Abstract
Purpose
High mortality rate due to liver cirrhosis has been reported over the globe in the previous years. Early detection of cirrhosis may help in controlling the disease progression toward hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The lack of trained CT radiologists and increased patient population delays the diagnosis and further management. This study proposes a computer-aided diagnosis system for detecting cirrhosis and HCC in a very efficient and less time-consuming approach.
Methods
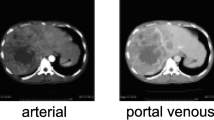
Contrast-enhanced CT dataset of 40 patients (n = 40; M:F = 5:3; age = 25–55 years) with three groups of subjects: healthy (n = 14), cirrhosis (n = 12) and cirrhosis with HCC (n = 14), were retrospectively analyzed in this study. A novel method for the automatic 3D segmentation of liver using modified region-growing segmentation technique was developed and compared with the state-of-the-art deep learning-based technique. Further, histogram parameters were calculated from segmented CT liver volume for classification between healthy and diseased (cirrhosis and HCC) liver using logistic regression. Multi-phase analysis of CT images was performed to extract 24 temporal features for detecting cirrhosis and HCC liver using support vector machine (SVM).
Results
The proposed method produced improved 3D segmentation with Dice coefficient 90% for healthy liver, 86% for cirrhosis and 81% for HCC subjects compared to the deep learning algorithm (healthy: 82%; cirrhosis: 78%; HCC: 70%). Standard deviation and kurtosis were found to be statistically different (p < 0.05) among healthy and diseased liver, and using logistic regression, classification accuracy obtained was 92.5%. For detecting cirrhosis and HCC liver, SVM with RBF kernel obtained highest slice-wise and patient-wise prediction accuracy of 86.9% (precision = 0.93, recall = 0.7) and 80% (precision = 0.86, recall = 0.75), respectively, than that of linear kernel (slice-wise: accuracy = 85.4%, precision = 0.92, recall = 0.67; patient-wise: accuracy = 73.33%, precision = 0.75, recall = 0.75).
Conclusions
The proposed computer-aided diagnosis system for detecting cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) showed promising results and can be used as effective screening tool in medical image analysis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM et al (2011) Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 61:69–90
Mokdad AA, Lopez AD, Shahraz S et al (2014) A systematic analysis. BMC Med 12:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-014-0145-y
Zhang XF, Meng B, Qi X et al (2009) Prognostic factors after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with hepatitis B virus-related cirrhosis: the surgeon’s role in survival. Eur J Surg Oncol 35:622–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejso.2008.08.003
Egger J (2013) Manual refinement system for graph-based segmentation results in the medical domain. J Med Syst 36:2829–2839. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10916-011-9761-7.Manual
Campadelli P, Casiraghi E, Esposito A (2009) Liver segmentation from computed tomography scans: a survey and a new algorithm. Artif Intell Med 45:185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2008.07.020
Heimann T, Van Ginneken B, Styner MA et al (2009) Comparison and evaluation of methods for liver segmentation from CT datasets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:1251–1265. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2009.2013851
Zhou JY, Wong DWK, Ding F et al (2010) Liver tumour segmentation using contrast-enhanced multi-detector CT data: performance benchmarking of three semiautomated methods. Eur Radiol 20:1738–1748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-010-1712-z
Kumar SS, Moni RS, Rajeesh J (2013) Automatic liver and lesion segmentation: a primary step in diagnosis of liver diseases. Signal Image Video Process 7:163–172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-011-0223-y
Ruskó L, Bekes G, Németh G, Fidrich M (2007) Fully automatic liver segmentation for contrast-enhanced CT images MICCAI Wshp 3D segmentation. Clin A Gd Chall 2:143–150
Zhao Y, Zan Y, Wang X, Li G (2010) Fuzzy C-means clustering-based multilayer perceptron neural network for liver CT images automatic segmentation. Chin Control Decis Conf CCDC 2010:3423–3427. https://doi.org/10.1109/CCDC.2010.5498558
Goryawala M, Gulec S, Bhatt R et al (2014) A low-interaction automatic 3D liver segmentation method using computed tomography for selective internal radiation therapy. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/198015
Conze P, Noblet V, Rousseau F, et al (2016) Random forests on hierarchical multi-scale supervoxels for liver tumor segmentation in dynamic contrast-enhanced CT scans. In: 2016 IEEE 13th International symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI), pp 416–419
Moghbel M, Mashohor S, Mahmud R, Saripan BMI (2016) Automatic liver segmentation on computed tomography using random walkers for treatment planning. EXCLI J 15:500–517
Wu W, Zhou Z, Wu S, Zhang Y (2016) Automatic liver segmentation on volumetric CT images using supervoxel-based graph cuts. Comput Math Methods Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9093721
Hoogi A, Subramaniam A, Veerapaneni R, Rubin DL (2017) Adaptive estimation of active contour parameters using convolutional neural networks and texture analysis. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 36:781–791. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2016.2628084
Chan TF, Vese LA (1977) Donald Middleton, LDS Br Dent. J 142:73. https://doi.org/10.1109/83.902291
Mala K, Sadasivam V (2005) Automatic segmentation and classification of diffused liver diseases using wavelet based texture analysis and neural network. In: Proceedings INDICON 2005 An International Conference IEEE India Council, 2005, pp 216–219. https://doi.org/10.1109/INDCON.2005.1590158
Luo S, Hu Q, He X et al (2009) Automatic liver parenchyma segmentation from abdominal CT images using support vector machines. ICME Int Conf Complex Med Eng C. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICCME.2009.4906625
Christ PF, Elshaer MEA, Ettlinger F, et al (2016) Automatic liver and lesion segmentation in CT using cascaded fully convolutional neural networks and 3D conditional random fields. Lecture notes computer science (including subset lecture notes artificial intelligence lecture notes bioinformatics) 9901 LNCS:415–423. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-46723-8_48
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention—MICCAI, pp 234–241
Hameed RS, KS S (2012) Assessment of neural network based classifiers to diagnose focal liver lesions using CT images. Proc Eng 38:4048–4056. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2012.06.464
Stoitsis J, Valavanis I, Mougiakakou SG et al (2006) Computer aided diagnosis based on medical image processing and artificial intelligence methods. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res 569:591–595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nima.2006.08.134
Mougiakakou SG, Valavanis IK, Nikita A, Nikita KS (2007) Differential diagnosis of CT focal liver lesions using texture features, feature selection and ensemble driven classifiers. Artif Intell Med 41:25–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2007.05.002
Chen Y, Luo J, Dong C et al (2013) Computer-aided diagnosis and quantification of cirrhotic livers based on morphological analysis and machine learning. Comput Math Methods Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/264809
Bilello M, Gokturk SB, Desser T et al (2004) Automatic detection and classification of hypodense hepatic lesions on contrast-enhanced venous-phase CT. Med Phys 31:2584–2593. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.1782674
Ruskó L, Perényi Á (2014) Automated liver lesion detection in CT images based on multi-level geometric features. Int J CARS 9:577–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0949-9
Quatrehomme A, Millet I, Hoa D, et al (2012) Assessing the classification of liver focal lesions by using multi-phase computer tomography scans. In: MICCAI international workshop on medical content-based retrieval for clinical decision support, pp 80–91
Duda D, Krętowski M, Bezy-wendling J (2006) Texture characterization for hepatic tumor recognition in multiphase CT. Biocybern Biomed Eng 26:15–24
Ye J, Sun Y, Wang S, et al (2009) Multi-phase CT image based hepatic lesion diagnosis by SVM. In: 2nd IEEE international conference on biomedical engineering and informatics, pp 1–5
Chi Y, Zhou J, Venkatesh KS et al (2013) Computer-aided focal liver lesion detection. Int J CARS 8:511–525. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-013-0832-8
Soler L, Hostettler A, Agnus V, et al (2012) 3D Image reconstruction for comparison of algorithm database : a patient-specific anatomical and medical image database, p 67091
Gonzalez and Woods Image Processing 2 edition.pdf
Chen Y, Wang Z, Zhao W, Yang X (2009) Liver segmentation from CT images based on region growing method. In: 3rd International conference on bioinformatics and biomedical engineering, Beijing, pp 1–4. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICBBE.2009.5163018
Tsiprin MG, Irgen LA, Kerch GM, Silis YY (1980) Apparatus for isometric heating and thermomechanical testing of films and fibers. Mech Compos Mater 15:649–651. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00605598
Lee JH, Lee JM, Kim SJ et al (2012) Enhancement patterns of hepatocellular carcinomas on multiphasic multidetector row CT: comparison with pathological differentiation. Br J Radiol 85:e573–e583. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr/86767895
Marrero JA, Ahn J, Reddy RK (2014) ACG clinical guideline: the diagnosis and management of focal liver lesions. Am J Gastroenterol 109:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2014.213
Achanta R, Shaji A, Smith K et al (2012) SLIC superpixels compared to state-of-the-art superpixel methods. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 34:2274–2281. https://doi.org/10.1109/TPAMI.2012.120
Lloyd SP (1982) Least squares quantization in PCM. IEEE Trans Inf Theory 28:129–137. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIT.1982.1056489
Cortes C, Vapnik V (1995) Supprot-vector networks. Mach Learn 297:273–297. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0285.2009.00840.x
Pedregosa F, Weiss R, Brucher M (2011) Nscep 12:2825–2830. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13398-014-0173-7.2
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose regarding this study. AN performed this study during his stay at IIT Delhi. AN is currently employed with IBM Research, India.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nayak, A., Baidya Kayal, E., Arya, M. et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma using multi-phase abdomen CT. Int J CARS 14, 1341–1352 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-019-01991-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-019-01991-5