Abstract
Purpose
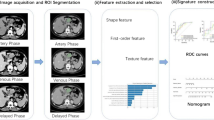
To build and validate a radiomics nomogram integrated with the radiomics signature and subjective CT characteristics to predict the Ki-67 expression level of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs). Moreover, the purpose was to compare the performance of pathological Ki-67 expression level with predicted Ki-67 expression level in estimating the prognosis of GISTs patients.
Methods
According to pathological results, patients were classified into high-Ki-67 labeling index group (Ki-67 LI ≥ 5%) and low-Ki-67 LI group (Ki-67 LI < 5%). Radiomics features extracted from contrast-enhanced CT(CECT) images were selected and classified to build a radiomics signature. A combined model was built by incorporating radiomics signature and determinant subjective CT characteristics using multivariate logistic regression analysis. The diagnostic performance of the radiomics signature, subjective CT model and combined model were explored by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis and Delong test. The model with best diagnostic performance was then set up for the prediction nomogram. Recurrence-free survival (RFS) rates were compared utilizing Kaplan–Meier curve.
Results
The generated combined model yielded the best diagnostic performance with area under the curve (AUC) values of 0.738 [95% confidence interval (CI): 0.669–0.807] and 0.772 (95% CI 0.683–0.860) in the training set and testing set respectively. The nomogram based on the combined model demonstrated good calibration in the training set and testing set (both P > 0.05). Patients of high-Ki-67 LI group predicted by our nomogram had a poorer RFS than patients of low–Ki-67 LI group (P < 0.0001).
Conclusion
This radiomics nomogram based on CECT had a satisfactory performance in predicting both the Ki-67 expression level and prognosis noninvasively in patients with GISTs, which may serve as an effective imaging tool that can assist in guiding personalized clinical treatment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nishida T, Blay JY, Hirota S, Kitagawa Y, Kang YK (2016) The standard diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of gastrointestinal stromal tumors based on guidelines. Gastric Cancer 19:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-015-0526-8
von Mehren M, Joensuu H (2018) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Clin Oncol 36:136–143. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2017.74.9705
Sicklick JK, Lopez NE (2013) Optimizing surgical and imatinib therapy for the treatment of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. J Gastrointest Surg 17:1997–2006. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-013-2243-0
Joensuu H, Hohenberger P, Corless CL (2013) Gastrointestinal stromal tumour. Lancet 382:973–983. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60106-3
Hedenström P, Nilsson B, Demir A, Andersson C, Enlund F, Nilsson O, Sadik R (2017) Characterizing gastrointestinal stromal tumors and evaluating neoadjuvant imatinib by sequencing of endoscopic ultrasound-biopsies. World J Gastroenterol 23:5925–5935. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i32.5925
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182:311–322
Petrelli F, Viale G, Cabiddu M, Barni S (2015) Prognostic value of different cut-off levels of Ki-67 in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 64196 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 153:477–479. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-015-3559-0
Yang C, Su H, Liao X, Han C, Yu T, Zhu G, Wang X, Winkler CA, O’Brien SJ, Peng T (2018) Marker of proliferation Ki-67 expression is associated with transforming growth factor beta 1 and can predict the prognosis of patients with hepatic B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res 10:679–696. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S162595
Lei B, Liu S, Qi W, Zhao Y, Li Y, Lin N, Xu X, Zhi C, Mei J, Yan Z, Wan L, Shen H (2013) PBK/TOPK expression in non-small-cell lung cancer: its correlation and prognostic significance with Ki67 and p53 expression. Histopathology 63:696–703. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12215
Liu X, Qiu H, Zhang P, Feng X, Chen T, Li Y, Tao K, Li G, Sun X, Zhou Z (2018) Ki-67 labeling index may be a promising indicator to identify “very high-risk” gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a multicenter retrospective study of 1022 patients. Hum Pathol 74:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2017.09.003
Pyo JS, Kang G, Sohn JH (2016) Ki-67 labeling index can be used as a prognostic marker in gastrointestinal stromal tumor: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Biol Markers 31:204–210. https://doi.org/10.5301/jbm.5000183
Belev B, Brčić I, Prejac J, Golubić ZA, Vrbanec D, Božikov J, Alerić I, Boban M, Razumović JJ (2013) Role of Ki-67 as a prognostic factor in gastrointestinal stromal tumors. World J Gastroenterol 19:523–527. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i4.523
Li H, Ren G, Cai R, Chen J, Wu X, Zhao J (2018) A correlation research of Ki67 index, CT features, and risk stratification in gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Cancer Med 7:4467–4474. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.1737
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278:563–577. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169
Mao B, Zhang L, Ning P, Ding F, Wu F, Lu G, Geng Y, Ma J (2020) Preoperative prediction for pathological grade of hepatocellular carcinoma via machine learning-based radiomics. Eur Radiol 30:6924–6932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-020-07056-5
Chen X, Yang Z, Yang J, Liao Y, Pang P, Fan W, Chen X (2020) Radiomics analysis of contrast-enhanced CT predicts lymphovascular invasion and disease outcome in gastric cancer: a preliminary study. Cancer Imaging 20:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-020-00302-5
Dercle L, Fronheiser M, Lu L, Du S, Hayes W, Leung DK, Roy A, Wilkerson J, Guo P, Fojo AT, Schwartz LH, Zhao B (2020) Identification of non-small cell lung cancer sensitive to systemic cancer therapies using radiomics. Clin Cancer Res 26:2151–2162. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-2942
Chen T, Ning Z, Xu L, Feng X, Han S, Roth HR, Xiong W, Zhao X, Hu Y, Liu H, Yu J, Zhang Y, Li Y, Xu Y, Mori K, Li G (2019) Radiomics nomogram for predicting the malignant potential of gastrointestinal stromal tumours preoperatively. Eur Radiol 29:1074–1082. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5629-2
Wang C, Li H, Jiaerken Y, Huang P, Sun L, Dong F, Huang Y, Dong D, Tian J, Zhang M (2019) Building CT radiomics-based models for preoperatively predicting malignant potential and mitotic count of gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Transl Oncol 12:1229–1236. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tranon.2019.06.005
Fu J, Fang MJ, Dong D, Li J, Sun YS, Tian J, Tang L (2020) Heterogeneity of metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumor on texture analysis: DWI texture as potential biomarker of overall survival. Eur J Radiol 125:108825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108825
Xu F, Ma X, Wang Y, Tian Y, Tang W, Wang M, Wei R, Zhao X (2018) CT texture analysis can be a potential tool to differentiate gastrointestinal stromal tumors without KIT exon 11 mutation. Eur J Radiol 107:90–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.07.025
Wu H, Han X, Wang Z, Mo L, Liu W, Guo Y, Wei X, Jiang X (2020) Prediction of the Ki-67 marker index in hepatocellular carcinoma based on CT radiomics features. Phys Med Biol 65:235048. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6560/abac9c
Ma W, Ji Y, Qi L, Guo X, Jian X, Liu P (2018) Breast cancer Ki67 expression prediction by DCE-MRI radiomics features. Clin Radiol 73:909.e1-909.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2018.05.027
Gu Q, Feng Z, Liang Q, Li M, Deng J, Ma M, Wang W, Liu J, Liu P, Rong P (2019) Machine learning-based radiomics strategy for prediction of cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Radiol 118:32–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.06.025
Joensuu H (2008) Risk stratification of patients diagnosed with gastrointestinal stromal tumor. Hum Pathol 39:1411–1419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2008.06.025
Brancatelli G, Federle MP, Grazioli L, Blachar A, Peterson MS, Thaete L (2001) Focal nodular hyperplasia: CT findings with emphasis on multiphasic helical CT in 78 patients. Radiology 219:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.219.1.r01ap0361
Miettinen M, Lasota J (2006) Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol 23:70–83. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.semdp.2006.09.001
Ye Z, Jiang H, Chen J, Liu X, Wei Y, Xia C, Duan T, Cao L, Zhang Z, Song B (2019) Texture analysis on gadoxetic acid enhanced-MRI for predicting Ki-67 status in hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study. Chin J Cancer Res 31:806–817. https://doi.org/10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.05.10
Peng J, Zhang J, Zhang Q, Xu Y, Zhou J, Liu L (2018) A radiomics nomogram for preoperative prediction of microvascular invasion risk in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Diagn Interv Radiol 24:121–127. https://doi.org/10.5152/dir.2018.17467
Joensuu H, Wardelmann E, Sihto H, Eriksson M, Sundby Hall K, Reichardt A, Hartmann JT, Pink D, Cameron S, Hohenberger P, Al-Batran SE, Schlemmer M, Bauer S, Nilsson B, Kallio R, Junnila J, Vehtari A, Reichardt P (2017) Effect of KIT and PDGFRA mutations on survival in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors treated with adjuvant imatinib: an exploratory analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol 3:602–609. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2016.5751
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
We confirm that all the four listed authors have participated actively in the study and the authors' contributions are as follows: conceptualization: XL; material preparation: BT; methodology: YZ; data collection and analysis: BT; QF; writing—original draft preparation: QF and BT; writing—review and editing: QF; study supervision and guarantors: XL. QF and BT contributed equally to the article. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee of the First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was waived by the institutional research committee.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, Q., Tang, B., Zhang, Y. et al. Prediction of the Ki-67 expression level and prognosis of gastrointestinal stromal tumors based on CT radiomics nomogram. Int J CARS 17, 1167–1175 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02575-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02575-6