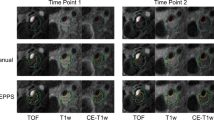
Abstract
Purpose
Intra-plaque hemorrhage (IPH) is associated with plaque instability. Therefore, the presence and volume of IPH in carotid arteries may be relevant in predicting the progression of atherosclerotic disease and the occurrence of clinical events. The aim of our work was to develop and evaluate a method for semi-automatic IPH segmentation in T1-weighted (T1w)-magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Material and methods
IPH segmentation is performed by a regional level set method that models the intensity of the IPH and the background in T1w-MRI to be smoothly varying. The method only requires minimal user interaction, i.e., one or more mouse clicks inside the hemorrhage serve as initialization. The parameters of the method are optimized using a leave-one-out strategy by maximizing the Dice similarity coefficient (DSC) between manual and semi-automatic segmentations. We evaluated the IPH segmentation method on 22 carotid arteries; 10 of which were annotated by two observers and 12 were scanned twice within a 2 week period.
Results
We obtained a DSC of 0.52 between the manual and level set segmentations on all 22 carotids. The inter-observer DSC on 10 arteries is 0.57, which is comparable to the DSC between the method and the manual segmentation (0.55). The correlation between the IPH volumes extracted from the level set segmentation and the manual segmentation is 0.88, which is close to the inter-observer volume correlation of 0.92. The reproducibility after rescanning 12 carotids yield an IPH volume correlation of 0.97. The robustness with respect to the initialization by manually clicking two sets of seed points in these 12 carotid artery pairs yields a volume correlation of 0.99.
Conclusion
Semi-automatic segmentation and quantification of IPHs are feasible with an accuracy in the range of the inter-observer variability. The method has excellent reproducibility with respect to rescanning and manual initialization.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaf N, Daniels L, Morgan PS, Auer D, MacSweeney ST, Moody AR, Gladman JR (2008) Detection of intraplaque hemorrhage by magnetic resonance imaging in symptomatic patients with mild to moderate carotid stenosis predicts recurrent neurological events. J Vasc Surg 47(2):337–342. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2007.09.064. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/B6WMJ-4RPSH92-P/2/2bbdaed07bbb88aed06a6f8b190ddd08
Barnett HJ, Taylor DW, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Ferguson GG, Haynes RB, Rankin RN, Clagett GP, Hachinski VC, Sackett DL et al (1998) Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. N Engl J Med 339(20):1415–1425
Bitar R, Moody AR, Leung G, Symons S, Crisp S, Butany J, Rowsell C, Kiss A, Nelson A, Maggisano R (2008) In vivo 3D high-spatial-resolution MR imaging of intraplaque hemorrhage. Radiology 249(1):259–267
Cappendijk VC, Cleutjens KBJM, Kessels AGH, Heeneman S, Schurink GWH, Welten RJTJ, Mess WH, Daemen MJAP, van Engelshoven JMA, Kooi ME (2005) Assessment of human atherosclerotic carotid plaque components with multisequence MR imaging: initial experience1. Radiology 234(2):487–492. doi:10.1148/radiol.2342032101. http://radiology.rsna.org/content/234/2/487.abstract
Caselles V, Kimmel R, Sapiro G, Sbert C (1997) Minimal surfaces based object segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 19:394–398
Chambless LE, Heiss G, Folsom AR, Rosamond W, Szklo M, Sharrett AR, Clegg LX (1997) Association of coronary heart disease incidence with carotid arterial wall thickness and major risk factors: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study, 1987–1993. Am J Epidemiol 146(6):483–494
Dice LR (1945) Measures of the amount of ecologic association between species. Ecology 26(3):297–302
Epstein FH, Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis: an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340(2):115–126. http://dx.doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199901143400207
Hofman A, van Duijn CM, Franco OH, Ikram MA, Janssen HL, Klaver CC, Kuipers EJ, Nijsten TE, Stricker BHC, Tiemeier H et al (2011) The Rotterdam study: 2012 objectives and design update. Eur J Epidemiol 26(8):657–686
Hofman JMA, Branderhorst W, ten Eikelder H, Cappendijk V, Heeneman S, Kooi M, Hilbers P, ter Haar Romeny B (2006) Quantification of atherosclerotic plaque components using in vivo MR and supervised classifiers. Magn Reson Med 55(4):790–799. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mrm.20828
Kolodgie FD, Gold HK, Burke AP, Fowler DR, Kruth HS, Weber DK, Farb A, Guerrero L, Hayase M, Kutys R, Narula J, Finn AV, Virmani R (2003) Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N Engl J Med 349(24):2316–2325. http://www.nejm.org/doi/abs/10.1056/NEJMoa035655
Li C, Kao CY, Gore JC, Ding Z (2008) Minimization of region-scalable fitting energy for image segmentation. IEEE Trans Image Process 17(10):1940–1949
Liu F, Xu D, Ferguson MS, Chu B, Saam T, Takaya N, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C, Kerwin WS (2006) Automated in vivo segmentation of carotid plaque MRI with morphology-enhanced probability maps. Magn Reson Med 55:659–668
Selwaness M, van den Bouwhuijsen Q, Verwoert G et al (2013) Blood pressure parameters and carotid intraplaque hemorrhage as measured by magnetic resonance imaging: the Rotterdam study. Hypertension 61(1):76–81
Smedby Ö, Bergstrand L (1996) Tortuosity and atherosclerosis in the femoral artery: what is cause and what is effect? Ann Biomed Eng 24(4):474–480
Takaya N, Yuan C, Chu B, Saam T, Polissar NL, Jarvik GP, Isaac C, McDonough J, Natiello C, Small R, Ferguson MS, Hatsukami TS (2005) Presence of intraplaque hemorrhage stimulates progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation 111(21):2768–2775. http://circ.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/111/21/2768
Thomas JB, Antiga L, Che SL, Milner JS, Hangan Steinman DA, Spence JD, Rutt BK, Steinman DA (2005) Variation in the carotid bifurcation geometry of young versus older adults: implications for geometric risk of atherosclerosis. Stroke 36(11):2450–2456. http://stroke.ahajournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/36/11/2450
Van den Bouwhuijsen QJ, Vernooij MW, Hofman A, Krestin GP, van der Lugt A, Witteman JC (2012) Determinants of magnetic resonance imaging detected carotid plaque components: the Rotterdam study. Eur Heart J 33(2):221–229
Van Engelen A, De Bruijne M, Klein S, Verhagen H, Groen H, Wentzel J, Van der Lugt A, Niessen W (2011) Plaque characterization in ex vivo mri evaluated by dense 3D correspondence with histology. In: SPIE medical imaging, international society for optics and photonics, p 796329
Wasserman BA (2010) Advanced contrast-enhanced MRI for looking beyond the lumen to predict stroke: building a risk profile for carotid plaque. Stroke 41:S12–S16
Conflict of interest
Hui Tang, Mariana Selwaness, Reinhard Hameeteman, Anouk van Dijk, Aad van der Lugt, Jacqueline C Witteman, Wiro J Niessen, Lucas J van Vliet and Theo van Walsum declare that they have no conflict of interest. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, H., Selwaness, M., Hameeteman, R. et al. Semi-automatic MRI segmentation and volume quantification of intra-plaque hemorrhage. Int J CARS 10, 67–74 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1010-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1010-3