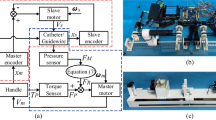
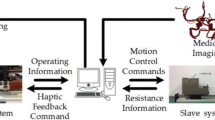
Abstract
Purpose
This paper describes the design, principles, performances, and applications of a novel image-guided master–slave robotic system for vascular intervention (VI), including the performance evaluation and in vivo trials.
Methods
Based on the peer-to-peer (P2P) remote communication system, the kinetics analysis, the sliding-mode neural network self-adaptive control model and the feedback system, this new robotic system can accomplish in real time a number of VI operations, including guidewire translation and rotation, balloon catheter translation, and contrast agent injection. The master–slave design prevents surgeons from being exposed to X-ray radiation, which means that they are not required to wear a heavy lead suit. We also conducted a performance evaluation of the new system, which assessed the speed, position tracking, and accuracy, as well as in vivo swine trials.
Results
The speed and position tracking effects are really good, which contribute to the high level of performance in terms of the translational (error ≤ 0.45%) and rotational (error ≤ 2.6°) accuracy. In addition, the accuracy of the contrast agent injection is less than 0.2 ml. The robotic system successfully performed both the stent revascularization of an arteria carotis and four in vivo trials. The haptic feedback data correspond with the robotic-assisted procedure, and peaks and troughs of data occur regularly.
Conclusions
By means of the performance evaluation and four successful in vivo trials, the feasibility and efficiency of the new robotic system are validated, which should prove helpful for further research.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Venketasubramanian N, Yoon BW, Pandian J, Navarro JC (2017) Stroke epidemiology in south, east, and South-East Asia: a review. J Stroke 19(3):286–294
World Health Organization (2017) World health statistics 2017: monitoring health for the SDGs. World Health Organization, Geneva
Rafii-Tari H, Payne CJ, Yang GZ (2014) Current and emerging robot-assisted endovascular catheterization technologies: a review. Ann Biomed Eng 42(4):697–715
Lin JC (2013) The role of robotic surgical system in the management of vascular disease. Ann Vasc Surg 27(7):976–983
Da L, Zhang D, Wang T (2008) Overview of the vascular interventional robot. Int J Med Robot Comp 4(4):289
Daneshmand M, Bilici O, Bolotnikova A, Anbarjafari G (2017) Medical robots with potential applications in participatory and opportunistic remote sensing: a review. Robot Auton Syst 95:160–180
Arai F, Fujimura R, Fukuda T, Negoro M (2002) New catheter driving method using linear stepping mechanism for intravascular neurosurgery. In: IEEE ICRA, 2002. Proceedings, Vol 3, pp 2944–2949
Xiao N, Guo J, Guo S, Tamiya T (2012) A robotic catheter system with real-time force feedback and monitor. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 35(3):283–289
Guo S, Kondo H, Wang J, Guo J, Tamiya T (2007) A new catheter operating system for medical applications. In: IEEE/ICME, pp 82–86
Srimathveeravalli G, Kesavadas T, Li X (2010) Design and fabrication of a robotic mechanism for remote steering and positioning of interventional devices. Int J Med Robot Comp 6(2):160–170
Aoide N, Hansen, Sensei (2012) Hansen medical. Sensei X robotic catheter system. http://dev-hansen.pantheonsite.io/us/en/cardiacarrhythmia/sensei-robotic-system/product-overview
Romo E, Hart SJ, Covington T (2016) Low friction instrument driver interface for robotic systems [P]. US 20160338783 A1
Pankratov MM (2011) Robotically assisted PCI with CorPath 200 system: early evidence of potential benefits for patient and physician. Cardiovasc Revasc Med 12(3):e40–e40
Pedersen A (2011) Trial to evaluate CorPath robotic system for PCI. Med Device Daily 15(18):1
Granada JF, Delgado JA, Uribe MP, Fernandez A, Blanco G, Leon MB, Weisz Giora (2011) First-in-human evaluation of a novel robotic-assisted coronary angioplasty system. JACC-Cardiovasc Interv 4(4):460–465
Khan EM, Ng GA, Neelagaru S, Abi-Samra FM, Lee J, Giudici M, Gohn D, Winkle RA, Sussman J, Knight BP, Berman A, Calkins H (2013) First experience with a novel robotic remote catheter system: amigo™ mapping trial. J Interv Card Electr 37(2):121–129
Won JY, Yi BJ, Cha HJ (2016) Review of new master/slave catheter driving vascular intervention robot system: intervention radiologist’s perspective. HMR 36(4):225
Shen H, Wang C, Xie L, Zhou S, Gu L, Xie H (2018) A novel remote-controlled robotic system for cerebrovascular intervention. Int J Med Robot Comput Assist Surg Mrcas, 14: e1943
Zeng Q, Zhou SJ, Shen H, Wang C (2018). A network communication protocols for robotic-assisted vascular intervention systems. BST
Li Zi-Yan, Jing-Li Fu, Chen Li-Qun (2009) Euler–lagrange equation from nonlocal-in-time kinetic energy of nonconservative system. Phys Lett A 374(2):106–109
Bai Z (2004) Study of a 3-dof parallel manipulator dynamics based on lagrange’s equation. J B Univ Aeronaut Astronaut 30(1):51–54
Xia HY, Zhan WB (2003) Application and development expression of lagrange equation. J Luoyang Teach Coll 2:27–29
Edwards C, Spurgeon S (1998) Sliding mode control: theory and applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Utkin VI, Chang HC (2007) Sliding mode control on electro-mechanical systems. Math Probl Eng 8(4–5):451–473
Liu J, Wang X (2011) Advanced sliding mode control for mechanical systems. Tsinghua University Press, Springer, Berlin
Liu J (2013) Radial basis function (rbf) neural network control for mechanical systems. Springer, Berlin, pp 19–53
Seshagiri S, Khalil HK (2000) Output feedback control of nonlinear systems using RBF neural networks. In: Proceedings of the ACC, 1999, Vol 11, pp 2808–2812
Welch G, Bishop G (1995). An introduction to the kalman filter. Course Notes 8 of ACM SIGGRAPH 2001, 8(7): 127–132
Evensen G (2003) The ensemble kalman filter: theoretical formulation and practical implementation. Ocean Dyn 53(4):343–367
Brown RG, Hwang PYC (1997) Introduction to random signals and applied Kalman filtering: with MATLAB exercises and solutions. Wiley, New York
Ovando-Shelley E, Santoyo E, de Oliveir M (2013) Intervention techniques. Geotechnical engineering for the preservation of monuments and historic sites, pp 75–91
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, No. 2015AA043203), Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61672341, 61471349), The project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai municipality (No. 17441903800), The project of major program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 61190124, 61190120), Basic Discipline Layout Project of Shenzhen City (No. JCYJ20150731154850923).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The authors declare that all human and animal studies have been approved and performed in accordance with ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, H., Wang, C., Xie, L. et al. A novel robotic system for vascular intervention: principles, performances, and applications. Int J CARS 14, 671–683 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-018-01906-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-018-01906-w