Abstract
Objective The muscles of mastication play a major role in the orodigestive system as the principal motive force for the mandible. An algorithm for segmenting these muscles from magnetic resonance (MR) images was developed and tested.
Materials and methods Anatomical information about the muscles of mastication in MR images is used to obtain the spatial relationships relating the muscle region of interest (ROI) and head ROI. A model-based technique that involves the spatial relationships between head and muscle ROIs as well as muscle templates is developed. In the segmentation stage, the muscle ROI is derived from the model. Within the muscle ROI, anisotropic diffusion is applied to smooth the texture, followed by thresholding to exclude bone and fat. The muscle template and morphological operators are employed to obtain an initial estimate of the muscle boundary, which then serves as the input contour to the gradient vector flow snake that iterates to the final segmentation.
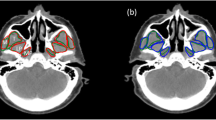
Results The method was applied to segmentation of the masseter, lateral pterygoid and medial pterygoid in 75 images. The overlap indices (κ) achieved are 91.4, 92.1 and 91.2%, respectively.
Conclusion A model-based method for segmenting the muscles of mastication from MR images was developed and tested. The results show good agreement between manual and automatic segmentations.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Noguchi N, Goto M (2003) Computer simulation system for orthognathic surgery. J Orthod Craniofac Res 6(1):176–178
Xia J, Samman N, Yeung RW, Wang D, Shen SG, Ip HH, Tideman H (2000) Computer-assisted three-dimensional surgical planning and simulation. 3D soft tissue planning and prediction. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 29(4):250–258
Wong TY, Fang JJ, Chung CH, Huang JS, Lee JW (2005) Comparison of 2 methods of making surgical models for correction of facial asymmetry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 63(2):200–208
Gladilin E, Zachow S, Deuflhard P, Hege HC (2004) Anatomy and physics-based facial animation for craniofacial surgery simulations. Med Biol Eng Comput 42(2):167–170
Meehan M, Teschner M, Girod S (2003) Three-dimensional simulation and prediction of craniofacial surgery. J Orthod Craniofac Res 6(1):103–107
Kass M, Witkin A, Terzopoulos D (1987) Snakes: active contour models. Int J Comput Vis 1(4):321–331
Ray N, Acton ST, Altes T, Lange EE, Brookeman JR (2003) Merging parametric active contours within homogeneous image regions for MRI-based lung segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 22(2):189–199
Pluempitiwiriyawej C, Moura JMF, Wu YJ, Ho C (2005) STACS: new active contour scheme for cardiac MR image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 24(5):593–603
Lee C, Huh S, Ketter TA, Unser M, (1998) Unsupervised connectivity-based thresholding segmentation of midsagittal brain MR images. Comput Biol Med 28(3):309–338
Kim DY, Park JW (2005) Connectivity-based local adaptive thresholding for carotid artery segmentation using MRA images. Image Vis Comput 23(14):1277–1287
Hu Q, Hou Z, Nowinski WL (2006) Supervised range-constrained thresholding. IEEE Trans Image Process 15(1): 228–240
Lundervold A, Duta N, Taxt T, Jain AK (1999) Model-guided segmentation of corpus callosum in MR images. IEEE Conf Comput Vis Pattern Recognit 1:231–237
Freedman D, Radke RJ, Zhang T, Jeong Y, Lovelock DM, Chen GT (2005) Model-based segmentation of medical imagery by matching distributions. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 24(3):281–292
Xu C, Prince JL (1998) Snakes, shapes, and gradient vector flow. IEEE Trans Image Process 7(3):359–369
Perona P, Malik J (1990) Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 12(7):629–639
Bezdek JC (1981) Pattern recognition with fuzzy objective function algorithm. Plenum, New York
Hu Q, Qian G, Nowinski WL (2005) Fast connected- component labelling in three-dimensional binary images based on iterative recursion. Comput Vis Image Underst 99(3):414–434
Canny J, (1986) A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 8(4):679–698
Leemput VK, Maes F, Vandermeulen D, Suetens P (1999) Automated model-based tissue classification of MR images of the brain. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18(10):897–908
Hu Q, Nowinski WL (2003) A rapid algorithm for robust and automatic extraction of the midsagittal plane of the human cerebrum from neuroimages based on local symmetry and outlier removal. NeuroImage 20(4):2153–2165
Malladi R, Sethian JA, Vermuri BC (1995) Shape modelling with front propagation: a level set approach. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17(2):158–174
Kolmogorov V, Zabin R (2004) What energy functions can be minimized via graph cuts?. IEEE Trans Pattern Analy Mach Intell 26(2):147–159
Lombaert H, Sun Y, Grady L, Xu C (2005) A multilevel banded graph cuts method for fast image segmentation. IEEE Int Conf Comput Vis 1:259–265
Nguyen HT, Worring M, Boomgaard RVD (2003) Watersnakes: energy-driven watershed segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(3):330–342
Pham DL, Prince JL, Dagher AP Xu C (1997) An automated technique for statistical characterization of brain tissues in magnetic resonance image. Int J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 11(8):1189–1211
Ge Y, Fitzpatrick JM, Dawant BM, Bao J, Kessler RM, Margolin RA (1996) Accurate localization of cortical convolutions in MR brain images. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 15(4):418–428
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ng, H.P., Ong, S.H., Hu, Q. et al. Muscles of mastication model-based MR image segmentation. Int J CARS 1, 137–148 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-006-0046-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-006-0046-4