Abstract
Purpose
Medical image segmentation is the most widely used technique in diagnostic and clinical research. However, accurate segmentation of target organs from blurred border regions and low-contrast adjacent organs in Computed tomography (CT) imaging is crucial for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Methods
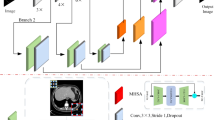
In this article, we propose a Multi-Scale Feature Pyramid Fusion Network (MS-Net) based on the codec structure formed by the combination of Multi-Scale Attention Module (MSAM) and Stacked Feature Pyramid Module (SFPM). Among them, MSAM is used to skip connections, which aims to extract different levels of context details by dynamically adjusting the receptive fields under different network depths; the SFPM including multi-scale strategies and multi-layer Feature Perception Module (FPM) is nested in the network at the deepest point, which aims to better focus the network's attention on the target organ by adaptively increasing the weight of the features of interest.
Results
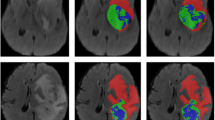
Experiments demonstrate that the proposed MS-Net significantly improved the Dice score from 91.74% to 94.54% on CHAOS, from 97.59% to 98.59% on Lung, and from 82.55% to 86.06% on ISIC 2018, compared with U-Net. Additionally, comparisons with other six state-of-the-art codec structures also show the presented network has great advantages on evaluation indicators such as Miou, Dice, ACC and AUC.
Conclusion
The experimental results show that both the MSAM and SFPM techniques proposed in this paper can assist the network to improve the segmentation effect, so that the proposed MS-Net method achieves better results in the CHAOS, Lung and ISIC 2018 segmentation tasks.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frid-Adar M, Diamant I, Klang E, Amitai M, Goldberger J, Greenspan H (2018) GAN-based synthetic medical image augmentation for increased CNN performance in liver lesion classification. Neurocomputing 321(321–331):7
Zhang C, Shu H, Yang G, Li F, Wen Y, Zhang Q, Dillenseger JL, Coatrieux JL (2020) HIFUNet: multi-class segmentation of uterine regions from MR images using global convolutional networks for HIFU surgery planning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(11):3309–3320. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.2991266
Jiang Y, Cao S, Tao S, Zhang H (2020) Skin lesion segmentation based on multi-scale attention convolutional neural network. IEEE Access 8:122811–122825. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3007512
Alom MZ, Aspiras T, Taha TM, Asari VK (2019) Skin cancer segmentation and classification with NABLA-N and inception recurrent residual convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1904.11126.
Kong Z, Xiong F, Zhang C, Fu Z, Zhang M, Weng J, Fan M (2020) Automated maxillofacial segmentation in panoramic dental x-ray images using an efficient encoder-decoder network. IEEE Access 8:207822–207833
Kwak JT, Hewitt SM (2017) Nuclear architecture analysis of prostate cancer via convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Access 5:18526–18533. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2747838
Wang S, Wang X, Hu Y, Shen Y, Yang Z, Gan M, Lei B (2020) Diabetic retinopathy diagnosis using multichannel generative adversarial network with semisupervision. IEEE Trans Autom Sci Eng 18(2):574–585
Alakwaa W, Nassef M, Badr A (2017) Lung cancer detection and classification with 3D convolutional neural network (3D-CNN). Lung Cancer 8(8):409
Kamnitsas K, Ledig C, Newcombe VF, Simpson JP, Kane AD, Menon DK, Rueckert D, Glocker B (2017) Efficient multi-scale 3D CNN with fully connected CRF for accurate brain lesion segmentation. Med Image Anal 36:61–78
Tang H, Liu X, Han K, Xie X, Chen X, Qian H, Liu Y, Sun S, Bai N (2021) Spatial context-aware self-attention model for multi-organ segmentation[C]. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF winter conference on applications of computer vision. 939–949.
van de Leemput SC, Prokop M, van Ginneken B, Manniesing R (2019) Stacked bidirectional convolutional LSTMs for deriving 3D non-contrast ct from spatiotemporal 4D CT. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(4):985–996
Bellos D, Basham M, Pridmore T, French AP (2021) Temporal refinement of 3D CNN semantic segmentations on 4D time-series of undersampled tomograms using hidden Markov models. Sci Rep 11(1):1–14
Mou L, Zhao Y, Fu H, Liu Y, Cheng J, Zheng Y, Su P, Yang J, Chen L, Frangi A, Akiba M, Liu J (2021) CS2-Net: deep learning segmentation of curvilinear structures in medical imaging. Med Image Anal 67:101874
Çiçek Ö, Abdulkadir A, Lienkamp SS, Brox T, Ronneberger O (2016) 3D U-Net: learning dense volumetric segmentation from sparse annotation. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention (pp. 424–432). Springer, Cham
Van De Leemput SC, Meijs M, Patel A, Meijer FJ, Van Ginneken B, Manniesing R (2019) Multiclass brain tissue segmentation in 4D CT using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Access 7:51557–51569
Myronenko A, Yang, D, Buch V, Xu D, Ihsani A, Doyle S, Michalski M, Tenenholtz N, Roth H (2019) 4D CNN for semantic segmentation of cardiac volumetric sequences. In: International workshop on statistical atlases and computational models of the heart (pp. 72–80). Springer, Cham
Zhang J, Xie Y, Wang Y, Xia Y (2021) Inter-slice context residual learning for 3D medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 40(2):661–672. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.3034995
Gao Y, Phillips JM, Zheng Y, Min R, Fletcher PT, Gerig G (2018) Fully convolutional structured LSTM networks for joint 4D medical image segmentation. In: 2018 IEEE 15th international symposium on biomedical imaging (ISBI 2018) (pp 1104–1108). IEEE
Li G, Chen X, Shi F, Zhu W, Tian J, Xiang D (2015) Automatic liver segmentation based on shape constraints and deformable graph cut in CT images. IEEE Trans Image Process 24(12):5315–5329. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2015.2481326
Zhang Y, He Z, Zhong C, Zhang Y, Shi Z (2017) Fully convolutional neural network with post-processing methods for automatic liver segmentation from CT. Chin Autom Congress (CAC) 2017:3864–3869. https://doi.org/10.1109/CAC.2017.8243454
Campadelli P, Casiraghi E, Esposito A (2009) Liver segmentation from computed tomography scans: a survey and a new algorithm[J]. Artif Intell Med 45(2–3):185–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.artmed.2008.07.020
Bauer C, Bischof H, Beichel R, Bornik A (2009) Comparison and evaluation of methods for liver segmentation from CT datasets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28(8):1251–1265
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 37(9):1904–1916
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2012) Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 25:1097–1105
Yuan H, Fan Z, Wu Y, Cheng J (2021) An efficient multi-path 3D convolutional neural network for false-positive reduction of pulmonary nodule detection. Int J Comput Assisted Radiol Surg 1–9
Zhu W, Huang Y, Zeng L, Chen X, Liu Y, Qian Z, DuFanXie NWX (2019) AnatomyNet: deep learning for fast and fully automated whole-volume segmentation of head and neck anatomy. Med Phys 46(2):576–589
Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T (2015) U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation [C]// MICCAI. In: Navab N, Hornegger J, Wells W, Frangi A (eds) Medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention – MICCAI 234–241
Zhou Z, Rahman Siddiquee MM, Tajbakhsh N, Liang J (2018) Unet++: a nested u-net architecture for medical image segmentation. In: Deep learning in medical image analysis and multimodal learning for clinical decision support (pp 3–11). Springer, Cham
Chen H, Dou Q, Yu L, Qin J, Heng PA (2018) VoxResNet: deep voxelwise residual networks for brain segmentation from 3D MR images. Neuroimage 170:446–455
Alom, M. Z., Hasan, M., Yakopcic, C., Taha, T. M., & Asari, V. K. (2018). Recurrent residual convolutional neural network based on u-net (r2u-net) for medical image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv:1802.06955.
Dobrenkii, A., Kuleev, R., Khan, A., Rivera, A. R., & Khattak, A. M. (2017, August). Large residual multiple view 3D CNN for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. In 2017 IEEE conference on computational intelligence in bioinformatics and computational biology (CIBCB) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Dai, Y., Gieseke, F., Oehmcke, S., Wu, Y., & Barnard, K. (2021). Attentional feature fusion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (pp. 3560–3569).
Oktay, O., Schlemper, J., Folgoc, L. L., Lee, M., Heinrich, M., Misawa, K., McDonagh, S., Hammerla, N. Y, Kainz, B., Glocker, B., & Rueckert, D. (2018). Attention u-net: Learning where to look for the pancreas. arXiv preprint arXiv:1804.03999.
Chen, Y., Wang, K., Liao, X., Qian, Y., Wang, Q., Yuan, Z., & Heng, P. A. (2019). Channel-Unet: a spatial channel-wise convolutional neural network for liver and tumors segmentation. Frontiers in genetics, 1110.
Gu Z, Cheng J, Fu H, Zhou K, Hao H, Zhao Y, Zhang T, Gao S, Liu J (2019) Ce-net: Context encoder network for 2d medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 38(10):2281–2292
Mou, L., Zhao, Y., Chen, L., Cheng, J., Gu, Z., Hao, H., Qi, H., Zheng, Y., Frangi, A., & Liu, J. (2019, October). CS-Net: channel and spatial attention network for curvilinear structure segmentation. In International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention (pp. 721–730). Springer, Cham.
Kavur AE, Gezer NS, Barış M, Şahin Y, Özkan S, Baydar B, Yüksel U, Kılıkçıer C, Olut S, Bozdağı Akar G, Ünal G, Dicle O, Selver MA (2020) Comparison of semi-automatic and deep learning-based automatic methods for liver segmentation in living liver transplant donors. Diagn Interv Radiol 26(1):11
Menze B. H, Jakab A., Bauer S., Kalpathy-Cramer, J., Farahani, K., Kirby, J., Burren, Y., Porz, N., Slotboom, J., Wiest, R., Lanczi, L., Gerstner, E., Weber, M., Arbel, T., B. A., Ayache, B. N., Buendia, P., Collins, D. L., Cordier, N., Corso, J. J., Criminisi, A.., Das, T., Delingette, H., Demiralp, Ç., Durst, C. R., Dojat, M., Doyle, S., Festa, J., Forbes, F., Geremia, E., Glocker, B., Golland, P., Guo, X., Hamamci, A., Iftekharuddin, K. M., Jena, R., John, N. M., Konukoglu, E., Lashkari, D., Mariz, J. A., Meier, R., Pereira, S., Precup, D., Price, S. J., Raviv, T. R., Reza, S. M. S., Ryan, M., Sarikaya, D., Schwartz, L., Shin, H., Shotton, J., Silva, C. A., Sousa, N., Subbanna, N. K., Szekely, G., Taylor, T. J., Thomas, O. M., Tustison, N. J., Unal, G., Vasseur, F., Wintermark, M., Ye, D. H., Zhao, L., Zhao, B., Zikic, D., Prastawa, M., Reyes, M. & Leemput, K. V. (2015). The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS)[J]. IEEE transactions on medical imaging, 2014, 34 (10): 1993–2024.
Kavur, A. E., Gezer, N. S., Baris, M., Aslan, S., Conze, P.H., Groza, V., Pham, D.D., Chatterjee, S., Ernst, P., Ozkan, S., Baydar, B., Lachionov, D., Han, S., Pauli, J., Isensee, F., Perkonigg, M., Sathish, R., Rajan, R., Sheet, D., Dovletov, G., Speck, O., Nurnberger, A., MaierJein, K.H, Akar, G.B., Unal, G., Dicle, O., & Selver, MA. "CHAOS challenge-combined (CT-MR) healthy abdominal organ segmentation." Medical Image Analysis 69 (2021): 101950.
Armato III, S.G., McLennan G, Bidaut L., McNitt-Gray, M.F., Meyer, C.R., Peeves, A.P, Zhao, B., Aberle, D.R, Henschke, C.L, Hoffman, E.A., Kazerooni, E.A., MacMahon, H., Beek, E.J.R., Yankelevitz, D., Biancardi, A.M., Cland, P.H., Brown, M.S., Engelmann, R.M., Laderach, G.E., Max, D., Pais, R.C., Qing, D.P.-Y., Roberts, R.Y., Smith, A.E., Starkey, A., Batra, P., Caligiuri, P., Farooqi, A., Gladish, G.W., Matilda,J.C., Munden, R.F., Petkovska, I., Quint, L.E., Schwartz,L.H.,Sundaram, B., Dodd, L.E., Fenimore, C., Gur, D., Petrick, N., Freymann, J., Kirby, J., Hughes, B., Casteele, A.V., Gupte, S., Sallam, M., Heath, M.D., Kuhn, M.H., Dharaiya, E., Burns, R., Fryd, D.S., Salganicoff, M., Anand, V., Shreter, U., Vastagh, S., Croft, B.Y., Clarke, L.R. The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans[J]. Medical physics, 2011, 38 (2): 915–931.
Codella, N., Rotemberg, V., Tschandl, P., Celebi, M. E., Dusza, S., Gutman, D., Helba, B., Kalloo, A., Liopyris, K., Marchetti, M., Kittler, H., & Halpern, A. (2019). Skin lesion analysis toward melanoma detection 2018: A challenge hosted by the international skin imaging collaboration (isic). arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.03368.
Tschandl P, Rosendahl C, Kittler H. The HAM10000 dataset, a large collection of multi-source dermatoscopic images of common pigmented skin lesions. Scientific Data. 2018; 5: 180161[J]. 2018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2018.161
Aroyo L, Welty C (2015) Truth is a lie: Crowd truth and the seven myths of human annotation. AI Mag 36(1):15–24
Wallner J, Mischak I, Egger J (2019) Computed tomography data collection of the complete human mandible and valid clinical ground truth models. Scientific data 6(1):1–14
Lösel PD, van de Kamp T, Jayme A, Ershov A, Faragó T, Pichler O, Jerome NT, Aadepu N, Bremer S, Chilingaryan SA, Heethoff M, Kopmann A, Odar J, SChmelzle, S., Zuber, M., Wittbrodt, J., Baumbach, T., & Heuveline, V. (2020) Introducing Biomedisa as an open-source online platform for biomedical image segmentation. Nat Commun 11(1):1–14
Wallner J, Hochegger K, Chen X, Mischak I, Reinbacher K, Pau M, Zmc T, Schwenzer-Zimmerer K, Zemann W, Schmalstieg D, Egger J (2018) Clinical evaluation of semi-automatic open-source algorithmic software segmentation of the mandibular bone: Practical feasibility and assessment of a new course of action. PLoS ONE 13(5):e0196378
Pfarrkirchner, B., Gsaxner, C., Lindner, L., Jakse, N., Wallner, J., Schmalstieg, D., & Egger, J. (2018, March). Lower jawbone data generation for deep learning tools under MeVisLab. In Medical Imaging 2018: Biomedical Applications in Molecular, Structural, and Functional Imaging (Vol. 10578, pp. 631–636). SPIE.
Li, C. (2021). Stroke Lesion Segmentation with Visual Cortex Anatomy Alike Neural Nets. arXiv preprint arXiv:2105.06544.
Kavur, A. E., Kuncheva, L. I., & Selver, M. A. (2020). Basic ensembles of vanilla-style deep learning models improve liver segmentation from ct images. arXiv preprint arXiv:2001.09647.
Kuncheva LI (2014) Combining pattern classifiers: methods and algorithms. John Wiley & Sons
Conze PH, Kavur AE, Cornec-Le Gall E, Gezer NS, Le Meur Y, Selver MA, Rousseau F (2021) Abdominal multi-organ segmentation with cascaded convolutional and adversarial deep networks. Artif Intell Med 117:102109
Chen, L., Song, H., Li, Q., Cui, Y., Yang, J., & Hu, X. T. (2019, November). Liver segmentation in CT images using a non-local fully convolutional neural network. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM) (pp. 639–642). IEEE.
Wickramasinghe, U., & Fua, P. (2021). Weakly Supervised Volumetric Image Segmentation with Deformed Templates. arXiv preprint arXiv:2106.03987.
Feng S, Zhao H, Shi F, Cheng X, Wang M, Ma Y, Xiang D, Zhu W, Chen X (2020) CPFNet: Context pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(10):3008–3018
Acknowledgements
The work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China with Grant 62065003. Supported by Guizhou Provincial Science and Technology Projects -ZK [2022] Key-020.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, B., Wang, Y., Ding, C. et al. Multi-scale feature pyramid fusion network for medical image segmentation. Int J CARS 18, 353–365 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02738-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-022-02738-5