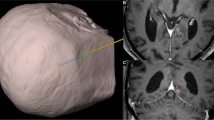
Abstract
Purpose
Flat-detector CT can be integrated with C-arm fluoroscopy for CT-guided neurosurgical and endovascular procedures. We studied the accuracy of this technique with laser assistance in targeting intracranial lesions in a cranial model.
Methods
An acrylic scale-model skull containing foam parenchyma was embedded with 2.16-mm-diameter targets. A flat-detector CT was acquired and registered to the skull’s position. Ten targets were accessed with biopsy needles under fluoroscopic guidance, flat-detector CT overlay, and laser assistance. Accuracy was measured from the needle tip to the target center using flat-detector CT.
Results
Ten targets were accessed successfully using XperGuide software. Needles were placed within 1.30 \(\pm \) 0.63 mm of target isocenter. Accuracy did not vary by entry site, operator, location, or lesion depth.
Conclusions
Laser-assisted flat-detector CT-guided targeting of all intracranial targets was successful with excellent accuracy. This technique can be applied to other minimally invasive neurosurgical procedures.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Braak SJ, van Strijen MJ, van Es HW, Nievelstein RA, van Heesewijk JP (2011) Effective dose during needle interventions: cone-beam CT guidance compared with conventional CT guidance. J Vasc Interv Radiol 22:455–461
Brommeland T, Hennig R (2000) A new procedure for frameless computer navigated stereotaxy. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:443–447 (discussion 447–448)
Brommeland T, Hennig R (2000) Mechanical accuracy of a new stereotactic guide. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 142:449–454
Cooke DL, Levitt M, Kim LJ, Hallam DK, Ghodke B (2010) Intraorbital access using fluoroscopic flat panel detector CT navigation and three-dimensional MRI overlay. J NeuroInterv Surg 2:249–251
Cooke DL, Levitt M, Kim LJ, Hallam DK, Ghodke B (2011) Transcranial access using fluoroscopic flat panel detector CT navigation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:E69–E70
Daly M, Siewerdsen J, Moseley D, Jaffray D, Irish J (2006) Intraoperative cone-beam CT for guidance of head and neck surgery: assessment of dose and image quality using a C-arm prototype. Med Phys 33:3767–3780
Damet J, Sans-Merce M, Miéville F, Becker M, Poletti PA, Verdun FR, Baechler S (2010) Comparison of organ doses and image quality between CT and flat panel XperCT scans in wrist and inner ear examinations. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 139:164–168
Doelken M, Struffert T, Richter G, Engelhorn T, Nimsky C, Ganslandt O, Hammen T, Doerfler A (2008) Flat-panel detector volumetric CT for visualization of subarachnoid hemorrhage and ventricles: preliminary results compared to conventional CT. Neuroradiology 50:517–523
Heran N, Song J, Namba K, Smith W, Niimi Y, Berenstein A (2006) The utility of DynaCT in neuroendovascular procedures. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:330–332
Kettenbach J, Kara L, Toporek G, Fuerst M, Kronreif G (2014) A robotic needle-positioning and guidance system for CT-guided puncture: Ex vivo results. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol 23:271–278
Kim I, Son B, Lee S, Sung J, Hong J (2007) Comparison of frame-based and frameless stereotactic hematoma puncture and subsequent fibrinolytic therapy for the treatment of supratentorial deep seated spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 50:86–90
Levitt MR, Vaidya SS, Su DK, Moe KS, Kim LJ, Sekhar LN, Hallam DK, Ghodke BV (2013) The riple-overlay technique for percutaneous diagnosis and treatment of lesions of the head and neck: combined three-dimensional guidance with magnetic resonance imaging, cone-beam computed tomography, and fluoroscopy. World Neurosurg 79:509–514
Li Q, Zamorano L, Pandya A, Perez R, Gong J, Diaz F (2002) The application accuracy of the NeuroMate robot-A quantitative comparison with frameless and frame-based surgical localization systems. Comput Aided Surg 7:90–98
Miracle AC, Mukherji SK (2009) Conebeam CT of the head and neck, part 1: physical principles. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1088–1095
Nesbit GM, Nesbit EG, Hamilton BE (2011) Integrated cone-beam CT and fluoroscopic navigation in treatment of head and neck vascular malformations and tumors. J Neurointerv Surg 3:186–190
Nett B, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Serarslan Y, Başkaya M, Chen G (2010) A simple technique for interventional tool placement combining fluoroscopy with interventional computed tomography on a C-arm system. Neurosurgery 67:49–56 (discussion 56–47)
Paleologos T, Dorward N, Wadley J, Thomas D (2014) Clinical validation of true frameless stereotactic biopsy: analysis of the first 125 consecutive cases. Neurosurgery 49:830–835 (discussion 835–837)
Quiñones-Hinojosa A, Ware M, Sanai N, McDermott M (2006) Assessment of image guided accuracy in a skull model: comparison of frameless stereotaxy techniques vs. frame-based localization. J Neurooncol 76:65–70
Racadio J, Babic D, Homan R, Rampton J, Patel M, Johnson N (2007) Live 3D guidance in the interventional radiology suite. AJR Am J Roentgenol 189:W357–W364
Ringel F, Ingerl D, Ott S, Meyer B (2009) VarioGuide: a new frameless image-guided stereotactic system–accuracy study and clinical assessment. Neurosurgery 64:365–371 (discussion 371–363)
Spelle L, Ruijters D, Babic D, Homan R, Mielekamp P, Guillermic J, Moret J (2009) First clinical experience in applying XperGuide in embolization of jugular paragangliomas by direct intratumoral puncture. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 4:527–533
Söderman M, Babic D, Holmin S, Andersson T (2008) Brain imaging with a flat detector C-arm : technique and clinical interest of XperCT. Neuroradiology 50:863–868
Tam A, Mohamed A, Pfister M, Chinndurai P, Rohm E, Hall A, Wallace MJ (2010) C-arm cone beam computed tomography needle path overlay for fluoroscopic guided vertebroplasty. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 35:1095–1099
Wang C, Nguyen G, Toncheva G, Jiang X, Ferrell A, Smith T, Yoshizumi T (2014) Evaluation of patient effective dose of neurovascular imaging protocols for C-arm cone-beam CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 202:1072–1077
Widmann G, Eisner W, Kovacs P, Fiegele T, Ortler M, Lang TB, Stoffner R, Bale R (2008) Accuracy and clinical use of a novel aiming device for frameless stereotactic brain biopsy. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 51:361–369
Widmann G, Stoffner R, Sieb M, Bale R (2009) Target registration and target positioning errors in computer-assisted neurosurgery: proposal for a standardized reporting of error assessment. Int J Med Robot 5:355–365
Willems P, Noordmans H, Ramos L, Taphoorn M, Berkelbach van der Sprenkel J, Viergever M, Tulleken CA (2003) Clinical evaluation of stereotactic brain biopsies with an MKM-mounted instrument holder. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:889–897 (discussion 897)
Yang Z, Hong B, Jia Z, Chen J, Ge J, Han J, Beilner J, Zhang Y, Fang Y, Liu J (2014) Treatment of supratentorial spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage using image-guided minimally invasive surgery: Initial experiences of a flat detector CT-based puncture planning and navigation system in the angiographic suite. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 35:2170–2175
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was not funded by any grant or outside entity.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
This article does not contain patient data.
Additional information
Daniel L. Cooke and Michael R. Levitt contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cooke, D.L., Levitt, M.R., Kim, L.J. et al. Laser-assisted flat-detector CT-guided intracranial access. Int J CARS 11, 467–472 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1271-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-015-1271-5