Abstract
Purpose
Development of new needle insertion force feedback algorithms requires comparison with a gold standard method. A new evaluation framework was formulated and tested on needle punctures for percutaneous transhepatic catheter drainage (PTCD).
Methods
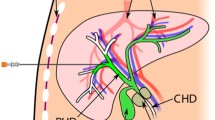
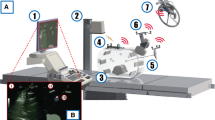
Needle insertion is an established procedure for minimally invasive interventions in the liver. Up-to-date, needle insertions are precisely planned using 2D axial CT slices from 3D data sets. To provide a 3D virtual reality and haptic training and planning environment, the full segmentation of patient data is often a mandatory step. To lessen the time required for manual segmentation, we propose direct haptic volume-rendering based on CT gray values and partially segmented patient data. The core contribution is a new force output evaluation method driven by a ray-casting technique that defines paths from the skin to target structures, i.e., the right hepatic duct near the juncture with the common hepatic duct. A ray-casting method computes insertion trajectories from the skin to the duct considering no-go structures and plausibility criteria. A rating system scores each trajectory. Finally, the best insertion trajectories are selected that reach the target. Along the selected paths, force output comparison between a reference system and the new haptic force output algorithm is carried out, quantified and visualized.
Results
The evaluation framework is presented along with an exemplary study of the liver using the atlas data set from a reference patient. In a comparison of our reference method to a newer algorithm, force outputs are found to be similar in 99 % of the paths.
Conclusion
The proposed evaluation framework allows reliable detection of problematic PTCD trajectories and provides valuable hints to improve force feedback algorithm development.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abolhassani N, Patel R, Moallem M (2007) Needle insertion into soft tissue: a survey. Med Eng Phys 29(4):413–431
Baegert C, Villard C, Schreck P, Soler L (2007) Multi-criteria trajectory planning for hepatic radiofrequency ablation. MICCAI Med Image Comput Comput Interv 4792:676–684
Basdogan C, Sedef M, Harders M, Wesarg S (2007) VR-based simulators for training in minimally invasive surgery. IEEE Comput Graph Appl 27(2):54–66
Bresenham JE (1965) Algorithm for computer control of a digital plotter. IBM Syst J 4(1):25–30
Campadelli P, Casiraghi E, Esposito A (2009) Liver segmentation from computed tomography scans: a survey and a new algorithm. Artif Intell Med 45(2–3):185–196
Dierckx P, Suetens P, Vandermeulen D (1988) An algorithm for surface reconstruction from planar contours using smoothing splines. J Comput Appl Math 23(3):367–388
Engel K (2006) Real-time volume graphics. Ak Peters Series. AK Peters, Limited
Färber M, Hoeborn E, Dalek D, Hummel F, Gerloff C, Bohn CA, Handels H (2008) Training and evaluation of lumbar punctures in a VR-environment using a 6DOF haptic device. MMVR16/Stud Health Technol. Inform 132:112–114
Färber M, Hummel F, Gerloff C, Handels H (2009) Virtual reality simulator for the training of lumbar punctures. Methods Inf Med 48(5):493–501
Heimann T, van Ginneken B, Styner M, Arzhaeva Y, Aurich V, Bauer C, Beck A, Becker C, Beichel R, Bekes G, Bello F, Binnig G, Bischof H, Bornik A, Cashman P, Chi Y, Cordova A, Dawant B, Fidrich M, Furst J, Furukawa D, Grenacher L, Hornegger J, Kainmuller D, Kitney R, Kobatake H, Lamecker H, Lange T, Lee J, Lennon B, Li R, Li S, Meinzer HP, Nemeth G, Raicu D, Rau AM, van Rikxoort E, Rousson M, Rusko L, Saddi K, Schmidt G, Seghers D, Shimizu A, Slagmolen P, Sorantin E, Soza G, Susomboon R, Waite J, Wimmer A, Wolf I (2009) Comparison and evaluation of methods for liver segmentation from CT datasets. Trans Med Imaging 28(8):1251–1265
Liwu L (1997) Practical clinical ultrasound diagnosis. World Scientific Publishing Company
Lundin K, Ynnerman A, Gudmundsson B (2002) Proxy-based haptic feedback from volumetric density data. Eurohaptics Conference pp 104–109
Mastmeyer A, Fortmeier D, Handels H (2012) Direct haptic volume rendering in lumbar puncture simulation. Stud Health Technol Inform 173:280–286
Mastmeyer A, Fortmeier D, Handels H (2012) Anisotropic diffusion for direct haptic volume rendering in lumbar puncture simulation. In: Tolxdorff T, Deserno TM, Handels H, Meinzer HP (Hrsg.), Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin, (2012) Informatik aktuell. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 286–291
Mastmeyer A, Fortmeier D, Maghsoudi E, Simon M, Handels H (2013) Patch-based label fusion using local confidence-measures and weak segmentations. SPIE Medical Imaging 2013
Mastmeyer A, Hecht T, Fortmeier D, Handels H (2013) Raycasting based evaluation framework for needle insertion force feedback algorithms. In: Tolxdorff T, Deserno TM, Handels H, Meinzer HP (Hrsg.), Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin, (2013) Informatik aktuell. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–8
Mharib AM, Ramli AR, Mashohor S, Mahmood RB (2011) Survey on liver CT image segmentation methods. Artif Intell Rev 37(2):83–95
Murphy MJ (2004) Tracking moving organs in real time. Semin Radiat Oncol 14(1):91–100
Nath S, Chen Z, Yue N, Trumpore S, Peschel R (2000) Dosimetric effects of needle divergence in prostate seed implant using 125l and 103pd radioactive seeds. Med Phys 27(5):1058–1066
Pereira PL (2007) Actual role of radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases. Eur Radiol 17(8):2062–2070
Ruspini DC, Kolarov K, Khatib O (1997) The haptic display of complex graphical environments. In: Proceedings of the 24th annual conference on Computer graphics and interactive techniques SIGGRAPH vol 97, pp 345–352
Seitel A, Engel M, Sommer CM, Radeleff BA, Caroline EV, Baegert C, Fangerau M, Fritzsche KH, Yung K, Meinzer HP, Maier-Hein L (2011) Computer-assisted trajectory planning for percutaneous needle insertions. Med Phys 38(6):3246–3259
Ullrich S, Grottke O, Fried E, Frommen T, Liao W, Rossaint R, Kuhlen T, Deserno TM (2009) An intersubject variable regional anesthesia simulator with a virtual patient architecture. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 4(6):561–570
Ullrich S, Kuhlen T (2012) Haptic palpation for medical simulation in virtual environments. IEEE Trans Vis Comput Gr 18(4):617–625
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG, HA 2355/10-1).
Conflict of interest
Andre Mastmeyer has no conflict of interest. Tobias Hecht has no conflict of interest. Dirk Fortmeier has no conflict of interest. Heinz Handels has no conflict of interest.
Informed consent Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. The identity of the subjects under study is not revealed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mastmeyer, A., Hecht, T., Fortmeier, D. et al. Ray-casting based evaluation framework for haptic force feedback during percutaneous transhepatic catheter drainage punctures. Int J CARS 9, 421–431 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0959-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0959-7