Abstract
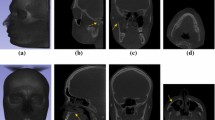
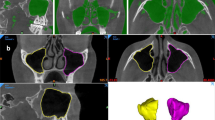
Purpose Segmentation of the maxillary sinuses for three-dimensional (3D) reconstruction, visualization and volumetry is sought using an automated algorithm applied to cone beam computed tomographic (CBCT) data sets.
Materials and Methods Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) data sets of three subjects aged 9, 17, and 27 were used in 3D segmentation and reconstruction. The maxillary sinuses were obtained by propagation from one start point in the right sinus and one start point in the left sinus to the whole regions of both sinuses. The procedure was based on voxel intensity distributions and common anatomic structures, specifically each middle meatus of the nasal cavity. A program was written in C++ and VTK languages to demonstrate the surface topological shapes of the maxillary sinuses.
Results The developed segmentation algorithm separated maxillary sinuses successfully permitting accurate comparisons. It was robust and efficient. 3D morphological features of the maxillary sinuses were observed from three human subjects.
Conclusions Automated segmentation of maxillary sinuses from CBCT data sets is feasible using the proposed method. This tool might be useful for visualization, pathological diagnosis, and treatment planning of maxillary sinus disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others

Abbreviations
- CBCT:
-
Cone beam computed tomography
- 3D:
-
Three-dimensional
- 2D:
-
Two dimensional
- mm:
-
Millimeter
References
Kawarai Y, Fukushima K, Ogawa T, Nishizaki K, Gunduz M, Fujimoto M, Masuda Y (1999) Volume quantification of healthy paranasal cavity by three-dimensional CT imaging. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) Suppl 540:45–49
Sirikci A, Bayazit Y, Gumüsburun E, Bayram M, Kanlikana M (2001) A new approach to the classification of maxillary sinus hypoplasia with relevant clinical implications. Surg Radiol Anat 22:243–347
Erdem T, Aktas D, Erdem G, Miman MC, Ozturan O. (2002) Maxillary sinus hypoplasia. Rhinology 40:150–153
Farman AG. (2002) Pathologic conditions of the maxillary sinus. Panoramic Imaging News2(3):1–6
Nishimura TD, Taki M, Tsubamoto NE, Shigehara N (2005) Variation in maxillary sinus anatomy among platyrrhine monkeys. J Hum Evol 49:370–389
Sivash E, Sirikci A, Bayazit Y, Gumüsburun E, Erbagci H, Bayram M, Kanlykama M (2002) Anatomic variations of the paranasal sinus area in pediatric patients with chronic sinusitis. Surg Radiol Anat 24:399–404
Duker J, Fabinger A (1978) Evaluation of the basal parts of the maxillary sinus by means of panoramic tomography. Dtsch Zahnarztl Z 33:823–826
Nortjé CJ, Farman AG, Joubert JJ de V (1979) Pathological conditions involving the maxillary sinus: their appearances on panoramic dentalradiographs. Brit J Oral Surg 17:27–32
Ohba T, Ogawa Y, Shinohara Y, Hiromatsu T, Uchida A, Toyoda Y (1994) Limitations of panoramic radiology in the detection of bone effects in the posterior wall of the maxillary sinus. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 23:149–153
Epstein JP, Waisglass M, Bhimji S, Le N, Stevenson-Moore P (1996) A comparison of computed tomography and panoramic radiography in assessing malignancy of the maxillary antrum. Eur J Cancer Oral Oncol 32B:191–201
Savolainen S, Eskelin M, Jousimies-Somer H, Ylikoski J (1997) Radiological findings in the maxillary sinuses of symptomless young men. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 529:153–157
Koscielny S (1999) The paranasal sinuses as metastatic site of renal cell carcinoma. Larungorhinootologie 78:441–444
Barghouth G, Prior J, Lepori D, Duvoisin B, Schnyder P, Gudinchet F (2002) Paranasal sinuses in children: size evaluation of maxillary sphenoid, and frontal sinuses by magnetic resonance imaging and proposal of volume index percentile curve. Eur Radiol 12:1451–1458
Sánchez Fernández JM, Anta Escuredo JA, Sánchez Del Rey A and Santaolalla Montoya F (2000) Morphometric study of the paranasal sinuses in normal and pathological conditions. Acta Otolaryngol 120:273–278
Toida N (1937) Study of nasal cavity in Chinese. J Med Mantura 27:743–752
Anagnostopoulou S, Vesieratos D, Spyropoulos N (1991) Classification of human maxillary sinuses according to their geometric features. Anat Anz 173:121–30
Moriguchi S (1989) Measurement of normal maxillary sinus. Stomato-pharyngol 38:1322
Kim H-J, Yoon H-R, Kim K-D, Kang M-K, Kwak H-H, Park H-D, Han S-H, Park C-S (2002) Personal-computer-based three-dimensional reconstruction and simulation of maxillary sinus. Surgical and Radiologic Anat 24:392–398
Jun B-C, Song S-W, Park C-S, Lee D-H, Cho K-J (2005) The analysis of maxillary sinus aeration according to aging process; volume assessment by 3-dimensional reconstruction by high-resolution CT scanning. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:429–434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, H., Scarfe, W.C. & Farman, A.G. Maxillary Sinus 3D Segmentation and Reconstruction from Cone Beam CT Data Sets. Int J CARS 1, 83–89 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-006-0041-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-006-0041-9