Abstract
Purpose
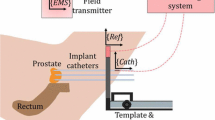
This paper presents and evaluates stochastic computer algorithms used to automatically detect and track marked catheter tip during MR-guided catheterization. The algorithms developed employ extraction and matching of regional features of the catheter tip to perform the localization.
Method
To perform the tracking, a probability map that indicates the possible locations of the catheter tip in the MR images is first generated. This map is generated from the similarity to a given marker template. The method to assess the similarity between the marker template image and the different positions on each MR frame is based on speeded-up robust features extracted from the gradient image. The probability map is then used in two different stochastic localization frameworks mean shift (MS) localization and Kalman filter (KF) to track the position of the catheter using pairs of orthogonal projection of 2D MR images. The algorithm developed was tested on catheter tip marked with LC resonant circuit (of size \(2\,\hbox {mm}\,\times \,2\,\hbox {cm}\)) tuned to the Larmor frequency of the MRI scanner and for different image resolutions (1, 3, 5 and 7 mm squared pixel).
Results
The tracking performance was very robust for the two algorithms MS and KF with image resolution as low as 3 mm where the localization error was about 1 mm for KF and 0.9 mm for MS. For the 5-mm resolution images, the error was 2.2 mm for both KF and MS, and for the 7-mm resolution images, the error was 3.6 and 3.7 mm for KF and MS, respectively.
Conclusion
Both KF and MS gave comparable results when it comes to accuracy for the different image resolutions. The results showed that the two tracking algorithms tracked the catheter tip with high robustness for image resolution of 3 mm and with acceptable reliability for image resolution as poor as 5 mm with the resonant marker configuration used.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horvath KA, Li M, Mazilu D, Guttman MA, McVeigh ER (2007) Real-time magnetic resonance imaging guidance for cardiovascular procedures. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 19(4):330–335
Ratnayaka K, Lederman RJ (2010) Interventional cardiovascular MR—the next stage in pediatric cardiology. Prog Pediatr Cardiol 28(1–2):59–67. doi:10.1016/j.ppedcard.2009.10.008
Saikus CE, Lederman RJ (2009) Interventional cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging: a new opportunity for image-guided interventions. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2(11):1321–1331. doi:10.1016/j.jcmg.2009.09.002
Dumoulin CL, Souza SP, Darrow RD (1993) Real-time position monitoring of invasive devices using magnetic resonance. Magn Reson Med 29(3):411–415. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910290322
Ladd ME, Zimmermann GG, McKinnon GC, von Schulthess GK, Dumoulin CL, Darrow RD, Hofmann E, Debatin JF (1998) Visualization of vascular guidewires using MR tracking. J Magn Reson Imaging 8(1):251–253
Nitz WR, Oppelt A, Renz W, Manke C, Lenhart M, Link J (2001) On the heating of linear conductive structures as guide wires and catheters in interventional MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(1):105–114
Dempsey MF, Condon B, Hadley DM (2001) Investigation of the factors responsible for burns during MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 13(4):627–631. doi:10.1002/jmri.1088
Rubin DL, Ratner AV, Young SW (1990) Magnetic susceptibility effects and their application in the development of new ferromagnetic catheters for magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 25(12):1325–1332
Omary RA, Unal O, Koscielski DS, Frayne R, Korosec FR, Mistretta CA, Strother CM, Grist TM (2000) Real-time MR imaging-guided passive catheter tracking with use of gadolinium-filled catheters. J Vasc Interv Radiol 11(8):1079–1085
Quick HH, Zenge MO, Kuehl H, Kaiser G, Aker S, Massing S, Bosk S, Ladd ME (2005) Interventional magnetic resonance angiography with no strings attached: wireless active catheter visualization. Magn Reson Med 53(2):446–455. doi:10.1002/mrm.20347
Umathum R, Krafft A, de Oliveira A, Bock M (2009) Inductively coupled coils for local SNR-enhancement during MR-guided prostate biopsy. In: 17th annual ISMRM scientific meeting and exhibition, 18–24 Apr 2009, p 4434
Hegde S, Miquel ME, Boubertakh R, Gilderdale D, Muthurangu V, Keevil SF, Young I, Hill DL, Razavi RS (2006) Interactive MR imaging and tracking of catheters with multiple tuned fiducial markers. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(7):1175–1179. doi:10.1097/01.rvi.0000228466.09982.8b
Rea M, Elhawary H, Tse Z, McRobbie D, Lamperth M, Young I (2008) 3D real-time tracking using passive fiducial markers and image processing. In: 16th annual ISMRM scientific meeting and exhibition, Toronto, Ontario, Canada, 3–9 May 2008, p 1215
Rea M, McRobbie D, Elhawary H, Tse ZTH, Lamperth M, Young I (2009) Sub-pixel localisation of passive micro-coil fiducial markers in interventional MRI. Magn Reson Mater Phys Biol Med 22(2):71–76
Busse H, Trampel R, Gründer W, Moche M, Kahn T (2007) Method for automatic localization of MR-visible markers using morphological image processing and conventional pulse sequences: feasibility for image-guided procedures. J Magn Reson Imaging 26(4):1087–1096
Kalman RE (1960) A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems. J Basic Eng 82(1):35–45
Cheng Y (1995) Mean shift, mode seeking, and clustering. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 17(8):790–799
Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P (2000) Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, 2000. IEEE, pp 142–149
Bay H, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L (2006) Surf: speeded up robust features. Comput Vis ECCV 2006:404–417
Bakker CJG, Seppenwoolde JH, Vincken KL (2005) Dephased mri. Magn Reson Med 55(1):92–97
Murillo AC, Guerrero J, Sagues C (2007) Surf features for efficient robot localization with omnidirectional images. In: IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, 2007. IEEE, pp 3901–3907
Reid I (2001) Estimation II: discrete-time Kalman filter (Lecture Note 2). Retrieved from http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~ian/Teaching/Estimation/LectureNotes2.pdf
Maskell S, Gordon N (2001) A tutorial on particle filters for on-line nonlinear/non-Gaussian Bayesian tracking. In: Target tracking: algorithms and applications (Ref. No. 2001/174), IEE, 2001, vol 12. IET, pp 2/1–2/15
Wan EA, Van Der Merwe R (2000) The unscented Kalman filter for nonlinear estimation. In: Adaptive systems for signal processing, communications, and control symposium 2000. AS-SPCC. The IEEE 2000. IEEE, pp 153–158
Shan C, Wei Y, Tan T, Ojardias F (2004) Real time hand tracking by combining particle filtering and mean shift. In: Proceedings of the sixth IEEE international conference on automatic face and gesture recognition, 2004. IEEE, pp 669–674
Valgren C, Lilienthal A (2007) SIFT, SURF and seasons: long-term outdoor localization using local features. In: Proceedings of the European conference on mobile robots (ECMR), pp 253–258
Se S, Lowe D, Little J (2002) Global localization using distinctive visual features. In: IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelligent robots and systems, 2002. IEEE, pp 226–231
Dorkó G, Schmid C (2003) Selection of scale-invariant parts for object class recognition. In: Proceedings of the ninth IEEE international conference on computer vision, 2003. IEEE, pp 634–639
Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C (2005) A performance evaluation of local descriptors. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 27(10):1615–1630
Juan L, Gwun O (2009) A comparison of sift, pca-sift and surf. Int J Image Process 3(4):143–152
Will K, Schimpf S, Brose A, Fischbach F, Ricke J, Schmidt B, Rose G (2010) Pre-tuned resonant marker for iMRI using aerosol deposition on polymer catheters. In: SPIE medical imaging. International Society for Optics and Photonics, p 76251Z
Krug J, Will K, Rose G (2010) Simulation and experimental validation of resonant electric markers used for medical device tracking in magnetic resonance imaging. In: 2010 Annual international conference of the IEEE engineering in medicine and biology society (EMBC). IEEE, pp 1878–1881
Konings MK, Bartels LW, Smits HFM, Bakker CJG (2000) Heating around intravascular guidewires by resonating RF waves. J Magn Reson Imaging 12(1):79–85
Martin AJ, Baek B, Acevedo-Bolton G, Higashida RT, Comstock J, Saloner DA (2008) MR imaging during endovascular procedures: an evaluation of the potential for catheter heating. Magn Reson Med 61(1):45–53
Celik H, Ulutürk A, Talı T, Atalar E (2007) A catheter tracking method using reverse polarization for MR-guided interventions. Magn Reson Med 58(6):1224–1231
Seppenwoolde JH, Viergever MA, Bakker CJG (2003) Passive tracking exploiting local signal conservation: the white marker phenomenon. Magn Reson Med 50(4):784–790
Bieri O, Patil S, Quick H, Scheffler K (2007) Morphing steady-state free precession. Magn Reson Med 58(6):1242–1248
Acknowledgments
The research leading to these results has received funding from the European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under Grant Agreement No 238802 (IIIOS project).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eldirdiri, A., Courivaud, F., Palomar, R. et al. Catheter tip tracking for MR-guided interventions using discrete Kalman filter and mean shift localization. Int J CARS 9, 313–322 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0933-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0933-4