Abstract
Purpose
US-guided percutaneous focal liver tumor ablations have been considered promising curative treatment techniques. To address cases with invisible or poorly visible tumors, registration of 3D US with CT or MRI is a critical step. By taking advantage of deep learning techniques to efficiently detect representative features in both modalities, we aim to develop a 3D US-CT/MRI registration approach for liver tumor ablations.
Methods
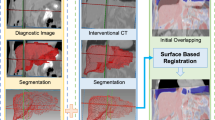
Facilitated by our nnUNet-based 3D US vessel segmentation approach, we propose a coarse-to-fine 3D US-CT/MRI image registration pipeline based on the liver vessel surface and centerlines. Then, phantom, healthy volunteer and patient studies are performed to demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed registration approach.
Results
Our nnUNet-based vessel segmentation model achieved a Dice score of 0.69. In healthy volunteer study, 11 out of 12 3D US-MRI image pairs were successfully registered with an overall centerline distance of 4.03±2.68 mm. Two patient cases achieved target registration errors (TRE) of 4.16 mm and 5.22 mm.
Conclusion
We proposed a coarse-to-fine 3D US-CT/MRI registration pipeline based on nnUNet vessel segmentation models. Experiments based on healthy volunteers and patient trials demonstrated the effectiveness of our registration workflow. Our code and example data are publicly available in this repository.







Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Our code is publicly available (https://github.com/Xingorno/3DUS_CT-MRI_Rigid_registration).
References
Tani S, Tatli S, Hata N, Garcia-Rojas X, Olubiyi OI, Silverman SG, Tokuda J (2016) Three-dimensional quantitative assessment of ablation margins based on registration of pre-and post-procedural mri and distance map. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 11(6):1133–1142
Kim PN, Choi D, Rhim H, Rha SE, Hong HP, Lee J, Choi J-I, Kim JW, Seo JW, Lee EJ, Lim KH (2012) Planning ultrasound for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation to treat small (3 cm) hepatocellular carcinomas detected on computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: a multicenter prospective study to assess factors affecting ultrasound visibility. J Vasc Interv Radiol 23(5):627–634
Xing S, Romero JC, Cool DW, Mujoomdar A, Chen EC, Peters TM, Fenster A (2022) 3d us-based evaluation and optimization of tumor coverage for us-guided percutaneous liver thermal ablation. IEEE Trans Med Imaging
Roche A, Pennec X, Malandain G, Ayache N (2001) Rigid registration of 3-d ultrasound with mr images: a new approach combining intensity and gradient information. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 20(10):1038–1049
Viola P, Wells WM III (1997) Alignment by maximization of mutual information. Int J Comput Vision 24(2):137–154
Wein W, Brunke S, Khamene A, Callstrom MR, Navab N (2008) Automatic ct-ultrasound registration for diagnostic imaging and image-guided intervention. Med Image Anal 12(5):577–585
Heinrich MP, Jenkinson M, Bhushan M, Matin T, Gleeson FV, Brady M, Schnabel JA (2012) Mind: Modality independent neighbourhood descriptor for multi-modal deformable registration. Med Image Anal 16(7):1423–1435
Shechtman E, Irani M (2007) Matching local self-similarities across images and videos. In: 2007 IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, pp 1–8 . IEEE
Penney GP, Blackall JM, Hamady M, Sabharwal T, Adam A, Hawkes DJ (2004) Registration of freehand 3d ultrasound and magnetic resonance liver images. Med Image Anal 8(1):81–91
Lange T, Papenberg N, Heldmann S, Modersitzki J, Fischer B, Lamecker H, Schlag PM (2009) 3d ultrasound-ct registration of the liver using combined landmark-intensity information. Int J Comput Assist Radiol Surg 4(1):79–88
Hering A, Hansen L, Mok TC, Chung AC, Siebert H, Häger S, Lange A, Kuckertz S, Heldmann S, Shao W, Vesal S, Rusu M, Sonn G, Estienne T, Vakalopoulou M, Han L, Huang Y, Yap P-T, Brudfors M, Balbastre Y, Joutard S, Modat M, Lifshitz G, Raviv D, Lv J, Li Q, Jaouen V, Visvikis D, Fourcade C, Rubeaux M, Pan W, Xu Z, Jian B, De Benetti F, Wodzinski M, Gunnarsson N, Sjölund J, Grzech D, Qiu H, Li Z, Thorley A, Duan J, Großbröhmer C, Hoopes A, Reinertsen I, Xiao Y, Landman B, Huo Y, Murphy K, Lessmann N, Van Ginneken B, Dalca AV, Heinrich MP (2022) Learn2reg: comprehensive multi-task medical image registration challenge, dataset and evaluation in the era of deep learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging
Thomson BR, Smit JN, Ivashchenko OV, Kok NF, Kuhlmann KF, Ruers TJ, Fusaglia M (2020) Mr-to-us registration using multiclass segmentation of hepatic vasculature with a reduced 3d u-net. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 275–284 Springer
Zeng Q, Mohammed S, Pang EH, Schneider C, Honarvar M, Lobo J, Hu C, Jago J, Ng G, Rohling R, Salcudean SE (2022) Learning-based us-mr liver image registration with spatial priors. In: International conference on medical image computing and computer-assisted intervention, pp 174–184 Springer
Myronenko A, Song X (2010) Point set registration: coherent point drift. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 32(12):2262–2275
Simpson AL, Antonelli M, Bakas S, Bilello M, Farahani K, Van Ginneken B, Kopp-Schneider A, Landman BA, Litjens G, Menze B, Ronneberger O, Summers RM, Bilic P, Christ PF, Do RK, Gollub M, Golia-Pernicka J, Heckers SH, Jarnagin WR, McHugo MK, Napel S, Vorontsov E, Maier-Hein L, Jorge Cardoso M (2019) A large annotated medical image dataset for the development and evaluation of segmentation algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv:1902.09063
Hirose O (2020) A Bayesian formulation of coherent point drift. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 43(7):2269–2286
Laimer G, Schullian P, Jaschke N, Putzer D, Eberle G, Alzaga A, Odisio B, Bale R (2020) Minimal ablative margin (mam) assessment with image fusion: an independent predictor for local tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma after stereotactic radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol 30:2463–2472
Shady W, Petre EN, Do KG, Gonen M, Yarmohammadi H, Brown KT, Kemeny NE, D’Angelica M, Kingham PT, Solomon SB, Sofocleous CT (2018) Percutaneous microwave versus radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases: ablation with clear margins (a0) provides the best local tumor control. J Vasc Interv Radiol 29(2):268–275
Hansen L, Heinrich MP (2021) Deep learning based geometric registration for medical images: How accurate can we get without visual features? In: International conference on information processing in medical imaging, pp 18–30 . Springer
Antonsanti P-L, Benseghir T, Jugnon V, Ghosn M, Chassat P, Kaltenmark I, Glaunès J (2022) How to register a live onto a liver? partial matching in the space of varifolds. arXiv preprint arXiv:2204.05665
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research Grants 154314 and 143232, the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research Grant RA#262, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada Grant 1248179, the Canadian Foundation for Innovation Grant 20994, and the Ontario Research Fund-Research Excellence Round 10. The authors also acknowledge the generous hardware contribution by NVIDIA Inc.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The Western University Health Science Research Ethics Board has approved our patient data collection trial. The patient trial was carried out in accordance with the Ethical Conduct for Research Involving Humans (TCPS 2).
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xing, S., Romero, J.C., Roy, P. et al. 3D US-CT/MRI registration for percutaneous focal liver tumor ablations. Int J CARS 18, 1159–1166 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-023-02915-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11548-023-02915-0