Abstract
Purpose
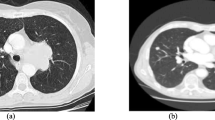
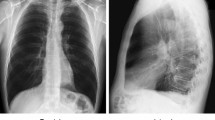
Our particular motivator is the need for screening HIV+ populations in resource-constrained regions for the evidence of tuberculosis, using posteroanterior chest radiographs (CXRs).
Method
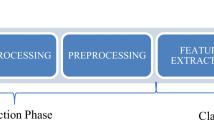
The proposed method is motivated by the observation that abnormal CXRs tend to exhibit corrupted and/or deformed thoracic edge maps. We study histograms of thoracic edges for all possible orientations of gradients in the range \([0, 2\pi )\) at different numbers of bins and different pyramid levels, using five different regions-of-interest selection.
Results
We have used two CXR benchmark collections made available by the U.S. National Library of Medicine and have achieved a maximum abnormality detection accuracy (ACC) of 86.36 % and area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.93 at 1 s per image, on average.
Conclusion
We have presented an automatic method for screening pulmonary abnormalities using thoracic edge map in CXR images. The proposed method outperforms previously reported state-of-the-art results.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Chest x-ray screening project at the US National Library of Medicine (URL: http://lhncbc.nlm.nih.gov/project/computer-aided-tb-screening-chest-x-rays).
References
World Health Organization (WHO), global tuberculosis report (2014)
Kumar V, Abbas A, Fausto N, Mitchell R (2007) Robbins BasicPathology. ser. Robbins Pathology. Elsevier Health Sciences
Panteix G, Gutierrez MC, Boschiroli ML, Rouviere M, Plaidy A, Pressac D, Porcheret H, Chyderiotis G, Ponsada M, Oortegem KV, Salloum S, Cabuzel S, Banuls AL, de Perre PV, Godreuil S (2010) Pulmonary tuberculosis due to Mycobacterium microti: a study of six recent cases in France. J Med Microbiol 59:984–989
(2006) Diagnostics for tuberculosis : global demand and market potential. World Health Organization on behalf of the Special Programme for Research and Training in Tropical Diseases Geneva, p 36
(2011) Tuberculosis: clinical diagnosis and management of tuberculosis, and measures for its prevention and control. NICE Clinical Guideline 117: Tuberculosis
Boehme CC, Nabeta P (2010) Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampin resistance. N Engl J Med 363(11):1005–1015
Seoudi N, Mitchell S, Brown T, Dashti F, Amin A, Drobniewski F (2012) Rapid molecular detection of tuberculosis and rifampicin drug resistance: retrospective analysis of a national uk molecular service over the last decade. Thorax 67:361–367
(2006) Improving the diagnosis and treatment of smear-negative pulmonary and extrapulmonary tuberculosis among adults and adolescents: recommendations for HIV-prevalent and resource-constrained settings. World Health Organization Geneva
Schaefer-Prokop C, Neitzel U, Venema H, Uffmann M, Prokop M (2008) Digital chest radiography: an update on modern technology, dose containment and control of image quality. Eur Radiol 18(9):1818–1830
van Ginneken B, Ter Haar Romeny B, Viergever M (2001) Computer-aided diagnosis in chest radiography: a survey. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(12):1228–1241
van Ginneken B, Hogeweg L, Prokop M (2009) Computer-aided diagnosis in chest radiography: beyond nodules. Eur J Radiol 72(2):226–230
Lodwick GS (1966) Computer-aided diagnosis in radiology: a research plan. Invest Radiol 1(1):72
Sakai S, Soeda H, Takahashi N, Okafuji T, Yoshitake T, Yabuuchi H, Yoshino I, Yamamoto K, Honda H, Doi K (2006) Computer-aided nodule detection on digital chest radiography: validation test on consecutive T1 cases of resectable lung cancer. J Digit Imag 19(4):376–382
Freedman MT, Lo S-CB, Seibel JC, Bromley CM (2011) Lung nodules: improved detection with software that suppresses the rib and clavicle on chest radiographs. Radiology 260(1):265–273
Shen R, Cheng I, Basu A (2010) A hybrid knowledge-guided detection technique for screening of infectious pulmonary tuberculosis from chest radiographs. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 57(11):2646–2656
van Ginneken B, Katsuragawa S, ter Haar Romeny BM, Doi K, Viergever MA (2002) Automatic detection of abnormalities in chest radiographs using local texture analysis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21(2):139–149
Hogeweg L, Mol C, de Jong PA, Dawson R, Ayles H, van Ginneken B (2010) Fusion of local and global detection systems to detect tuberculosis in chest radiographs. In: 13th international conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 650–657
Jaeger S, Karargyris A, Candemir S, Folio L, Siegelman J, Callaghan FM, Xue Z, Palaniappan K, Singh RK, Antani S, Thoma GR, Wang Y, Lu P, McDonald CJ (2014) Automatic tuberculosis screening using chest radiographs. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(2):233–245
Dalal N, Triggs B (2005) Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: IEEE conference on computer visual and pattern recognition, pp 886–893
Chaisson RE, Martinson NA (2008) Tuberculosis in Africa combating an HIV-driven crisis. N Engl J Med 358(11):1089–1092
Santosh KC, Vajda S, Antani S, Thoma G (2015) Automatic pulmonaryabnormality screening using thoracic edge map. IEEE, Sao Carlos, Brazil
Candemir S, Jaeger S, Musco J, Xue Z, Karargyris A, Antani S, Thoma G, Palaniappan K (2014) Lung segmentation in chest radiograps using anatomical atlases with non-rigid registration. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 33(2):577–590
Jones R, Soille P (1996) Periodic lines: Definition, cascades, and application to granulometrie. Pattern Recognit Lett 17(8):1057–1063
Canny J (1986) A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 8(6):679–698
Opelt A, Pinz A, Zisserman A (2006) Incremental learning of object detectors using a visual shape alphabet. In: IEEE conference on computer visual and pattern recognition, vol 1, pp 3–10
Bosch A, Zisserman A, Munoz X (2007) Representing shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In: ACM international conference on image and video retrieval, pp 401–408
Lazebnik S, Schmid C, Ponce J (2006) Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In: IEEE conference on computer visual and pattern recognition, pp 2169–2178
Bishop CM (1995) Neural networks for pattern recognition. Oxford University Press Inc, New York
Fawcett T (2006) An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit Lett 27(8):861–874
Karargyris A, Siegelman J, Tzortzis D, Jaeger S, Candemir S, Xue Z, Santosh KC, Vajda S, Antani SK, Folio L, Thoma GR (2016) Combination of texture and shape features to detect pulmonary abnormalities in digital chest X-rays. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(1):99–106
Chauhan A, Chauhan D, Rout C (2014) Role of Gist and PHOG features in computer-aided diagnosis of tuberculosis without segmentation. PLoS ONE 9(11):e112980
Santosh KC, Candemir S, Jaeger S, Karargyris A, Antani S, Thoma GR, Folio L (2015) Automatically detecting rotation in chest radiographs using principal rib-orientation measure for quality control. Intern J Pattern Recognit Artif Intell 29(2):1557001
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Library of Medicine (NLM) and Lister Hill National Center for Biomedical Communications (LHNCBC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K.C. Santosh, Szilárd Vajda, Sameer Antani and George R Thoma declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical standards
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santosh, K.C., Vajda, S., Antani, S. et al. Edge map analysis in chest X-rays for automatic pulmonary abnormality screening. Int J CARS 11, 1637–1646 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1359-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-016-1359-6