Abstract
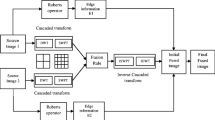
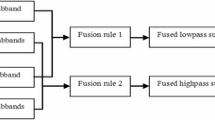
This paper presents a new wavelet-based multi-focus image fusion approach using method noise and anisotropic diffusion for two separate cases, i.e., with and without a reference image. It is specifically designed for real-time surveillance applications. It is a multi-step image fusion approach. Firstly, stationary wavelet transform (SWT) is performed to get low and high-frequency coefficients. Secondly, the input images' LL bands are fused using average operation. The rest of the respective bands are fused using a new correlation coefficient (CC) based fusion strategy using the threshold value calculated by structural similarity index metric (SSIM). Then inverse SWT is performed to reconstruct the fused coefficients. Thirdly, anisotropic diffusion-based method noise thresholding is introduced to recover the unprocessed and still damaged input images' components. Finally, the proposed approach's performance has experimented with various qualitative (visual perception) and quantitative factors (performance metrics). The experimental outcomes show that the proposed approach generates fine edges, high visual quality, high clarity of objects, and less degradation. The proposed multi-step hybrid technique is implemented to generate high-quality fused images. The experimental outcomes verify the achievement of the proposed approach.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ma, J., Ma, Y., Li, C.: Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: a survey. Inform. Fusion 45, 153–178 (2019)
Singh, P., Diwakar, M., Shankar, A., Shree, R., Kumar, M.: A review on SAR image and its despeckling. Arch. Comput. Methods Eng. 187, 1–21 (2021)
Singh, P., Shankar, A.: A novel optical image denoising technique using convolutional neural network and anisotropic diffusion for real-time surveillance applications. J. Real-Time Image Process. 108, 1–18 (2021)
Singh, P. K., Ashok, A.: A new multi-focus image fusion technique for an efficient surveillance. In: 2019 4th International conference on internet of things: smart innovation and usages (IoT-SIU), Ghaziabad, India, 2019, pp 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/IoT-SIU.2019.8777593
Singh, P., et al.: A new SAR image despeckling using correlation based fusion and method noise thresholding. J. King Saud Univ. Comp. Inform. Sci. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2018.03.009
Bhatt, M. B., Arya, D., Mishra, A. N., Singh, M., Singh, P., Gautam, M.: A new wavelet-based multifocus image fusion technique using method noise-median filtering. In: 2019 4th International Conference on Internet of Things: Smart Innovation and Usages (IoT-SIU), Ghaziabad, India, 2019, pp. 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1109/IoT-SIU.2019.8777615
Singh, P., Diwakar, M.: Wavelet-based multi-focus image fusion using average method noise diffusion (AMND). Recent Adv. Comp. Sci. Commun. 14, 2422 (2021). https://doi.org/10.2174/2666255813999200720163938
Liu, C., Long, Y., Mao, J.: Energy efficient multi-focus image fusion based on neighbour distance and morphology. Optik 127, 11354–11363 (2016)
Burt, P., Adelson, E.: The laplacian pyramid as a compact image code. IEEE Trans. Comput. 31(4), 532–540 (1983)
Petrovic, V.S., Xydeas, C.S.: Gradient-based multiresolution image fusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 13(2), 228–237 (2004)
Liu, Z., Tsukada, K., Hanasaki, K., Ho, Y., Dai, Y.: Image fusion by using steerable pyramid. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 22(9), 929–939 (2001)
Amolins, K., Zhang, Y., Dare, P.: Wavelet based image fusion techniques an introduction, review and comparison. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens 62(4), 249–263 (2007)
Li, H., Manjunath, B., Mitra, S.: Multisensor image fusion using the wavelet transform. Graph. Model Image Process. 57(3), 235–245 (1995)
Tian, J., Chen, L.: Adaptive multi-focus image fusion using a wavelet-based statistical sharpness measure. Signal Process. 92(9), 2137–2146 (2012)
Redondo, R., Šroubek, F., Fischer, S., Cristóbal, G.: Multifocus image fusion using the log-gabor transform and a multisize windows technique. Inf. Fusion 10(2), 163–171 (2009)
Pajares, G., de la Cruz, J.M.: A wavelet-based image fusion tutorial. Pattern Recogn. 37(9), 1855–1872 (2004)
Naidu, V. P. S.: Multi-resolution image fusion by FFT. In 2011 International Conference on Image Information Processing. IEEE, pp. 1–6 (2011)
Tessens, L., Ledda, A., Pizurica, A., Philips, W.: Extending the depth of field in microscopy through curvelet-based frequency-adaptive image fusion. In: IEEE Int. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 1 (2007), pp. I-861–I-864
Li, S., Yang, B.: Multifocus image fusion by combining curvelet and wavelet transform. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 29(9), 1295–1301 (2008)
Candes, E., Demanet, L., Donoho, D., Ying, L.: Fast discrete curvelet transforms. Multiscale Model. Simul. 5(3), 861–899 (2006)
Zhang, Q., Guo, B.L.: Multifocus image fusion using the non-sub sampled contourlet transform. Signal Process. 89(7), 1334–1346 (2009)
Yang, L., Guo, B., Ni, W.: Multimodality medical image fusion based on multiscale geometric analysis of contourlet transform. Neurocomputing 72(1–3), 203–211 (2008)
Qiguang, M., Baoshu, W.: A novel image fusion method using contourlet transform. Int. Conf. Commun. Circuits Syst 1, 548–552 (2006)
Samet, A., Cemal, K.: Multi-focus image fusion using Stationary Wavelet Transform (SWT) with Principal Component Analysis (PCA). In: 10th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), 30 Nov–2 Dec 2017
Muhammad, S.F., Arif, M., Somaya, A.A.M.: Multi-focus image fusion using content adaptive blurring. Inform. Fusion 45, 96–112 (2019)
Aymaz, S., Köse, C.: A novel image decomposition-based hybrid technique with super-resolution method for multi-focus image fusion. Inform. Fusion 45, 113–127 (2019)
Naidu, V.P.S., Raol, J.R.: Pixel-level image fusion using wavelets and principal component analysis. Def. Sci. J. 58(3), 338–352 (2008)
Jagalingam, P., Hegde, A.V.: a review of quality metrics for fused image. In: International Conference on Water Resources, Coastal and Ocean Engineering (ICWRCOE 2015), Aquatic Procedia 4, pp 133–142
Liu, Yu., Xun Chen, Hu., Peng, and Zengfu Wang. : Multi-focus image fusion with a deep convolutional neural network. Information Fusion 36, 191–207 (2017)
Dynamic weighted discrimination power analysis: a novel approach for face and palmprint recognition in DCT domain. Int. J. Phys. Sci., 5(17), 2543–2554 (2010)
Leng, L., Zhang, J.: Palmhash code vs. palmphasor code. Neurocomputing 108, 1–12 (2013)
Leng, L., Li, M., Kim, C., Bi, X.: Dual-source discrimination power analysis for multi-instance contactless palmprint recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 76(1), 333–354 (2017)
Martin, E.: Novel method for stride length estimation with body area network accelerometers. In: 2011 IEEE Topical Conference on Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems. IEEE, pp 79–82 (2011)
Broughton, S. A.: Wavelet Based Methods in Image Processing. www.rose-hulman.edu. Accessed 02 May 2017
Akansu, A.N., Smith, M.J.T.: Subband and wavelet transforms: design and applications. Kluwer Academic Publishers (1995)
Akansu, A.N., Medley, M.J.: Wavelet, subband and block transforms in communications and multimedia. Kluwer Academic Publishers (1999)
Akansu, A.N., Duhamel, P., Lin, X., de Courville, M.: Orthogonal transmultiplexers in communication: a review. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 46(4), 979–995 (1998). (Special Issue on Theory and Applications of Filter Banks and Wavelets)
Stationary wavelet transform, Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stationary_wavelet_transform, Accessed 12 Dec 2021
Zhang, Y.: Feature extraction of brain MRI by stationary wavelet transform and its applications. J. Biol. Syst. 18(s1), 115–132 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1142/S0218339010003652
Dong, Z.: Magnetic resonance brain image classification via stationary wavelet transform and generalized Eigenvalue proximal support vector machine. J. Med. Imaging Health Inform. 5(7), 1395–1403 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1166/jmihi.2015.1542
Prabhishek, S., Raj, S.: A new homomorphic and method noise thresholding based despeckling of SAR image using anisotropic diffusion. J. King Saud Univ. Comp. Inform. Sci. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2017.06.006
Singh, P., Shree, R.: A comparative study to noise models and image restoration techniques. Int. J. Comp. Appl. 149(1), 18 (2016)
Choongsang, C., Sangkeun, L.: Effective five directional partial derivatives-based image smoothing and a parallel structure design. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 25(4), 1617–1625 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2526785
Wang, Z., Simoncelli, E.P., Bovik, A.C.: Multiscale structural similarity for image quality assessment. In: Conference Record of the Thirty-Seventh Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, (2004). 2: 1398–1402. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACSSC.2003.1292216
Shi, W., Zhu, C.Q., Tian, Y., Nichol, J.: Wavelet-based image fusion and quality assessment. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 6(3–4), 241–251 (2005)
Singh, P., Shree, R.: A new SAR image despeckling using directional smoothing filter and method noise thresholding. Eng. Sci. Tech. Int. J. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2018.05.009
Perona, P., Malik, J.: Scale space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 12(8), 629639 (1990)
Samadzadegan, F., Dadrasjavan, F.: Evaluating the sensitivity of image fusion quality metrics to image degradation in satellite imagery. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-011-0117-z
Basic Intensity Quantification with ImageJ, Available at: https://www.unige.ch/medecine/bioimaging/files/1914/1208/6000/Quantification.pdf, Accessed 01 Jan 2021
Calculate Standard Deviation, Available at: https://explorable.com/calculate-standard-deviation, Accessed 20 Jan 2021
Multi focus image dataset, Available at: http://mansournejati.ece.iut.ac.ir/content/lytro-multi-focus-dataset, Accessed 20 Jan 2021
Naidu, V.P.S.: Image fusion technique using multi-resolution singular value decomposition. Def. Sci. J. 61(5), 479–484 (2011)
Liu, Y., Liu, S., Wang, Z.: A general framework for image fusion based on multi-scale transform and sparse representation. Inf. Fusion 24, 147–164 (2015)
Nejati, M., Samavi, S., Shirani, S.: Multi-focus image fusion using dictionary-based sparse representation. Inform. Fusion 25, 72–84 (2015)
Kumar, B.K.S.: Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter. Signal Image Video Process. 9(5), 1193–1204 (2015)
Fu, G.P., Hong, S.H., Li, F.L., Wang, L.: A novel multi-focus image fusion method based on distributed compressed sensing. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 67, 102760 (2020)
Liu, Z., Chai, Yi., Yin, H., Zhou, J., Zhu, Z.: A novel multi-focus image fusion approach based on image decomposition. Inform. Fusion 35, 102–116 (2017)
Guo, R., Shen, X.J., Dong, X.Y., Zhang, X.L.: Multi-focus image fusion based on fully convolutional networks. Front. Inform. Technol. Electron. Eng. 21(7), 1019–1033 (2020)
Farid, M.S., Mahmood, A., Al-Maadeed, S.A.: Multi-focus image fusion using content adaptive blurring. Inform. Fusion 45, 96–112 (2019)
Goshtasby, A.A., Nikolov, S.: Guest editorial: image fusion: advances in the state of the art. Inform. Fusion 8(2), 114–118 (2007)
Multi focus image dataset, Available at: http://dsp.etfbl.net/mif/, Accessed 20 Jan 2021
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P., Diwakar, M., Cheng, X. et al. A new wavelet-based multi-focus image fusion technique using method noise and anisotropic diffusion for real-time surveillance application. J Real-Time Image Proc 18, 1051–1068 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-021-01125-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11554-021-01125-8