Abstract
Purpose
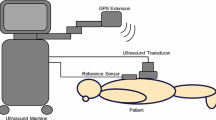
Epidural and spinal needle insertions, as well as facet joint denervation and injections are widely performed procedures on the lumbar spine for delivering anesthesia and analgesia. Ultrasound (US)-based approaches have gained popularity for accurate needle placement, as they use a non-ionizing, inexpensive and accessible modality for guiding these procedures. However, due to the inherent difficulties in interpreting spinal US, they yet to become the clinical standard-of-care.
Methods
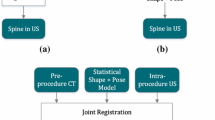
A novel statistical shape \(+\) pose \(+\) scale (s \(+\) p \(+\) s) model of the lumbar spine is jointly registered to preoperative magnetic resonance (MR) and US images. An instance of the model is created for each modality. The shape and scale model parameters are jointly computed, while the pose parameters are estimated separately for each modality.
Results
The proposed method is successfully applied to nine pairs of preoperative clinical MR volumes and their corresponding US images. The results are assessed using the target registration error (TRE) metric in both MR and US domains. The s \(+\) p \(+\) s model in the proposed joint registration framework results in a mean TRE of 2.62 and 4.20 mm for MR and US images, respectively, on different landmarks.
Conclusion
The joint framework benefits from the complementary features in both modalities, leading to significantly smaller TREs compared to a model-to-US registration approach. The s \(+\) p \(+\) s model also outperforms our previous shape \(+\) pose model of the lumbar spine, as separating scale from pose allows to better capture pose and guarantees equally-sized vertebrae in both modalities. Furthermore, the simultaneous visualization of the patient-specific models on the MR and US domains makes it possible for clinicians to better evaluate the local registration accuracy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdi S, Datta S, Lucas LF (2005) Role of epidural steroids in the management of chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of effectiveness and complications. Pain Phys 8(1):127–143
Ahmed MN, Yamany SM, Mohamed N, Farag AA, Moriarty T (2002) A modified fuzzy C-means algorithm for bias field estimation and segmentation of MRI data. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 21(3):193–199
Behnami D, Seitel A, Rasoulian A, Anas EMA, Lessoway VA, Osborn J, Rohling R, Abolmaesumi P (2016) Joint registration of ultrasound, CT and a shape \(+\) pose statistical model of the lumbar spine for guiding anesthesia. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 30(9):1–10
Bø LE, Palomar R, Selbekk T, Reinertsen I (2014) Registration of mr to percutaneous ultrasound of the spine for image-guided surgery. In: Yao J, Klinder T, Li S (eds) Computational methods and clinical applications for spine imaging. Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics, vol 17. Springer, Berlin, pp 209–218
Boisvert J, Cheriet F, Pennec X, Labelle H, Ayache N (2008) Articulated spine models for 3D reconstruction from partial radiographic data. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 55(11):2565–2574
Boswell MV, Colson JD, Spillane WF (2005) Therapeutic facet joint interventions in chronic spinal pain: a systematic review of effectiveness and complications. Pain Phys 8(1):101–114
Brendel B, Winter S, Rick A, Stockheim M, Ermert H (2002) Registration of 3D CT and ultrasound datasets of the spine using bone structures. Comput Aided Surg 7(3):146–155
Brudfors M, Seitel A, Rasoulian A, Lasso A, Lessoway VA, Osborn J, Maki A, Rohling RN, Abolmaesumi P (2015) Towards real-time, tracker-less 3D ultrasound guidance for spine anaesthesia. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12:1–11
Center P, Covington L, Parr A (2009) Lumbar interlaminar epidural injections in managing chronic low back and lower extremity pain: a systematic review. Pain Phys 12(1):163–188
Chen EC, Mousavi P, Gill S, Fichtinger G, Abolmaesumi P (2010) Ultrasound guided spine needle insertion. In: SPIE medical imaging. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham, p. 762538
Conroy PH, Luyet C, McCartney CJ, McHardy PG (2013) Real-time ultrasound-guided spinal anaesthesia: a prospective observational study of a new approach. Anesthesiol Res Pract 2013:7. doi:10.1155/2013/525818
Gill S, Abolmaesumi P, Fichtinger G, Boisvert J, Pichora D, Borshneck D, Mousavi P (2012) Biomechanically constrained groupwise ultrasound to CT registration of the lumbar spine. Med Image Anal 16(3):662–674
Hacihaliloglu I, Rasoulian A, Rohling RN, Abolmaesumi P (2013) Statistical shape model to 3D ultrasound registration for spine interventions using enhanced local phase features. In: Mori k, Sakuma I, Sato Y, Barillot C, Navab N (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI 2013. LNCS, vol. 8150. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 361–368. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-40763-5
Khallaghi S, Mousavi P, Gong RH, Gill S, Boisvert J, Fichtinger G, Pichora D, Borschneck D, Abolmaesumi P (2010) Registration of a statistical shape model of the lumbar spine to 3D ultrasound images. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI 2010. Springer, Berlin, pp 68–75
Liu SS, Strodtbeck WM, Richman JM, Wu CL (2005) A comparison of regional versus general anesthesia for ambulatory anesthesia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesth Analg 101(6):1634–1642
Loizides A, Peer S, Plaikner M, Spiss V, Galiano K, Obernauer J, Gruber H (2011) Ultrasound-guided injections in the lumbar spine. Med Ultrason 13(1):54–58
Moore J, Clarke C, Bainbridge D, Wedlake C, Wiles A, Pace D, Peters T (2009) Image guidance for spinal facet injections using tracked ultrasound. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI 2009. Springer, Berlin, pp 516–523
Niazi A, Chin K, Jin R, Chan V (2014) Real-time ultrasound-guided spinal anesthesia using the SonixGPS ultrasound guidance system: a feasibility study. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 58(7):875–881
de Oliveira Filho GR (2002) The construction of learning curves for basic skills in anesthetic procedures: an application for the cumulative sum method. Anesth Analg 95(2):411–416
Rasoulian A, Rohling R, Abolmaesumi P (2013) Lumbar spine segmentation using a statistical multi-vertebrae anatomical shape \(+\) pose model. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 32(10):1890–1900
Rasoulian A, Rohling RN, Abolmaesumi P (2013) Augmentation of paramedian 3D ultrasound images of the spine. In: Information processing in computer-assisted interventions. Springer, Berlin, pp 51–60
Rasoulian A, Seitel A, Osborn J, Sojoudi S, Nouranian S, Lessoway VA, Rohling RN, Abolmaesumi P (2015) Ultrasound-guided spinal injections: a feasibility study of a guidance system. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 10(9):1417–1425
Rodgers A, Walker N, Schug S, McKee A, Kehlet H, Van Zundert A, Sage D, Futter M, Saville G, Clark T, MacMahon S (2000) Reduction of postoperative mortality and morbidity with epidural or spinal anaesthesia: results from overview of randomised trials. BMJ 321(7275):1493
Rubin DI (2007) Epidemiology and risk factors for spine pain. Neurol Clin 25(2):353–371
Schumann S (2016) State of the art of ultrasound-based registration in computer assisted orthopedic interventions. In: Computational radiology for orthopaedic interventions. Springer, Berlin, pp 271–297
Seitel A, Sojoudi S, Osborn J, Rasoulian A, Nouranian S, Lessoway VA, Rohling RN, Abolmaesumi P (2016) Ultrasound-guided spine anesthesia: feasibility study of a guidance system. Ultrasound Med Biol 42(12):3043–3049
Sprigge J, Harper S (2008) Accidental dural puncture and post dural puncture headache in obstetric anaesthesia: presentation and management: a 23-year survey in a district general hospital. Anaesthesia 63(1):36–43
Suhm N, Jacob A, Nolte LP, Regazzoni P, Messmer P (2000) Surgical navigation based on fluoroscopy clinical application for computer-assisted distal locking of intramedullary implants. Comput Aided Surg 5(6):391–400
Suzani A, Rasoulian A, Fels S, Rohling RN, Abolmaesumi P (2014) Semi-automatic segmentation of vertebral bodies in volumetric MR images using a statistical shape \(+\) pose model. In: SPIE medical imaging. International Society for Optics and Photonics, Bellingham, pp 90,360P–90,360P
Tran D, Kamani AA, Al-Attas E, Lessoway VA, Massey S, Rohling RN (2010) Single-operator real-time ultrasound-guidance to aim and insert a lumbar epidural needle. Can J Anesth/Journal canadien d’anesthésie 57(4):313–321
Ungi T, Abolmaesumi P, Jalal R, Welch M, Ayukawa I, Nagpal S, Lasso A, Jaeger M, Borschneck DP, Fichtinger G, Mousavi P (2012) Spinal needle navigation by tracked ultrasound snapshots. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 59(10):2766–2772
Yan CX, Goulet B, Pelletier J, Chen SJS, Tampieri D, Collins DL (2011) Towards accurate, robust and practical ultrasound-CT registration of vertebrae for image-guided spine surgery. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 6(4):523–537
Yoon SH, OBrien SL, Tran M (2013) Ultrasound guided spine injections: advancement over fluoroscopic guidance? Curr Phys Med Rehabil Rep 1(2):104–113
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research and Council of Canada (NSERC) and in part by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Behnami, D., Sedghi, A., Anas, E.M.A. et al. Model-based registration of preprocedure MR and intraprocedure US of the lumbar spine. Int J CARS 12, 973–982 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1552-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-017-1552-2