan MN (2020) Semantic segmentation to identify bladder layers from H &E images. Diagn Pathol 15(1):1–8
Shkolyar E, Jia X, Chang TC, Trivedi D, Mach KE, Meng MQ-H, Xing L, Liao JC (2019) Augmented bladder tumor detection using deep learning. Eur Urol 76(6):714–718
Yu J, Cai L, Chen C, Fu X, Wang L, Yuan B, Yang X, Lu Q (2022) Cascade path augmentation UNet for bladder cancer segmentation in MRI. Med Phys 49(7):4622–4631
Huang X, Yue X, Xu Z, Chen Y (2022) Harnessing deep bladder tumor segmentation with logical clinical knowledge. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, Springer, pp 725–735
Zhang Q, Liang Y, Zhang Y, Tao Z, Li R, Bi H (2023) A comparative study of attention mechanism based deep learning methods for bladder tumor segmentation. Int J Med Inf 171:104984
Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen L-C (2018) MobileNetV2: inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4510–4520
Dai Y, Gieseke F, Oehmcke S, Wu Y, Barnard K (2021) Attentional feature fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision, pp 3560–3569
Chen L-C, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H (2018) Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 801–818
Lian X, Pang Y, Han J, Pan J (2021) Cascaded hierarchical atrous spatial pyramid pooling module for semantic segmentation. Pattern Recog 110:107622
Wang P, Chen P, Yuan Y, Liu D, Huang Z, Hou X, Cottrell G (2018) Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation. In: 2018 IEEE winter conference on applications of computer vision (WACV), pp 1451–1460
Hou Q, Zhang L, Cheng M-M, Feng J (2020) Strip Pooling: rethinking spatial pooling for scene parsing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 4003–4012
Cheng R, Razani R, Taghavi E, Li E, Liu B (2021) 2-S3Net: attentive feature fusion with adaptive feature selection for sparse semantic segmentation network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 12547–12556
Liu Y, Shao Z, Hoffmann N (2021) Global attention mechanism: retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions. arXiv:2112.05561
Woo S, Park J, Lee J-Y, Kweon IS (2018) CBAM: convolutional block attention module. In: Proceedings of the european conference on computer vision (ECCV), pp 3–19
Hu J, Shen L, Sun G (2018) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 7132–7141
El Jurdi R, Petitjean C, Honeine P, Cheplygina V, Abdallah F (2021) High-level prior-based loss functions for medical image segmentation: a survey. Comput Vis Image Underst 210:103248
Li X, Sun X, Meng Y, Liang J, Wu F, Li J (2019) Dice loss for data-imbalanced NLP tasks. arXiv:1911.02855
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, Huang Z, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M et al (2015) ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. Int J Comput Vis 115(3):211–252
Zhao H, Shi J, Qi X, Wang X, Jia J (2017) Pyramid scene parsing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 2881–2890
Sun K, Zhao Y, Jiang B, Cheng T, Xiao B, Liu D, Mu Y, Wang X, Liu W, Wang J (2019) High-resolution representations for labeling pixels and regions. arXiv:1904.04514
Zhang W, Pang J, Chen K, Loy CC (2021) K-Net: towards unified image segmentation. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:10326–10338
Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, Hu H, Wei Y, Zhang Z, Lin S, Guo B (2021) Swin Transformer: hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, pp 10012–10022
Yu C, Gao C, Wang J, Yu G, Shen C, Sang N (2021) BiSeNetv2: bilateral network with guided aggregation for real-time semantic segmentation. Int J Comput Vis 129:3051–3068
Xie E, Wang W, Yu Z, Anandkumar A, Alvarez JM, Luo P (2021) SegFormer: simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 34:12077-12090
Jha D, Smedsrud PH, Riegler MA, Halvorsen P, Lange T, Johansen D, Johansen, HD (2020) Kvasir-SEG: a segmented polyp dataset. In: MultiMedia modeling: 26th international conference, MMM 2020, Daejeon, South Korea, January 5–8, 2020, Proceedings, Part II 26, Springer, pp 451–462
Bernal J, Sánchez FJ, Fernández-Esparrach G, Gil D, Rodríguez C, Vilariño F (2015) WM-DOVA maps for accurate polyp highlighting in colonoscopy: validation vs. saliency maps from physicians. Comput Med Imaging Graph 43:99–111
Zhou S, Tian S, Yu L, Wu W, Zhang D, Peng Z, Zhou Z (2023) ReFixMatch-LS: reusing pseudo-labels for semi-supervised skin lesion classification. Med Biol Eng Comput 61(5):1033–1045
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Lai, L., Li, Y. et al. A lightweight bladder tumor segmentation method based on attention mechanism. Med Biol Eng Comput 62, 1519–1534 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-024-03018-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11517-024-03018-x