Abstract
Purpose
As some of the most important factors for treatment decision of lung cancer (which is the deadliest neoplasm) are staging and histology, this work aimed to associate quantitative contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) features from malignant lung tumors with distant and nodal metastases (according to clinical TNM staging) and histopathology (according to biopsy and surgical resection) using radiomics assessment.
Methods
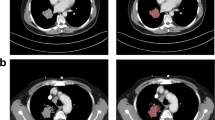
A local cohort of 85 patients were retrospectively (2010–2017) analyzed after approval by the institutional research review board. CT images acquired with the same protocol were semiautomatically segmented by a volumetric segmentation method. Tumors were characterized by quantitative CT features of shape, first-order, second-order, and higher-order textures. Statistical and machine learning analyses assessed the features individually and combined with clinical data.
Results
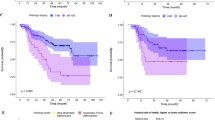
Univariate and multivariate analyses identified 40, 2003, and 45 quantitative features associated with distant metastasis, nodal metastasis, and histopathology (adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma), respectively. A machine learning model yielded the highest areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves of 0.92, 0.84, and 0.88 to predict the same previous patterns.
Conclusion
Several radiomic features (including wavelet energies, information measures of correlation and maximum probability from co-occurrence matrix, busyness from neighborhood intensity-difference matrix, directionalities from Tamura’s texture, and fractal dimension estimation) significantly associated with distant metastasis, nodal metastasis, and histology were discovered in this work, presenting great potential as imaging biomarkers for pathological diagnosis and target therapy decision.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wong MC, Lao XQ, Ho KF, Goggins WB, Tse SLA (2017) Incidence and mortality of lung cancer: global trends and association with socioeconomic status. Sci Rep 7:14300
Howlader N, Noone AM, Krapcho M, Miller D, Bishop K, Altekruse SF, Kosary CL, Yu M, Ruhl J, Tatalovich Z, Mariotto A, Lewis DR, Chen HS, Feuer EJ, Cronin KA (2016) SEER cancer statistics review, 1975–2013. www.seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2013/. Accessed 22 July 2019
Cooper WA, O’Toole S, Boyer M, Horvath L, Mahar A (2011) What’s new in non-small cell lung cancer for pathologists: the importance of accurate subtyping, EGFR mutations and ALK rearrangements. Pathology 43:103–115
Koenigkam-Santos M, Muley T, Warth A, Paula W, Lederlin M, Schnabel P, Schlemmer HP, Kauczor HU, Heussel CP, Puderbach M (2014) Morphological computed tomography features of surgically resectable pulmonary squamous cell carcinomas: impact on prognosis and comparison with adenocarcinomas. Eur J Radiol 83:1275–1281
Tailor TD, Schmidt RA, Eaton KD, Wood D, Pipavath S (2015) The pseudocavitation sign of lung adenocarcinoma: a distinguishing feature and imaging biomarker of lepidic growth. J Thorac Imaging 30:308–313
Yip S, Liu Y, Parmar C, Li Q, Liu S, Qu F, Ye Z, Gillies R, Aerts H (2017) Associations between radiologist-defined semantic and automatically computed radiomic features in non-small cell lung cancer. Sci Rep 7:3519
Giger M (2018) Machine learning in medical imaging. J Am Coll Radiol 15:512–520
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278:563–577
Larue RT, Defraene G, Ruysscher De, Lambin P, van Elmpt W (2017) Quantitative radiomics studies for tissue characterization: a review of technology and methodological procedures. Br J Radiol 90:20160665
Aerts H, Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Parmar C, Grossmann P, Carvalho S, Bussink J, Monshouwer R, Haibe-Kains B, Rietveld D, Hoebers F, Rietbergen M, Leemans C, Dekker A, Quackenbush J, Gillies R, Lambin P (2014) Decoding tumour phenotype by noninvasive imaging using a quantitative radiomics approach. Nat Commun 5:4006
Halpenny DF, Plodkowski A, Riely G, Zheng J, Litvak A, Moscowitz C, Ginsberg M (2017) Radiogenomic evaluation of lung cancer—Are there imaging characteristics associated with lung adenocarcinomas harboring BRAF mutations? Clin Imaging 42:147–151
Sacconi B, Anzidei M, Leonardi A, Boni F, Saba L, Scipione R, Anile M, Rengo M, Longo F, Bezzi M, Venuta F, Napoli A, Laghi A, Catalano C (2017) Analysis of CT features and quantitative texture analysis in patients with lung adenocarcinoma: a correlation with EGFR mutations and survival rates. Clin Radiol 72:443–450
Permuth J, Choi J, Balarunathan Y, Kim J, Chen DT, Chen L, Orcutt S, Doepker M, Gage K, Zhang G, Latifi K, Hoffe S, Jiang K, Coppola D, Centeno B, Magliocco A, Li Q, Trevino J, Merchant N, Gillies R, Malafa M (2016) Combining radiomic features with a miRNA classifier may improve prediction of malignant pathology for pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Oncotarget 7:85785
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Cramer J, Finet J, Robin J, Pujol S, Bauer C, Jennings D, Fennessy F, Sonka M, Buatti J, Aylward S, Miller J, Pieper S, Kikinis R (2012) 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the quantitative imaging network. Magn Reson Imaging 30:1323–1341
Egger J, Kapur T, Fedorov A, Pieper S, Miller J, Veeraraghavan H, Freisleben B, Golby A, Nimsky C, Kikinis R (2013) GBM volumetry using the 3D Slicer medical image computing platform. Sci Rep 3:1364
Velazquez E, Parmar C, Jermoumi M, Mak R, van Baardwijk A, Fennessy F, Lewis J, Ruysscher D, Kikinis R, Lambin P, Aerts H (2013) Volumetric CT-based segmentation of NSCLC using 3D-Slicer. Sci Rep 3:3529
Parmar C, Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Jermoumi M, Carvalho S, Mak R, Mitra S, Shankar B, Kikinis R, Haibe-Kains B, Lambin P, Aerts H (2014) Robust radiomics feature quantification using semiautomatic volumetric segmentation. PLoS ONE 9:e102107
Pinter C, Lasso A, Wang A, Jaffray D, Fichtinger G (2012) SlicerRT: radiation therapy research toolkit for 3D Slicer. Med Phys 39:6332–6338
Zhang L, Fried DV, Fave XJ, Hunter L, Yang J, Court L (2015) IBEX: an open infrastructure software platform to facilitate collaborative work in radiomics. Med Phys 42:1341–1353
Lux M, Marques O (2013) Visual information retrieval using Java and LIRE. Morgan & Claypool Publishers, Williston
Schneider C, Rasband W, Eliceiri K (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9:671–675
Frank E, Hall M, Witten I (2016) The WEKA workbench. Online appendix for data mining: practical machine learning tools and techniques. Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington
Zameer A, Arshad J, Khan A, Raja M (2017) Intelligent and robust prediction of short term wind power using genetic programming based ensemble of neural networks. Energy Convers Manag 134:361–372
Ferreira Junior J, Koenigkam-Santos M, Cipriano F, Fabro A, Azevedo-Marques P (2018) Radiomics-based features for pattern recognition of lung cancer histopathology and metastases. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 159:23–30
Emaminejad N, Qian W, Guan Y, Tan M, Qiu Y, Liu H, Zheng B (2016) Fusion of quantitative image and genomic biomarkers to improve prognosis assessment of early stage lung cancer patients. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 63:1034–1043
Coroller T, Grossmann P, Hou Y, Velazquez E, Leijenaar R, Hermann G, Lambin P, Haibe-Kains B, Mak R, Aerts H (2015) CT-based radiomic signature predicts distant metastasis in lung adenocarcinoma. Radiother Oncol 114:345–350
Shroff GS, Benveniste MF, Groot PM, Wu C, Viswanathan C, Papadimitrakopoulou V, Truong M (2017) Targeted therapy and imaging findings. J Thorac Imaging 32:313–322
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, Yang C, Chu D, Saijo N, Sunpaweravong P, Han B, Margono B, Ichinose Y, Nishiwaki Y, Ohe Y, Yang J, Chewaskulyong B, Jiang H, Duffield E, Watkins C, Armour A, Fukuoka M (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin–paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361:947–957
Tamura T, Kurishima K, Nakazawa K, Kagohashi K, Ishikawa H, Satoh H, Hizawa N (2015) Specific organ metastases and survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Clin Oncol 3:217–221
Zhou H, Dong D, Chen B, Fang M, Cheng Y, Gan Y, Zhang R, Zhang L, Zang Y, Liu Z, Zheng H, Li W, Tian J (2018) Diagnosis of distant metastasis of lung cancer: based on clinical and radiomic features. Transl Oncol 11:31–36
Litjens G, Kooi T, Bejnordi B, Setio A, Ciompi F, Ghafoorian M, van der Laak J, van Ginneken B, Sánchez C (2017) A survey on deep learning in medical image analysis. Med Image Anal 42:60–88
Zhu X, Dong D, Chen Z, Fang M, Zhang L, Song J, Yu D, Zang Y, Liu Z, Shi J, Tian J (2018) Radiomic signature as a diagnostic factor for histologic subtype classification of non-small cell lung cancer. Eur Radiol 28:2772–2778
Digumarthy SR, Padole AM, Gullo R, Sequist LV, Kalra MK (2019) Can CT radiomic analysis in NSCLC predict histology and EGFR mutation status? Medicine 98:e13963
Ferreira JR, Azevedo-Marques PM, Oliveira MC (2017) Selecting relevant 3D image features of margin sharpness and texture for lung nodule retrieval. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 12:509–517
Guo Y, Bennamoun M, Sohel F, Lu M, Wan J, Kwok N (2016) A comprehensive performance evaluation of 3D local feature descriptors. Int J Comput Vis 116:66–89
Dhara AK, Mukhopadhyay S, Saha P, Garg M, Khandelwal N (2016) Differential geometry-based techniques for characterization of boundary roughness of pulmonary nodules in CT images. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11:337–349
D’Antonoli TA, Farchione A, Lenkowicz J, Chiappetta M, Cicchetti G, Martino A, Ottavianelli A, Manfredi R, Margaritora S, Bonomo L, Valentini V, Larici AR (2019) CT radiomics signature of tumor and peritumoral lung parenchyma to predict nonsmall cell lung cancer postsurgical recurrence risk. Acad Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2019.05.019
Levman JE, Martel AL (2011) A margin sharpness measurement for the diagnosis of breast cancer from magnetic resonance imaging examinations. Acad Radiol 18:1577–1581
Ferreira JR Jr, Oliveira MC, Azevedo-Marques PM (2018) Characterization of pulmonary nodules based on features of margin sharpness and texture. J Digit Imaging 31:451–463
LeCun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G (2015) Deep learning. Nature 521:436–444
Chartrand G, Cheng P, Vorontsov E, Drozdzal M, Turcotte S, Pal C, Kadoury S, Tang A (2017) Deep learning: a primer for radiologists. Radiographics 37:2113–2131
Shen W, Zhou M, Yang F, Yu D, Dong D, Yang C, Zang Y, Tian J (2017) Multi-crop convolutional neural networks for lung nodule malignancy suspiciousness classification. Pattern Recognit 61:663–673
Paul R, Hawkins S, Balagurunathan Y, Schabath M, Gillies R, Hall L, Goldgof D (2016) Deep feature transfer learning in combination with traditional features predicts survival among patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Tomography 2:388–395
Funding
This study was funded by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - Brasil (CAPES) - Finance Code 001, Programa de Doutorado Sanduíche no Exterior (PDSE-CAPES) [Grant Number 88881.134004/2016-01], Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) [Grants Numbers 2016/17078-0 and 2014/50889-7].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (Comitê de Ética em Pesquisa do Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina de Ribeirão Preto da Universidade de São Paulo, reference number 1.996.131) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferreira-Junior, J.R., Koenigkam-Santos, M., Magalhães Tenório, A.P. et al. CT-based radiomics for prediction of histologic subtype and metastatic disease in primary malignant lung neoplasms. Int J CARS 15, 163–172 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-019-02093-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-019-02093-y