Abstract
Purpose
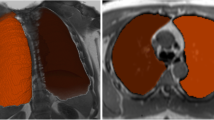
A novel fully automatic lung segmentation method for magnetic resonance (MR) images of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is presented. The main goal of this work was to ease the tedious and time-consuming task of manual lung segmentation, which is required for region-based volumetric analysis of four-dimensional MR perfusion studies which goes beyond the analysis of small regions of interest.
Methods
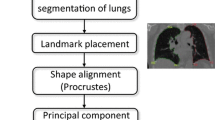
The first step in the automatic algorithm is the segmentation of the lungs in morphological MR images with higher spatial resolution than corresponding perfusion MR images. Subsequently, the segmentation mask of the lungs is transferred to the perfusion images via nonlinear registration. Finally, the masks for left and right lungs are subdivided into a user-defined number of partitions. Fourteen patients with two time points resulting in 28 perfusion data sets were available for the preliminary evaluation of the developed methods.
Results
Resulting lung segmentation masks are compared with reference segmentations from experienced chest radiologists, as well as with total lung capacity (TLC) acquired by full-body plethysmography. TLC results were available for thirteen patients. The relevance of the presented method is indicated by an evaluation, which shows high correlation between automatically generated lung masks with corresponding ground-truth estimates.
Conclusion
The evaluation of the developed methods indicates good accuracy and shows that automatically generated lung masks differ from expert segmentations about as much as segmentations from different experts.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biederer J, Beer M, Hirsch W, Wild J, Fabel M, Puderbach M, van Beek EJR (2012) MRI of the lung (2/3). Why..when..how? Insights Imaging 3(4):355–371
Boehler T, van Straaten D, Wirtz S, Peitgen H-O (2011) A robust and extendible framework for medical image registration focused on rapid clinical application deployment. Comput Biol Med 41(6):340–349
Böttger T, Grunewald K, Schöbinger M, Fink C, Risse F, Kauczor H-U, Meinzer H-P, Wolf I (2007) Implementation and evaluation of a new workflow for registration and segmentation of pulmonary MRI data for regional lung perfusion assessment. Phys Med Biol 52(5):1261–1275
De Nunzio G, Tommasi E, Agrusti A, Cataldo R, De Mitri I, Favetta M, Maglio S, Massafra A, Quarta M, Torsello M, Zecca I, Bellotti R, Tangaro S, Calvini P, Camarlinghi N, Falaschi F, Cerello P, Oliva P (2011) Automatic lung segmentation in CT images with accurate handling of the hilar region. J Digit Imaging 24(1):11–27
DuBois AB, Botelho SY, Bedell GN, Marshall R, Comroe JH Jr (1956) A rapid plethysmographic method for measuring thoracic gas volume: a comparison with a nitrogen washout method for measuring functional residual capacity in normal subjects. J Clin Invest 35(3):322–326
Fink C, Puderbach M, Bock M, Lodemann K-P, Zuna I, Schmähl A, Delorme S, Kauczor H-U (2004) Regional lung perfusion: assessment with partially parallel three-dimensional MR imaging. Radiology 231(1):175–184
Garfield JL, Marchetti N, Gaughan JP, Steiner RM, Criner GJ (2012) Total lung capacity by plethysmography and high-resolution computed tomography in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 7:119–126
Haber E, Modersitzki J (2007) Intensity gradient based registration and fusion of multi-modal images. Methods Inf Med 46(3):292–299
Heimann T, Eichinger M, Bauman G, Bischoff A, Puderbach M, Meinzer H-P (2012) Automated scoring of regional lung perfusion in children from contrast enhanced 3D MRI. In: Proceedings of the SPIE, vol 8315
Kohlmann P, Jobst B, Sedlaczek O, Anjorin FA, Ley S, Strehlow J, Krass S, Peitgen, H-O, Kauczor H-U, Wielpütz MO (2012) Validation of an automatic lung segmentation method for MRI-based lung perfusion studies. J Thorac Imaging (European Society of Thoracic Imaging: Abstracts From the 2012 20th Anniversary Congress) 27(5):W115–W163
Kuhnigk J-M (2008) Quantitative analysis of lung morphology and function in computed tomographic images. Ph.D. thesis, University of Bremen
Kunert T, Heimann T, Schröter A, Schöbinger M, Böttger T, Thorn M, Wolf I, Engelmann U, Meinzer H-P (2004) An interactive system for volume segmentation in computer-assisted surgery. In: Proceedings of the SPIE, pp 799–809
Lassen B, Kuhnigk J-M, Friman O, Krass S, Peitgen H-O (2010) Automatic segmentation of lung lobes in CT images based on fissures, vessels, and bronchi. In: Proceedings of the IEEE ISBI, pp 560–563
Ley S, Ley-Zaporozhan J (2012) Pulmonary perfusion imaging using MRI: clinical application. Insights Imaging 3(1):61–71
Modersitzki J (2009) FAIR: flexible algorithms for image registration. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics (SIAM), vol 6. Philadelphia
Nikolaou K, Schoenberg SO, Brix G, Goldman JP, Attenberger U, Kuehn B, Dietrich O, Reiser MF (2004) Quantification of pulmonary blood flow and volume in healthy volunteers by dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging using a parallel imaging technique. Invest Radiol 39(9):537–545
Ohno Y, Hatabu H, Murase K, Higashino T, Kawamitsu H, Watanabe H, Takenaka D, Fujii M, Sugimura K (2004) Quantitative assessment of regional pulmonary perfusion in the entire lung using three-dimensional ultrafast dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging: preliminary experience in 40 subjects. J Magn Reson Imaging 20(3):353–365
Rühaak J, Heldmann S, Kipshagen T, Fischer B (2013) Highly accurate fast lung CT registration. In: Proceedings of the SPIE, vol 8669
Risse F, Kuder TA, Kauczor H-U, Semmler W, Fink C (2009) Suppression of pulmonary vasculature in lung perfusion MRI using correlation analysis. Eur Radiol 19(11):2569–2575
Schwarz T, Tetzlaff R, Heimann T, Eichinger M, Wolf I, Meinzer H-P (2009) 4D MRT Lungen-Volumetrie und funktionale Analyse mittels deformierbarer Formmodelle. In: Meinzer H-P, Deserno TM, Handels H, Tolxdorff T (eds) Bildverarbeitung für die Medizin 2009. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 282–286
Selle D, Preim B, Schenk A, Peitgen H-O (2002) Analysis of vasculature for liver surgical planning. IEEE Trans Med Imag 21(11):1344–1357
Sensakovic WF, Armato SG III, Starkey A, Caligiuri P (2006) Automated lung segmentation of diseased and artifact-corrupted magnetic resonance sections. Med Phys 33(9):3085–3093
Sled JG, Zijdenbos AP, Evans AC (1998) A non-parametric method for automatic correction of intensity non-uniformity in MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imag 17:87–97
van Rikxoort E, van Ginneken B, Kerkstra S (2011) Lobe and lung analysis 2011 (LOLA11). http://www.lola11.com/
van Rikxoort EM, Prokop M, de Hoop B, Viergever MA, Pluim JPW, van Ginneken B (2010) Automatic segmentation of pulmonary lobes robust against incomplete fissures. IEEE Trans Med Imag 29(6):1286–1296
Wielpütz MO, Kauczor H-U (2012) MRI of the lung: state of the art. Diagn Interv Radiol 18(4):344–353
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by the Competence Network Asthma/COPD funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (FKZ 01GI0881-0888). Patient data are courtesy of University Hospital Heidelberg.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohlmann, P., Strehlow, J., Jobst, B. et al. Automatic lung segmentation method for MRI-based lung perfusion studies of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J CARS 10, 403–417 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1090-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-014-1090-0